[1] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[2] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(5):280-296.
[3] 任全娥.大数据背景下的文献计量学研究进展与学科融合[J].情报理论与实践,2019,42(1):48-52.
[4] 潘颖,孙瑜峥,刘岩.科技文献阅读中语素意识研究的可视化分析[J].情报科学,2019,37(12):123-127.
[5] CHEN C, IBEKWE SJF, HOU J. The structure and dynamics of cocitation clusters: a multiple‐perspective cocitation analysis. J Am Soc Inform Sci Tech. 2010;61(7):1386-1409.
[6] CHEN C. Cascading citation expansion. J Inf Sci Theory Pract. 2018;6(2): 6-13.
[7] 黄茂茂,胡月,王彬川,等.缺血性脑卒中康复近10年国际文献计量学及可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3725-3733.
[8] NG JY. Global research trends at the intersection of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and traditional, integrative, and complementary and alternative medicine:a bibliometric analysis. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020;20(1):353.
[9] GUO S, WANG L, XIE Y, et al. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of stem cells therapy for spinal cord injury based on web of science and citespace in the last 20 years. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:246-258.
[10] SEDANI A, YAKKANTI R, ALLEGRA P, et al. Thromboprophylaxis across orthopaedic surgery: bibliometric analysis of the most cited articles. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;16:157-167.
[11] ZHENG H, JIANG J, XU S, et al. Nanoparticle-induced ferroptosis: detection methods, mechanisms and applications. Nanoscale. 2021; 13(4):2266-2285.
[12] COZZI A, ORELLANA DI, SANTAMBROGIO P, et al. Stem cell modeling of neuroferritinopathy reveals iron as a determinant of senescence and ferroptosis during neuronal aging. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;13(5):832-846.
[13] LI X, ZENG J, LIU Y, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of action of quercetin and quercetin diels-alder anti-dimer on erastin-induced ferroptosis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(3):205-223.
[14] NOBUTA H, YANG N, NG YH, et al. Oligodendrocyte death in pelizaeus-merzbacher disease is rescued by iron chelation. Cell Stem Cell. 2019; 25(4):531-541.
[15] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541.
[16] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331.
[17] FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, SCHNEIDER M, PRONETH B, et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1180-1191.
[18] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13(1):91-98.
[19] JIANG L, KON N, LI T, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520(7545):57-62.
[20] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285.
[21] VANDEN BT, LINKERMANN A, JOUAN LS, et al. Regulated necrosis:the expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(2):135-147.
[22] DIXON SJ, STOCKWELL BR. The role of iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(1):9-17.
[23] XIE Y, HOU W, SONG X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(3):369-379.
[24] YANG WS, STOCKWELL BR. Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(3):165-176.
[25] 王甜甜,陈淳媛,杨雷,等.Nrf2/HO-1信号轴在氧化应激性疾病中的机制[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2019,44(1):74-80.
[26] 胡艳红,张凡,张楚焌,等.程序性细胞死亡形式研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2018,20(12):85-89.
[27] 李容,王新文,杨晓辉,等.细胞命运之终点—细胞死亡[J].科学通报,2016,61(18):1983-1987.
[28] 周文博,孔晨飞,秦高伟,等.铁死亡发生机制的研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2018,45(1):16-22.
[29] 关鹏,石振华,李亚青,等.铁死亡:一种新的细胞死亡方式[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2013,40(2):137-140.
[30] 姜懿纳,阳松威,张欣,等.铁死亡的机制及其在神经疾病中的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2018,34(2):166-170.
[31] 陈斌,成宜军,陈正鸿,等.脑出血后神经细胞死亡机制的研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2018,15(3):153-156.
[32] 任汐鹰,刘勤献,王海英.p53与细胞死亡[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018,34(6):588-594.
[33] 姜昕.学术论文关键词标引研究[J].辽宁师专学报(自然科学版), 2020,22(3):104-108.
[34] HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P, BERGHE TV. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(6):830-849.
[35] ZHENG J, CONRAD M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(6):920-937.
[36] OH BM, LEE SJ, PARK GL, et al. Erastin inhibits septic shock and inflammatory gene expression via suppression of the NF-κB pathway. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12):2210-2222.
[37] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[38] LACHAIER E, LOUANDRE C, GODIN C, et al. Sorafenib induces ferroptosis in human cancer cell lines originating from different solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(11):6417-6422.
[39] HAMBRIGHT WS, FONSECA RS, CHEN L, et al. Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 2017;12: 8-17.
[40] CONRAD M, LORENZ SM, PRONETH B. Targeting ferroptosis: new hope for as-yet-incurable diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2021;27(2):113-122.
[41] LINKERMANN A, SKOUTA R, HIMMERKUS N, et al. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(47):16836-16841.
[42] LEE YS, LEE DH, CHOUDRY HA, et al. Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress:cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16(7):1073-1076.
[43] LEE Y-S, KALIMUTHU K, PARK YS, et al. BAX-dependent mitochondrial pathway mediates the crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2020;25(9):625-631.
[44] JIANG X, HE C, LIN W. Supramolecular metal-based nanoparticles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021;61: 143-153.
[45] XU Y, QIN Z, MA J, et al. Recent progress in nanotechnology based ferroptotic therapies for clinical applications. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020; 880:173198-173206.
[46] GAO M, DENG J, LIU F, et al. Triggered ferroptotic polymer micelles for reversing multidrug resistance to chemotherapy. Biomaterials. 2019;223:119486-119496.
[47] YANG Y, TIAN Q, WU S, et al. Blue light-triggered Fe(2+)-release from monodispersed ferrihydrite nanoparticles for cancer iron therapy. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120739-120749.
[48] MO Y, DUAN L, YANG Y, et al. Nanoparticles improved resveratrol brain delivery and its therapeutic efficacy against intracerebral hemorrhage. Nanoscale. 2021;13(6):3827-3840. |
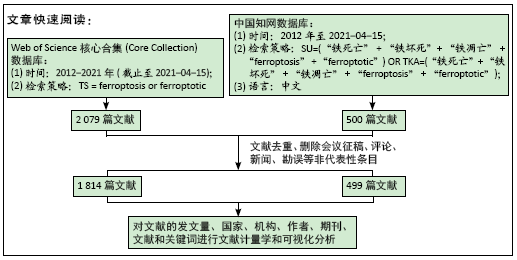

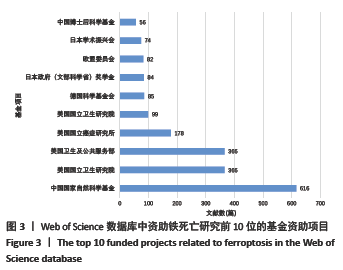
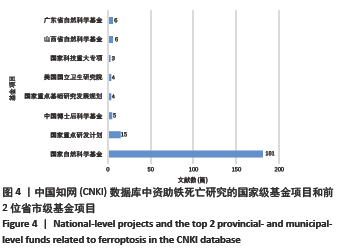
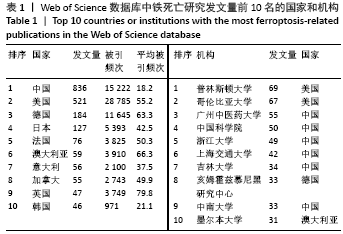
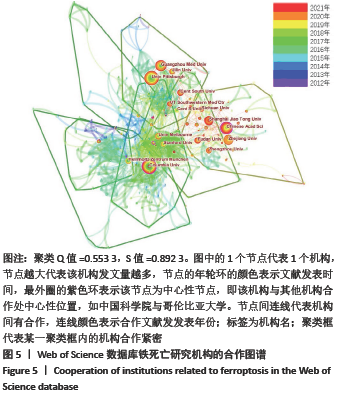
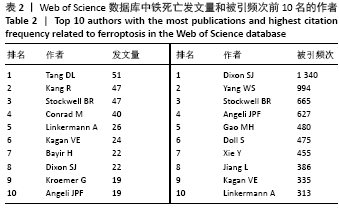

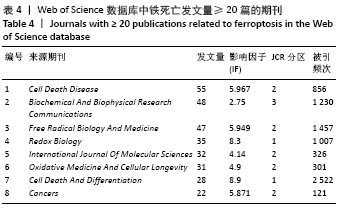
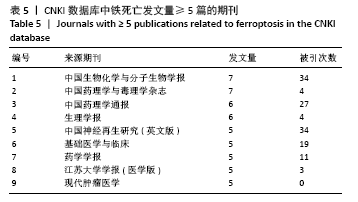
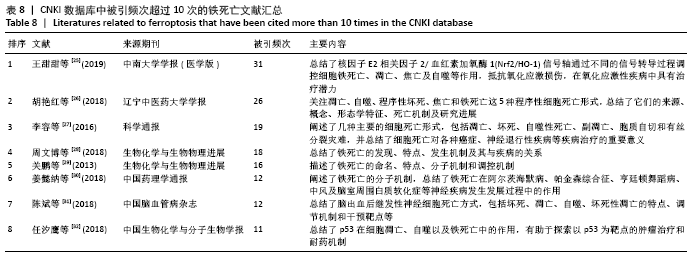
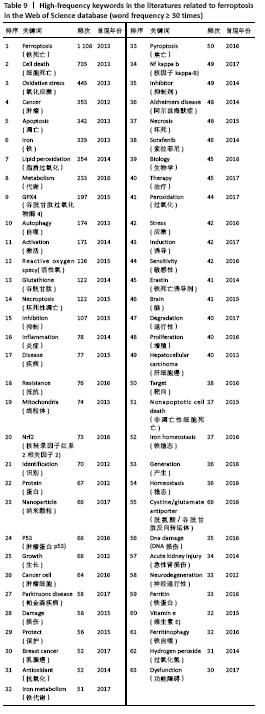
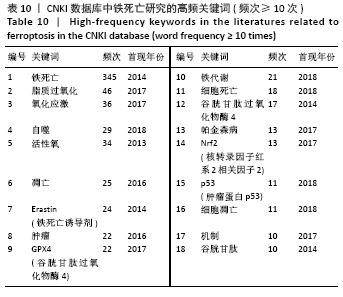

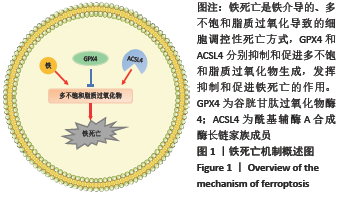 文献计量学指用数学和统计学等计量方法,研究文献和文献信息系统等一切知识载体的数量关系和发展规律,以及探讨科学动态特征的学科[3]。文献计量学分析的结果可以知识图谱的形式展示。知识图谱是显示科学知识发展进程与结构关系的一种图像,既是可视化的知识图形,又是序列化的知识谱系。知识图谱可由多种软件绘制,CiteSpace软件是目前最为流行的绘制软件之一,该软件由陈超美教授及其团队开发并更新,可以对特定领域进行文献计量学分析,并绘制一系列可视化知识图谱,以探寻科学研究领域演化的关键路径和前沿发展[4-6]。
文献计量学指用数学和统计学等计量方法,研究文献和文献信息系统等一切知识载体的数量关系和发展规律,以及探讨科学动态特征的学科[3]。文献计量学分析的结果可以知识图谱的形式展示。知识图谱是显示科学知识发展进程与结构关系的一种图像,既是可视化的知识图形,又是序列化的知识谱系。知识图谱可由多种软件绘制,CiteSpace软件是目前最为流行的绘制软件之一,该软件由陈超美教授及其团队开发并更新,可以对特定领域进行文献计量学分析,并绘制一系列可视化知识图谱,以探寻科学研究领域演化的关键路径和前沿发展[4-6]。