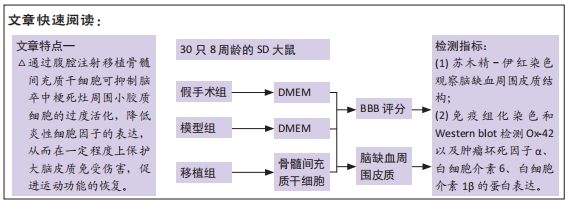
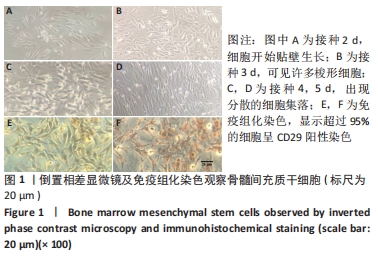
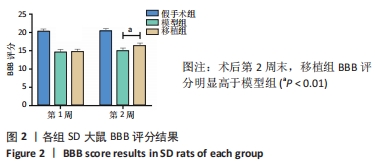
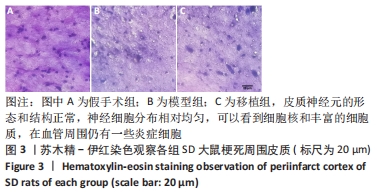
[1] KERR N, DIETRICH DW, BRAMLETT HM, et al. Sexually dimorphic microglia and ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(12):1308-1317.
[2] ZHANG D, LU Z, MAN J, et al. Wnt-3a alleviates neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke by modulating the responses of microglia/macrophages and astrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105760.
[3] YAN RY, WANG SJ, YAO GT, et al. The protective effect and its mechanism of 3-n-butylphthalide pretreatment on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(22):5275-5282.
[4] GOMEZ-NICOLA D, PERRY VH. Microglial dynamics and role in the healthy and diseased brain: a paradigm of functional plasticity. Neuroscientist. 2015; 21(2):169-184.
[5] DU L, ZHANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. Role of Microglia in Neurological Disorders and Their Potentials as a Therapeutic Target. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(10): 7567-7584.
[6] YEH CF, CHUANG TY, HUNG YW, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition enhances anti-inflammatory and antioxidative processes, modulates microglia polarization, and promotes recovery after ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:2927-2941.
[7] ABDALLAH BM, HAACK-SØRENSEN M, BURNS JS, et al. Maintenance of differentiation potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells immortalized by human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene despite [corrected] extensive proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 326(3):527-538.
[8] CHAO YH, PENG CT, HARN HJ, et al. Poor potential of proliferation and differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from children with severe aplastic anemia. Ann Hematol. 2010;89(7):715-723.
[9] SUN LY, HSIEH DK, SYU WS, et al. Cell proliferation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on biodegradable microcarriers enhances in vitro differentiation potential. Cell Prolif. 2010;43(5):445-456.
[10] XIE DM, LI YL, LI J, et al. CD51 distinguishes a subpopulation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with distinct migratory potential: a novel cell-based strategy to treat acute myocardial infarction in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):331.
[11] WEISS JN, LEVY S, BENES SC. Stem Cell Ophthalmology Treatment Study (SCOTS): bone marrow-derived stem cells in the treatment of Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(10):1685-1694.
[12] WANG X, ZHAI W, ZHU J, et al. Treatment of the bone marrow stromal stem cell supernatant by nasal administration-a new approach to EAE therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):325.
[13] NAKANO M, NAGAISHI K, KONARI N, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into damaged neurons and astrocytes. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:24805.
[14] HAO F, LI A, YU H, et al. Enhanced Neuroprotective Effects of Combination Therapy with Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Ginkgo biloba Extract (EGb761) in a Rat Model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2016;23(1):41-57.
[15] LI J, LIU Z, WANG L, et al. Thousand and one kinase 1 protects MCAO-induced cerebral ischemic stroke in rats by decreasing apoptosis and pro-inflammatory factors. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(10):BSR20190749.
[16] NASOUTI R, KHAKSARI M, MIRZAEE M, et al. Trehalose protects against spinal cord injury through regulating heat shock proteins 27 and 70 and caspase-3 genes expression. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;31(1):1-8.
[17] QIN C, ZHOU LQ, MA XT, et al. Dual Functions of Microglia in Ischemic Stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(5):921-933.
[18] ELDAHSHAN W, FAGAN SC, ERGUL A. Inflammation within the neurovascular unit: Focus on microglia for stroke injury and recovery. Pharmacol Res. 2019; 147:104349.
[19] HEINDL S, GESIERICH B, BENAKIS C, et al. Automated Morphological Analysis of Microglia After Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:106.
[20] SANDVIG I, AUGESTAD IL, HÅBERG AK, et al. Neuroplasticity in stroke recovery. The role of microglia in engaging and modifying synapses and networks. Eur J Neurosci. 2018;47(12):1414-1428.
[21] XIONG XY, LIU L, YANG QW. Functions and mechanisms of microglia/macrophages in neuroinflammation and neurogenesis after stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;142:23-44.
[22] CHEN E, LIU G, ZHOU X, et al. Concentration-dependent, dual roles of IL-10 in the osteogenesis of human BMSCs via P38/MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2018;32(9):4917-4929.
[23] PAN J, JIN JL, GE HM, et al. Malibatol A regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization in experimental stroke in a PPARγ-dependent manner. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:51.
[24] LI D, WANG C, YAO Y, et al. mTORC1 pathway disruption ameliorates brain inflammation following stroke via a shift in microglia phenotype from M1 type to M2 type. FASEB J. 2016;30(10):3388-3399.
[25] WON S, LEE JK, STEIN DG. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator promotes, and progesterone attenuates, microglia/macrophage M1 polarization and recruitment of microglia after MCAO stroke in rats. Brain Behav Immun. 2015;49:267-279.
[26] COLLMANN FM, PIJNENBURG R, HAMZEI-TAJ S, et al. Individual in vivo Profiles of Microglia Polarization After Stroke, Represented by the Genes iNOS and Ym1. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1236.
[27] TIAN X, LIU H, XIANG F, et al. β-Caryophyllene protects against ischemic stroke by promoting polarization of microglia toward M2 phenotype via the TLR4 pathway. Life Sci. 2019;237:116915.
[28] WANG J, XING H, WAN L, et al. Treatment targets for M2 microglia polarization in ischemic stroke. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105:518-525.
[29] CHEN AQ, FANG Z, CHEN XL, et al. Microglia-derived TNF-α mediates endothelial necroptosis aggravating blood brain-barrier disruption after ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):487.
[30] LIU Z, RAN Y, HUANG S, et al. Curcumin Protects against Ischemic Stroke by Titrating Microglia/Macrophage Polarization. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017; 9:233.
[31] FONFRIA E, MATTEI C, HILL K, et al. TRPM2 is elevated in the tMCAO stroke model, transcriptionally regulated, and functionally expressed in C13 microglia. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2006;26(3):179-198.
[32] ZHOU W, LIU Q, XU B. Improvement of bone defect healing in rats via mesenchymal stem cell supernatant. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(2):1500-1504.
[33] LIN J, WANG C, WU Z. Preliminary study on effects of human brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by intravenous transplantation on structure and function of rat injured spinal cord. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2010;24(8):982-987.
[34] WANG W, HUANG X, LI J, et al. Methane Suppresses Microglial Activation Related to Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Apoptotic Injury during Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:2190897.
[35] HE Y, MA X, LI D, et al. Thiamet G mediates neuroprotection in experimental stroke by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization and inhibiting NF-κB p65 signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(8):2938-2951.
[36] 朱婷,孙桂波,孟祥宝,等.小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞的极化及在脑卒中修复中的作用[J].中国药理学通报,2019,35(8):1046-1050.
[37] VON LEDEN RE, KHAYRULLINA G, MORITZ KE, et al. Age exacerbates microglial activation, oxidative stress, inflammatory and NOX2 gene expression, and delays functional recovery in a middle-aged rodent model of spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):161.
[38] 樊文香.缺血性脑卒中的机制研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2018, 49(6):751-759.
|