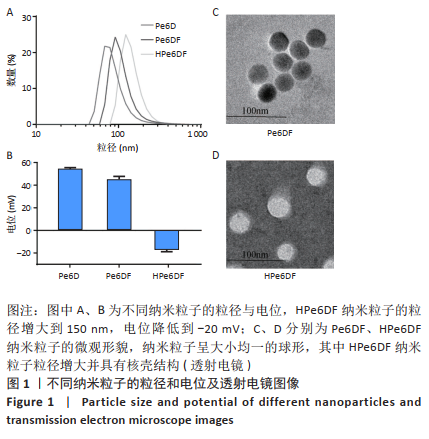
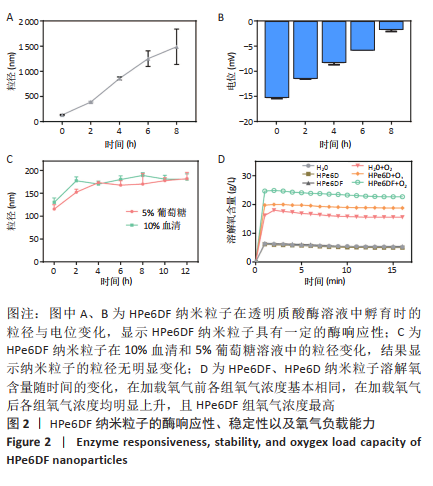
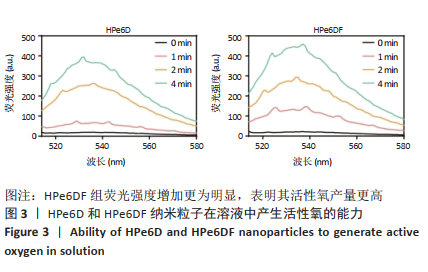
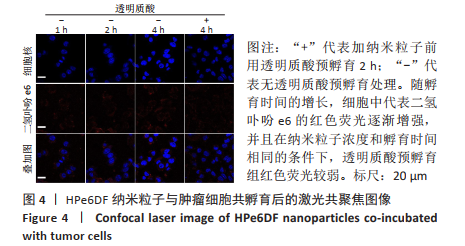
[1] CUI D, HUANG J, ZHEN X, et al. A Semiconducting Polymer Nano-prodrug for Hypoxia-Activated Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2019;58(18):5920-5924.
[2] KWIATKOWSKI S, KNAP B, PRZYSTUPSKI D, et al. Photodynamic therapy-mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;106:1098-1107.
[3] YUAN Y, ZHANG CJ, GAO M, et al. Specific Light-Up Bioprobe with Aggregation-Induced Emission and Activatable Photoactivity for the Targeted and Image-Guided Photodynamic Ablation of Cancer Cells. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54(6):1780-1786.
[4] WANG X, LI J, LI L, et al. Photodynamic Therapy-Induced Apoptosis of Keloid Fibroblasts is Mediated by Radical Oxygen Species In Vitro. Clin Lab. 2015;61(9):1257-1266.
[5] ZHAO H, XING D, CHEN Q. New insights of mitochondria reactive oxygen species generation and cell apoptosis induced by low dose photodynamic therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(18):2750-2761.
[6] SUN Y, ZHAO D, WANG G, et al. Recent progress of hypoxia-modulated multifunctional nanomedicines to enhance photodynamic therapy: opportunities, challenges, and future development. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(8):1382-1396.
[7] ZHANG K, ZHANG Y, MENG X, et al. Light-triggered theranostic liposomes for tumor diagnosis and combined photodynamic and hypoxia-activated prodrug therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;185:301-309.
[8] ZHANG X, WU M, LI J, et al. Light-Enhanced Hypoxia-Response of Conjugated Polymer Nanocarrier for Successive Synergistic Photodynamic and Chemo-Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018; 10(26):21909-21919.
[9] SHI C, LI M, ZHANG Z, et al. Catalase-based liposomal for reversing immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and enhanced cancer chemo-photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials. 2020;233:119755.
[10] ZHU W, DONG Z, FU T, et al. Modulation of Hypoxia in Solid Tumor Microenvironment with MnO2 Nanoparticles to Enhance Photodynamic Therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2016;26(30):5490-5498.
[11] CHEN S, HUANG B, PEI W, et al. Mitochondria-Targeting Oxygen-Sufficient Perfluorocarbon Nanoparticles for Imaging-Guided Tumor Phototherapy. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:8641-8658.
[12] TIAN J, ZHANG W. Polydopamine-Loaded Fluorinated Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Photosensitizer Nanoparticles for Synergetic Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy of Hypoxic Tumors. Huadong Ligong Daxue Xuebao. 2019;45(2):285-292.
[13] WANG Y, ZHANG F, LIN H, et al. Biodegradable Hollow MoSe2/Fe3O4 Nanospheres as the Photodynamic Therapy-Enhanced Agent for Multimode CT/MR/IR Imaging and Synergistic Antitumor Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(47):43964-43975.
[14] JI J, FAN Z, ZHOU F, et al. Improvement of DC vaccine with ALA-PDT induced immunogenic apoptotic cells for skin squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6(19):17135-17146.
[15] LARISCH P, VERWANGER T, LINECKER M, et al. The interrelation between a pro-inflammatory milieu and fluorescence diagnosis or photodynamic therapy of human skin cell lines. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2014;11(2):91-103.
[16] CHEN PW, UNO T, KSANDER BR. Tumor escape mutants develop within an immune-privileged environment in the absence of T cell selection. J Immunol. 2006;177(1):162-168.
[17] LANG K, ENTSCHLADEN F, WEIDT C, et al. Tumor immune escape mechanisms: impact of the neuroendocrine system. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006;55(7):749-760.
[18] VILLALBA M, RATHORE MG, LOPEZ-ROYUELA N, et al. From tumor cell metabolism to tumor immune escape. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013; 45(1):106-113.
[19] CRAMER GM, MOON EK, CENGEL KA, et al. Photodynamic Therapy and Immune Checkpoint Blockade(dagger). Photochem Photobiol. 2020;96(5):954-961.
[20] HWANG HS, CHERUKULA K, BANG YJ, et al. Combination of Photodynamic Therapy and a Flagellin-Adjuvanted Cancer Vaccine Potentiated the Anti-PD-1-Mediated Melanoma Suppression. Cells. 2020;9(11):2432.
[21] ZHANG Y, LIAO Y, TANG Q, et al. Biomimetic Nanoemulsion for Synergistic Photodynamic-Immunotherapy Against Hypoxic Breast Tumor. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60:10647-10653.
[22] MALACHOWSKI WP, METZ R, PRENDERGAST GC, et al. A new cancer immunosuppression target: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). A review of the IDO mechanism, inhibition and therapeutic applications. Drugs Futur. 2005;30(9):897-909.
[23] QIAN S, ZHANG M, CHEN Q, et al. IDO as a drug target for cancer immunotherapy: recent developments in IDO inhibitors discovery. RSC Adv. 2016;6(9):7575-7581.
[24] ZHANG H, LIU W, LIU Z, et al. Discovery of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors using machine learning based virtual screening. Medchemcomm. 2018;9(6):937-945.
[25] GAO A, CHEN B, GAO J, et al. Sheddable Prodrug Vesicles Combating Adaptive Immune Resistance for Improved Photodynamic Immunotherapy of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2020;20(1):353-362.
[26] LIU D, CHEN B, MO Y, et al. Redox-Activated Porphyrin-Based Liposome Remote-Loaded with Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) Inhibitor for Synergistic Photoimmunotherapy through Induction of Immunogenic Cell Death and Blockage of IDO Pathway. Nano Lett. 2019;19(10): 6964-6976.
[27] GUO Y, JIANG K, SHEN Z, et al. A Small Molecule Nanodrug by Self-Assembly of Dual Anticancer Drugs and Photosensitizer for Synergistic near-Infrared Cancer Theranostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017; 9(50):43508-43519.
[28] XIAO Y, AN FF, CHEN J, et al. The impact of light irradiation timing on the efficacy of nanoformula-based photo/chemo combination therapy. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(22):3692-3702.
[29] ZHU T, SHI L, YU C, et al. Ferroptosis Promotes Photodynamic Therapy: Supramolecular Photosensitizer-Inducer Nanodrug for Enhanced Cancer Treatment. Theranostics. 2019;9(11):3293-3307.
[30] KADLECOVA Z, RAJENDRA Y, MATASCI M, et al. DNA delivery with hyperbranched polylysine: A comparative study with linear and dendritic polylysine. J Controlled Release. 2013;169(3): 276-288.
[31] LV P, ZHOU C, ZHAO Y, et al. Modified epsilon-polylysine-grafted-PEI-beta-cyclodextrin supramolecular carrier for gene delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;168:103-111.
[32] WANG SJ, BOURGUIGNON LYW. Hyaluronan-CD44 promotes phospholipase C-mediated Ca2+ signaling and cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;132(1): 19-24.
[33] GAO SG, ZHANG MX, ZHU XJ, et al. Apoptotic effects of Photofrin-Diomed 630-PDT on SHEEC human esophageal squamous cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9):15098-15107.
[34] TU PH, HUANG Q, OU YS, et al. Aloe-emodin-mediated photodynamic therapy induces autophagy and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 through the ROS/JNK signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2016;35(6):3209-3215.
[35] XUE Q, WANG P, WANG XB, et al. Targeted inhibition of p38MAPK-enhanced autophagy in SW620 cells resistant to photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis. Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(7):1967-1975.
[36] DENG H, ZHOU Z, YANG W, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Targeting to Amplify Immunogenic Cell Death for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2020;20(3):1928-1933.
[37] ALZEIBAK R, MISHCHENKO TA, SHILYAGINA NY, et al. Targeting immunogenic cancer cell death by photodynamic therapy: past, present and future. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(1):e001926.
[38] DOIX B, TREMPOLEC N, RIANT O, et al. Low Photosensitizer Dose and Early Radiotherapy Enhance Antitumor Immune Response of Photodynamic Therapy-Based Dendritic Cell Vaccination. Front Oncol. 2019;9:811.
[39] GARG AD, DUDEK AM, FERREIRA GB, et al. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy. 2013;9(9):1292-1307.
[40] WU D, FAN YY, YAN HH, et al. Oxidation-sensitive polymeric nanocarrier-mediated cascade PDT chemotherapy for synergistic cancer therapy and potentiated checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Chem Eng J. 2021;404:126481. |
 文题释义:
文题释义: