中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (14): 2202-2206.doi: 10.12307/2022.484
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
抗氧化剂超氧化物歧化酶对大鼠肺巨噬细胞二氧化硅条件上清介导的肺成纤维细胞增殖及c-myc表达的影响
阚 泉1,张 岩2,王海涛1,李 冉1,田艳霞1,吕翠平1
- 1华北理工大学组胚教研室,河北省唐山市 063000;2华北理工大学附属医院,河北省唐山市 063000
Effects of superoxide dismutase on proliferation and c-myc expression of lung fibroblasts activated by supernatant of silicon dioxide-induced rat lung macrophages
Kan Quan1, Zhang Yan2, Wang Haitao1, Li Ran1, Tian Yanxia1, Lyu Cuiping1
- 1Department of Histology and Embryology, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan 063000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD):是能清除超氧阴离子自由基的抗氧化金属酶,它能够催化超氧阴离子自由基歧化生成氧和过氧化氢,在机体氧化与抗氧化平衡中起到重要的作用。有研究显示超氧化物歧化酶和肿瘤有着密切的关系。
肺泡巨噬细胞 (alveolar macrophages,AM):依赖于粒细胞–巨噬细胞集落刺激因子由胚胎单核细胞发育而来,在维持肺部免疫系统稳态以及宿主防御的过程中扮演着重要的角色。
背景:c-Myc是一种众所周知的致癌基因,在许多癌症中过表达。肺泡巨噬细胞是肺脏重要的功能细胞,它不但参与肺脏的免疫防御,吞噬侵入肺脏的细菌颗粒,还可分泌大量生物活性物质,维持肺脏和机体正常的生理功能。超氧化物歧化酶和肿瘤有着密切的关系。
目的:观察抗氧化剂超氧化物歧化酶对二氧化硅(SiO2)刺激的大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞培养上清诱导的大鼠肺成纤维细胞增殖及c-myc表达的影响。
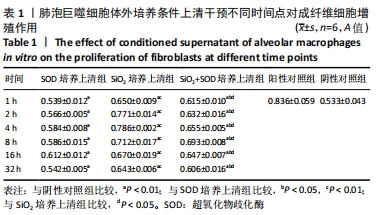
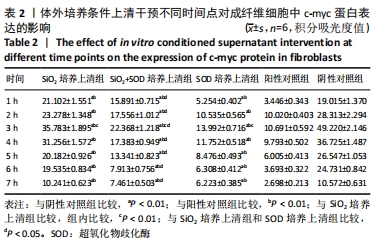
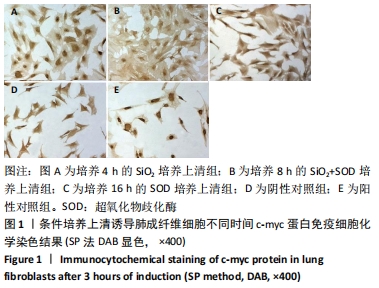
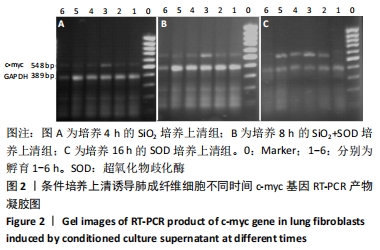
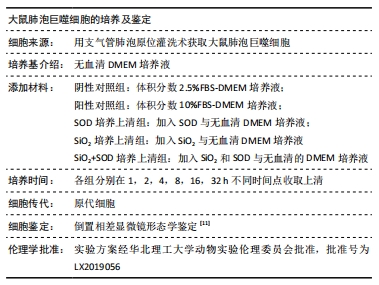
方法:采用肺泡原位灌洗技术获取肺泡巨噬细胞,①制备条件培养上清:超氧化物歧化酶培养上清(超氧化物歧化酶+肺泡巨噬细胞+不加血清DMEM)、二氧化硅培养上清(二氧化硅+肺泡巨噬细胞+不加血清DMEM)、二氧化硅+超氧化物歧化酶培养上清(二氧化硅+超氧化物歧化酶+肺泡巨噬细胞+不加血清DMEM);分别在培养1,2,4,8,16,32 h不同时间点收取上清;②肺成纤维细胞诱导培养:取第3代肺成纤维细胞,将条件上清与含体积分数5%FBS的DMEM按照1∶1比例配制进行诱导,实验分组为:阴性对照组(体积分数2.5%FBS-DMEM培养),阳性对照组(体积分数10%FBS-DMEM培养);超氧化物歧化酶培养上清组;二氧化硅培养上清组;二氧化硅+超氧化物歧化酶培养上清组;培养时间与上述时间点同步进行。采用MTT法、免疫细胞化学法和RT-PCR法分别检测肺成纤维细胞增殖、c-myc蛋白和mRNA的表达情况。实验方案经华北理工大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。
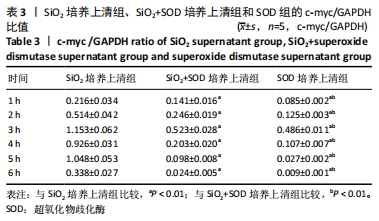
结果与结论:①与对照组相比较,二氧化硅培养上清组能够显著促进成纤维细胞增殖,使c-myc蛋白及mRNA表达水平上调;与二氧化硅培养上清组相比较,二氧化硅+超氧化物歧化酶培养上清组成纤维细胞增殖减少,c-myc蛋白及mRNA表达水平下调(P < 0.05);②结果说明,超氧化物歧化酶能够抑制二氧化硅刺激的肺泡巨噬细胞培养上清介导的肺成纤维细胞增殖和c-myc表达水平的上调。
缩略语:超氧化物歧化酶:superoxide dismutase,SOD
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5545-2352 (阚泉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: