[1] MEMEZAWA H, MINAMISAWA H, SMITH ML, et al. Ischemic penumbra in a model of reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1992;89(1):67-78.
[2] NEUMANN J, GUNZER M, GUTZEIT HO,et al. Microglia provide neuroprotection after ischemia. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):714-716.
[3] TAMURA A, GRAHAM D I, MCCULLOCH J, et al. Focal Cerebral Ischaemia in the Rat: 1. Description of Technique and Early Neuropathological Consequences Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):53-60.
[4] MCAULEY MA. Rodent models of focal ischemia.Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1995;7(2):153-180.
[5] HARRISON TC, SILASI G, BOYD JD, et al. Displacement of sensory maps and disorganization of motor cortex after targeted stroke in mice.Stroke. 2013;44(8):2300-2306.
[6] LIU NW, KE CC, ZHAO Y,et al. Evolutional Characterization of Photochemically Induced Stroke in Rats: a Multimodality Imaging and Molecular Biological Study. Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8(3):244-256.
[7] CHRISTOPH K, FELIX F, MICHAEL S, et al. Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:3445-3454.
[8] IADECOLA C, ANRATHER J.The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(7):796-808.
[9] O’DONNELL ME, TRAN L, LAM TI, et al. Bumetanide Inhibition of the Blood-Brain Barrier Na-K-Cl Cotransporter Reduces Edema Formation in the Rat Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Model of Stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004;24(9):1046-1056.
[10] RANSOM BRUCE R, RANSOM CHRISTOPHER B. Astrocytes: multitalented stars of the central nervous system. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;814:3-7.
[11] ROSENBLUM WI, EL-SABBAN F. Platelet aggregation in the cerebral microcirculation: effect of aspirin and other agents. Circ Res. 1977; 40(3):320-328.
[12] WATSON BD, DIETRICH WD, BUSTO R, et al. Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol. 1985;17(5):497-504.
[13] LEE JK, PARK MS, KIM YS, et al. Photochemically induced cerebral ischemia in a mouse model. Surg Neurol. 2007;67(6):620-625.
[14] KUROIWA T, XI G, HUA Y, et al. Development of a rat model of photothrombotic ischemia and infarction within the caudoputamen.Stroke. 2009;40(1):248-253.
[15] BACCETTO S L, LEHMANN C. Microcirculatory Changes in Experimental Models of Stroke and CNS-Injury Induced Immunodepression.Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5184.
[16] KLEINSCHNITZ C, BRAEUNINGER S, PHAM M, et al. Blocking of platelets or intrinsic coagulation pathway driven thrombosis does not prevent cerebral infarctions induced by photothrombosis. Stroke. 2008;39(4):1262-1268.
[17] KIM HS, KIM D, KIM RG, et al. A rat model of photothrombotic capsular infarct with a marked motor deficit: a behavioral, histologic, and microPET study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2014;34(4):683-689.
[18] SHIH AY, BLINDER P, TSAI PS, et al. The smallest stroke: occlusion of one penetrating vessel leads to infarction and a cognitive deficit. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(1):55-63.
[19] MACREZ R, ALI C, TOUTIRAIS O, et al. Stroke and the immune system: from pathophysiology to new therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10(5):471-480.
[20] BURDA J, SOFRONIEW M. Reactive Gliosis and the Multicellular Response to CNS Damage and Disease. Neuron. 2014;81(2):229-248.
[21] ZHANG W, TIAN T, GONG SX, et al. Microglia-associated neuroinflammation is a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):6-11.
[22] IADECOLA C, ANRATHER J. The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(7):796-808.
[23] DHEEN ST, KAUR C, LING EA. Microglial Activation and its Implications in the Brain Diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(11):1189-1197.
[24] BROWN GC. Nitric oxide and neuronal death. Nitric Oxide. 2010;23(3): 153-165.
[25] RUST R, GRNNERT L, GANTNER C, et al. Nogo-A targeted therapy promotes vascular repair and functional recovery following stroke.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(28):14270-14279.
[26] NIH LR, GOJGINI S, CARMICHAEL ST, et al. Dual-function injectable angiogenic biomaterial for the repair of brain tissue following stroke.Nat Mater. 2018;17(7):642-651.
[27] ANTINA DB, ANNET S, MARICEL GS, et al. Environmental enrichment during the chronic phase after experimental stroke promotes functional recovery without synergistic effects of EphA4 targeted therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(4):605-617.
[28] PATRICE V, THOMAS ME, MIGUEL CFJ, et al. Dynamic Brains and the Changing Rules of Neuroplasticity: Implications for Learning and Recovery.Front Psychol. 2017;8:1657.
[29] JONES TA, JEFFERSON SC. Reflections of experience-expectant development in repair of the adult damaged brain. Dev Psychobiol. 2011;53(5):466-475.
[30] HAO P, DUAN H, HAO F, et al. Neural repair by NT3-chitosan via enhancement of endogenous neurogenesis after adult focal aspiration brain injury. Biomaterials. 2017;140:88-102.
[31] MO L, YANG Z, ZHANG A, et al. The repair of the injured adult rat hippocampus with NT-3-chitosan carriers.Biomaterials. 2010;31(8): 2184-2192. |
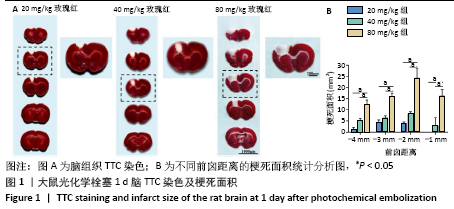
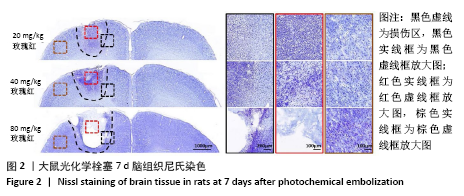
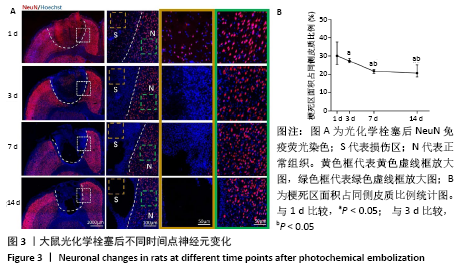
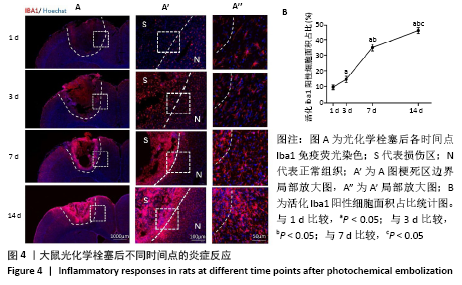
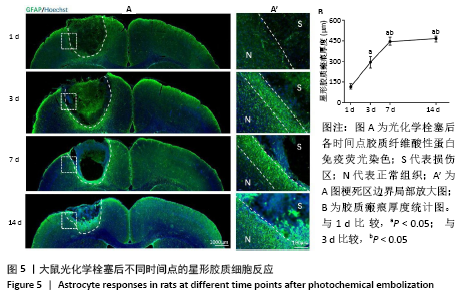
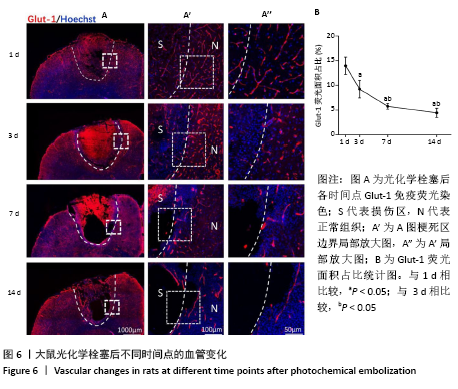
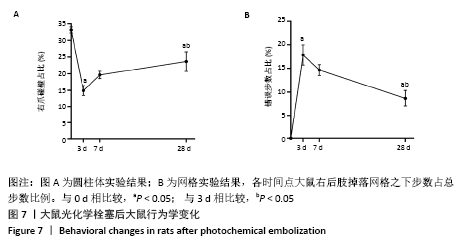

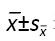 表示,采用 SPSS 16. 0统计软件进行统计学处理,采用shapiro-wilk检测数据正态分布情况,levene检测方差齐性,利用单因素方差分析比较多组的差异性,LSD事后多重比较分析组间差异性。P < 0.05被认为差异有显著性意义。
表示,采用 SPSS 16. 0统计软件进行统计学处理,采用shapiro-wilk检测数据正态分布情况,levene检测方差齐性,利用单因素方差分析比较多组的差异性,LSD事后多重比较分析组间差异性。P < 0.05被认为差异有显著性意义。