中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 225-231.doi: 10.12307/2022.037
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
电针干预大鼠大脑中动脉栓塞缺血再灌注模型丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路的变化
赖 涵1,王 娇1,董苗苗1,罗 梦1,王文豪1,周国平1,2
- 1南方医科大学中西医结合医院,广东省广州市 510315;2南方医科大学中医药学院,广东省广州市 510515
Electroacupuncture intervenes with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion due to middle cerebral artery occlusion
Lai Han1, Wang Jiao1, Dong Miaomiao1, Luo Meng1, Wang Wenhao1, Zhou Guoping1, 2
- 1Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510315, Guangdong Province, China; 2School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen acti-vatedprotrinkinase,MAPK)家族:MAPK在神经细胞的生长和增殖中起作用,MAPK信号通路在神经系统中广泛表达,并调节脑缺血再灌注损伤后神经细胞的修复或凋亡。MAPK的3个主要亚家族;细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、c-Jun N端激酶(JNK)和p38激酶参与调节脑缺血再灌注损伤后神经元细胞的功能障碍。
脑缺血再灌注损伤:脑缺血再灌注会导致炎症、氧化损伤和程序性细胞死亡,从而加剧脑组织损伤并严重影响中风患者的日常生活,当脑缺血再灌注发生时,MAPK家族开始发生调控作用。
背景:既往电针对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤保护作用及时效性的机制研究较少。
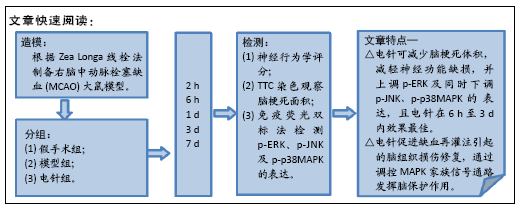
目的:观察不同时间电针对脑缺血再灌注大鼠MAPK家族3条信号通路中p-ERK、p-JNK及p-p38MAPK蛋白表达的影响,探索电针发挥脑保护作用的具体机制。
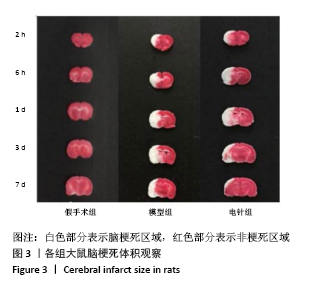
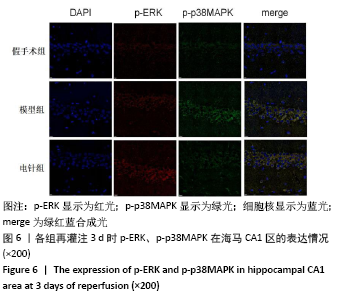
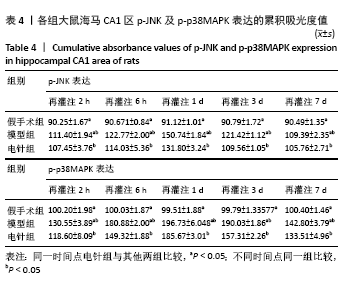
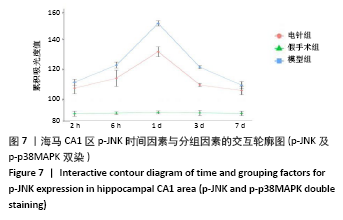
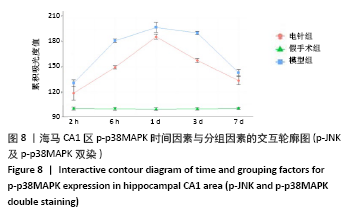
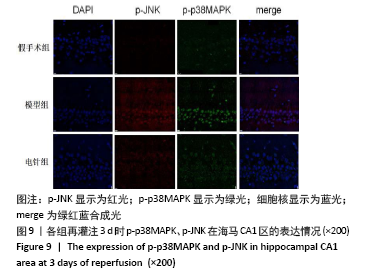
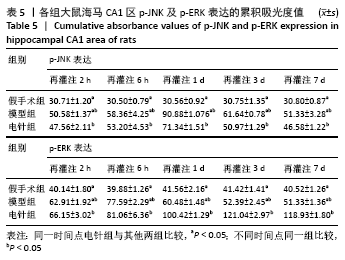
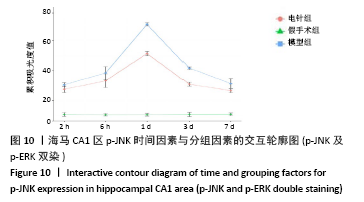
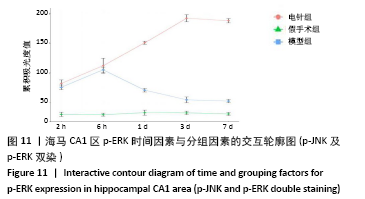
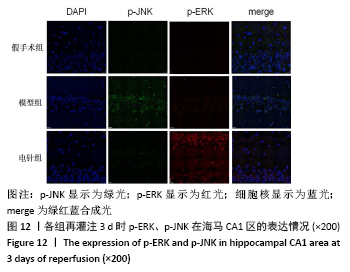
方法:150只SD雄性大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、电针组(后2组线栓法制备右侧大脑中动脉栓塞缺血模型),每组50只,每组再设脑缺血1.5 h后再灌注2 h、6 h、1 d、3 d、7 d共5个时间亚组,每亚组10只。电针各亚组在规定时间点行单次电针治疗,选取“合谷”“尺泽”“足三里”“三阴交”,予疏密波,频率2 Hz,强度1 mA,治疗20 min;电针的同一时间抓取模型组和假手术组的大鼠进行固定,但不进行电针干预。在相应时间点进行神经功能缺损评分,之后大鼠麻醉后取脑,TTC染色法观察脑梗死面积,免疫荧光双标法结合检测p-ERK、p-JNK、p-p38MAPK的表达。
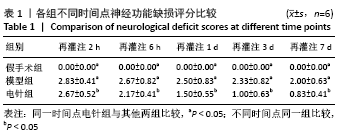
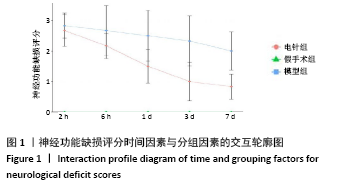
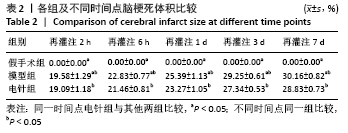
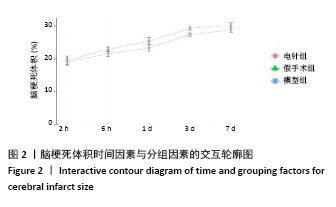
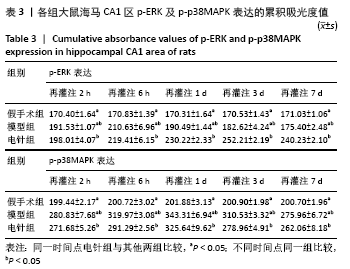
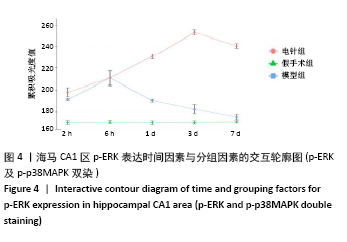
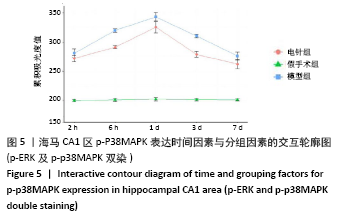
结果与结论:①与假手术组相比,模型组同时段各亚组神经功能缺损评分升高、脑梗死体积增大(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,电针组再灌注6 h、1 d、3 d亚组神经功能缺损评分显著降低、脑梗死体积明显减少(P < 0.05);②与模型组比较,电针组再灌注1,3 d出现p-ERK表达的明显上调(P < 0.05)及p-JNK的表达显著下降(P < 0.05),p-p38MAPK在再灌注6 h、3 d时下降明显再灌注;③结果说明电针可减少脑梗死体积,减轻神经功能缺损,并上调p-ERK同时下调p-JNK、p-p38MAPK的表达,且电针在再灌注6 h-3 d内效果最佳;电针促进缺血再灌注引起的脑组织损伤修复,通过调控MAPK家族信号通路发挥脑保护作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4613-4384 (周国平)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: