中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (17): 2702-2707.doi: 10.12307/2022.538
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
运动预适应干预低压低氧诱发肺损伤模型大鼠Nrf2/ARE信号通路的变化
尤 锟1,刘远新2
- 1西安石油大学体育系,陕西省西安市 710065;2西安体育学院 运动与健康科学学院,陕西省西安市 710068
Protective effect of exercise preconditioning on lung injury induced by hypobaric hypoxia in rats based on the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element signal pathway
You Kun1, Liu Yuanxin2
- 1Department of Physical Education, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an 710065, Shaanxi Province, China; 2School of Sports and Health Sciences, Xi’an Physical Education University, Xi’an 710068, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
运动预适应:主要通过反复的间歇性适宜运动训练,增加机体对缺氧和缺血的耐受力,从而达到心肌保护作用,这种保护作用主要体现在有两个主要的保护效应期:即早期保护效应时期和晚期保护效应时期。
抗氧化反应元件(antioxidant response element,ARE):是一种特异的DNA-启动子结合序列,主要位于谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶等保护性基因的5’端。ARE可被氧化性化合物激活,启动抗氧化酶和II相解毒酶基因的表达,从而保护细胞组织功能。
背景:低压低氧会影响大鼠肺功能,造成肺组织细胞凋亡诱发肺血管重塑;运动预适应能通过上调肺组织中核因子E2相关因子2/抗氧化反应元件信号通路改善肺血管重塑所致的肺损伤。
目的:基于核因子E2相关因子2/抗氧化反应元件信号通路探讨运动预适应对低压低氧诱发大鼠肺损伤的保护作用。
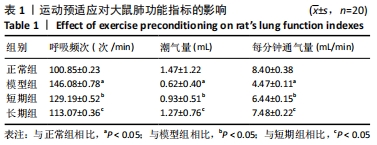
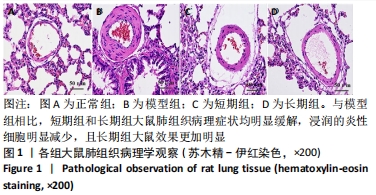
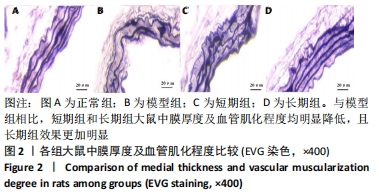
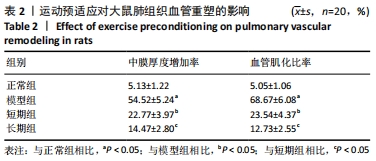
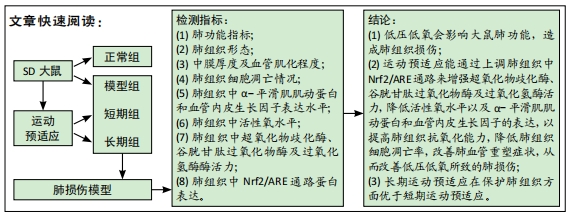
方法:将80只SD大鼠随机分为4组,每组20只,依次为正常组、模型组、短期运动预适应组(短期组)、长期运动预适应组(长期组) 。短期组大鼠进行持续1周的游泳训练;长期组以短期组方式持续运动3周,短期组、长期组于末次运动结束后次日与模型组大鼠置于低压舱中缓慢匀速减压至海拔8 000 m水平(以 10 m/s速度上升),连续低氧 48 h,建立低压低氧诱发大鼠肺损伤模型;正常组不做处理。苏木精-伊红染色观察大鼠肺组织病理学改变,弹力纤维(EVG)染色观察大鼠肺组织血管重塑,TUNEL染色检测大鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞的凋亡,免疫组化检测大鼠肺动脉组织中血管内皮生长因子和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的表达,活性氧试剂盒检测大鼠血活性氧水平,黄嘌呤氧化酶法检测大鼠肺组织中超氧化物歧化酶活性,二硫代二硝基苯甲酸检测谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性,钼酸铵-化学比色法检测过氧化氢酶活性,Western blot检测大鼠肺组织中核因子E2相关因子2 /抗氧化反应元件信号通路蛋白;记录大鼠每分钟呼吸频次、潮气量、每分钟通气量。
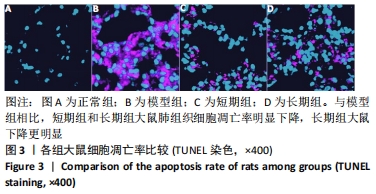
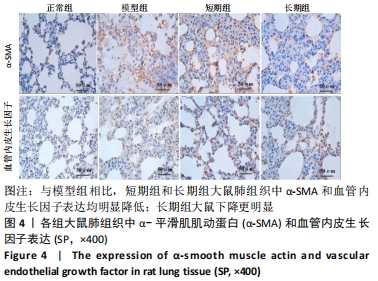
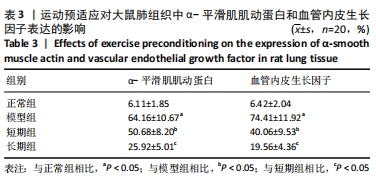
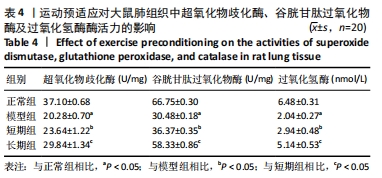
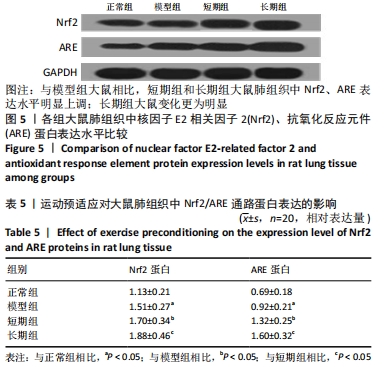
结果与结论:①与正常组相比,模型组大鼠的呼吸频次明显升高,潮气量和每分钟通气量明显降低,肺组织中肺小动脉中膜厚度及血管肌化程度明显增加,细胞凋亡率、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和血管内皮生长因子表达、活性氧水平及核因子E2相关因子2、抗氧化反应元件表达均明显上调,超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及过氧化氢酶的活力均明显降低;与模型组相比,短期组与长期组的呼吸频次明显降低,潮气量和每分钟通气量明显升高,肺组织中中膜厚度及血管肌化程度明显降低,细胞凋亡率、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和血管内皮生长因子表达、活性氧含量及核因子E2相关因子2、抗氧化反应元件表达均明显下调,超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及过氧化氢酶酶活力均明显升高,长期组变化更为明显;差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。②结果说明,低压低氧会影响大鼠肺功能,造成肺组织损伤;运动预适应能通过上调肺组织中核因子E2相关因子2/抗氧化反应元件通路来增强超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶及过氧化氢酶活力,降低活性氧水平以及α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和血管内皮生长因子的表达,以提高肺组织抗氧化能力,降低肺组织细胞凋亡率,改善肺血管重塑症状,从而改善低压低氧所致的肺损伤;且长期运动预适应在保护肺组织方面优于短期运动预适应。
缩略语:核因子E2相关因子2:nuclear factor E2-related factor 2,Nrf2;抗氧化反应元件:antioxidant response element,ARE;α-平滑肌肌动蛋白:α-smoothmus-cleactin,α-SMA
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4148-9362 (尤锟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: