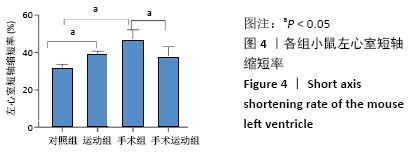
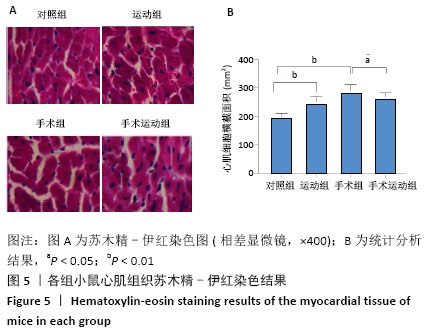
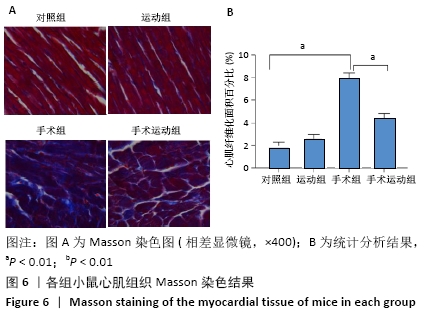
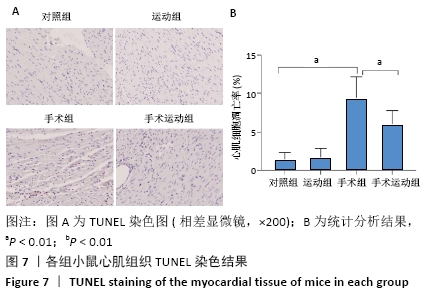
[1] ZHANG YB, PAN XF, CHEN J, et al. Combined lifestyle factors, all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2021;75(1):92-99.
[2] RESTREPO C, PATEL SK, RETHNAM V, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy and cognitive function: a systematic review. J Hum Hypertens. 2018; 32(3):171-179.
[3] SINGH MV, CICHA MZ, NUNEZ S, et al. Angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy are differentially mediated by TLR3- and TLR4-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019;316(5):H1027-H1038.
[4] TSCHÖPE C, KHERAD B, KLEIN O, et al. Cardiac contractility modulation: mechanisms of action in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and beyond. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019;21(1):14-22.
[5] SACO-LEDO G, VALENZUELA PL, RUIZ-HURTADO G, et al. Exercise Reduces Ambulatory Blood Pressure in Patients With Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9(24):e018487.
[6] YAMAKOSHI S, NAKAMURA T, MORI N,et al. Effects of exercise training on renal interstitial fibrosis and renin-angiotensin system in rats with chronic renal failure. J Hypertens. 2021;39(1):143-152.
[7] KAIDONIS X, NIU W, CHAN AY, et al. Adaptation to exercise-induced stress is not dependent on cardiomyocyte α1A-adrenergic receptors. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Feb 26:S0022-2828(21)00047-X.
[8] CATTADORI G, SEGURINI C, PICOZZI A, et al. Exercise and heart failure: an update. ESC Heart Fail. 2018;5(2):222-232.
[9] SCOTT JM, MARTIN D, PLOUTZ-SNYDER R, et al. Efficacy of Exercise and Testosterone to Mitigate Atrophic Cardiovascular Remodeling. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(9):1940-1949.
[10] MCGINNIS GR, BALLMANN C, PETERS B, et al. Interleukin-6 mediates exercise preconditioning against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308(11):H1423-1433.
[11] FENG R, CAI M, WANG X, et al. Early Aerobic Exercise Combined with HydrogenRich Saline as Preconditioning Protects Myocardial Injury Induced by Acute Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;187(3):663-676.
[12] SONG YJ, ZHONG CB, WANG XB. Heat shock protein 70: A promising therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(2):1190-1207.
[13] KRÜGER K, REICHEL T, ZEILINGER C. Role of heat shock proteins 70/90 in exercise physiology and exercise immunology and their diagnostic potential in sports. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(4):916-927.
[14] CAI WF, ZHANG XW, YAN HM, et al. Intracellular or extracellular heat shock protein 70 differentially regulates cardiac remodelling in pressure overload mice. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;88(1):140-149.
[15] TANIIKE M, YAMAGUCHI O, TSUJIMOTO I, et al. Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/p38 signaling pathway negatively regulates physiological hypertrophy. Circulation. 2008;117(4):545-552.
[16] PFLEGER J, GRESHAM K, KOCH WJ. G protein-coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in the heart. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(10): 612-622.
[17] RAMACHANDRA CJA, CONG S, CHAN X, et al.Oxidative stress in cardiac hypertrophy: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic targets. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:297-312.
[18] HE J, LUO Y, SONG J, et al. Non-coding RNAs and Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1229:231-245.
[19] MATSUURA TR, LEONE TC, KELLY DP. Fueling Cardiac Hypertrophy. Circ Res. 2020;126(2):197-199.
[20] MOORE MN, CLIMIE RE, OTAHAL P, et al. Exercise blood pressure and cardiac structure:A systematic review and meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. J Sci Med Sport. 2021;S1440-2440(21).
[21] BO B, ZHOU Y, ZHENG Q, et al. The Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Aerobic Exercise-Induced Cardiac Regeneration. Biomolecules. 2020;11(1):19.
[22] XU T, TANG H, ZHANG B, et al. Exercise preconditioning attenuates pressure overload-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(1):530-540.
[23] WEEKS KL, GAO X, DU XJ, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p110 Is a Master Regulator of Exercise-Induced Cardioprotection and PI3K Gene Therapy Rescues Cardiac Dysfunction. Circ Heart Fail. 2012;5(4): 523-534.
[24] BOSCH L, DE HAAN JJ, BASTEMEIJER M, et al. The transverse aortic constriction heart failure animal model: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail Rev. 2020 Apr 25. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-09960-w.
[25] DU P, CHANG Y, DAI F, et al. Role of heat shock transcription factor 1(HSF1)upregulated macrophage in ameliorating pressure overload-induced heart failure in mice. Gene. 2018;667:10-17.
[26] 邹书帆. KLF15 抑制小鼠心室超负荷所致心功能衰竭的作用及机制研究[D]. 重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2019.
[27] 孟永胜,蹇朝,朱昀,等.心室压力超负荷早期心肌纤维化的动态病理学变化[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2017,39(10):966-970.
[28] 徐同毅. miR-214-5p 调控 HSF1 在运动预处理减轻病理性心肌肥厚中的作用机制研究[D]. 上海:第二军医大学,2014.
[29] SRIVASTAVA K, NARANG R, BHATIA J, et al. Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 Gene and Its Correlation with Inflammatory Markers in Essential Hypertension. Plos One. 2016;11(3):e151060.
[30] MOYZIS AG, LALLY NS, LIANG W, et al. Mcl-1-mediated mitochondrial fission protects against stress but impairs cardiac adaptation to exercise. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;146:109-120.
[31] NI E, ZHAO L, YAO N, et al. The PXXP domain is critical for the protective effect of BAG3 in cardiomyocytes. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019; 46(5):435-443.
[32] QIAN ZQ, WANG YW, LI YL, et al. Icariin prevents hypertension-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;88:823-831.
[33] Wu Y, Qian Z, Fu S, et al. IcarisideII improves left ventricular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibiting the ASK1-JNK/p38 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;819:68-79.
[34] Mejías-Peña Y, Estébanez B, Rodriguez-Miguelez P, et al. Impact of resistance training on the autophagy-inflammation-apoptosis crosstalk in elderly subjects. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9(2):408-418.
[35] Aboutaleb N, Shamsaei N, Khaksari M, et al. Pre-ischemic exercise reduces apoptosis in hippocampal CA3 cells after cerebral ischemia by modulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 proteins ratio and prevention of caspase-3 activation. J Physiol Sci. 2015;65(5):435-443.
[36] Lin YY, Hong Y, Yu SH, et al. Antiapoptotic and mitochondrial biogenetic effects of exercise training on ovariectomized hypertensive rat hearts. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(6):1661-1672.
[37] Wang Y, Tian MM, Mi CJ, et al. Exercise protects the heart against myocardial infarction through upregulation of miR-1192. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;521(4):1061-1069.
[38] Qian ZQ, Wang YW, Li YL, et al. Icariin prevents hypertension-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;88:823-831.
[39] Wu Y, Qian Z, Fu S, et al. IcarisideII improves left ventricular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibiting the ASK1-JNK/p38 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;819:68-79.
|