中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (5): 729-734.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3007
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
针刀治疗胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠滑膜组织Bcl-2/Bax的表达
刘 青,万碧江
- 湖北中医药大学针灸骨伤学院,湖北省武汉市 430061
Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats
Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang
- College of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Orthopedics, Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
胶原诱导性关节炎:用牛Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和弗氏不完全佐剂制成的Ⅱ型乳剂进行二次免疫,诱导大鼠产生关节炎。由于其免疫炎症反应、病理变化和疾病表现与人类的类风湿关节炎具有高度相似性,是研究类风湿关节炎较理想的动物模型。
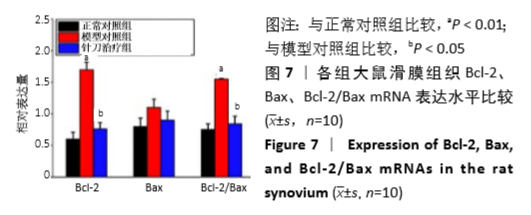
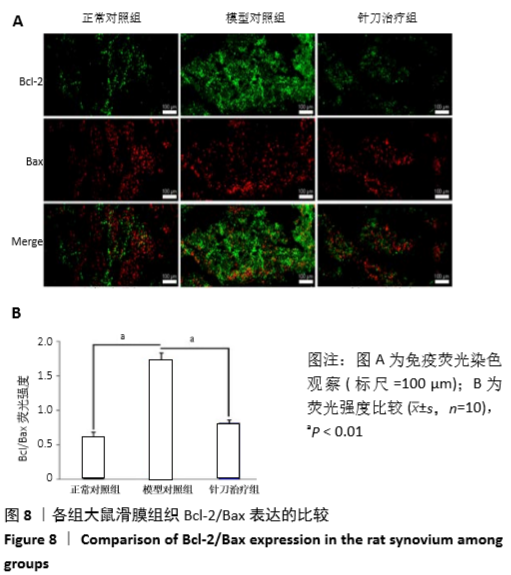
滑膜组织Bcl-2/Bax表达:Bcl-2蛋白家族是参与细胞凋亡的关键调节因子,在Bcl-2蛋白家族中Bcl-2是起主要作用的抗凋亡蛋白,Bax是重要的促凋亡蛋白,Bcl-2/Bax是启动细胞凋亡的“分子开关”,滑膜组织中Bcl-2/Bax比值的增高促进了类风湿关节炎的发生发展。
背景:临床研究表明,针刀治疗能够改善类风湿关节炎患者的症状,减轻关节肿胀,改善受损关节的活动功能,但尚无其具体作用机制的实验研究报道。
目的:观察针刀治疗对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠滑膜组织Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响。
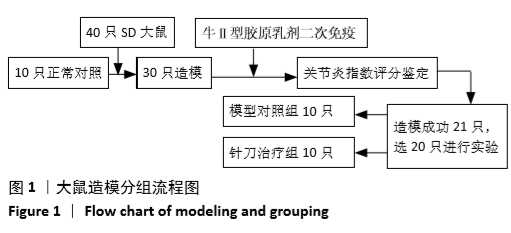
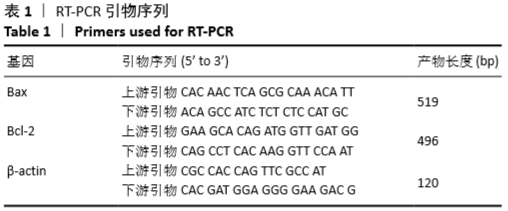
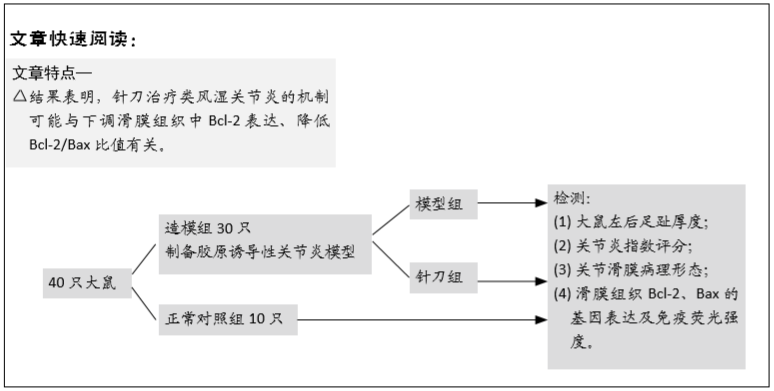
方法:将40只大鼠随机分为正常对照组10只,造模组30只。造模组大鼠采用二次免疫法制备胶原诱导性关节炎模型,随机选取20只造模成功大鼠随机分为模型组和针刀组。正常组和模型组不予处理;针刀组大鼠于左膝关节周围触及髌内外支持带、膝内外侧副韧带、髌底上缘中点及髌韧带的中点,每次选取上述2点予以针刀治疗,1次/周,共治疗3次。实验过程中监测大鼠一般情况,测量大鼠左后足趾厚度,进行关节炎指数评分;苏木精-伊红染色法观察关节滑膜病理形态;应用实时定量PCR法、免疫荧光技术分别检测滑膜组织Bcl-2、Bax的基因表达水平及免疫荧光强度。实验方案经湖北中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为00127518)。
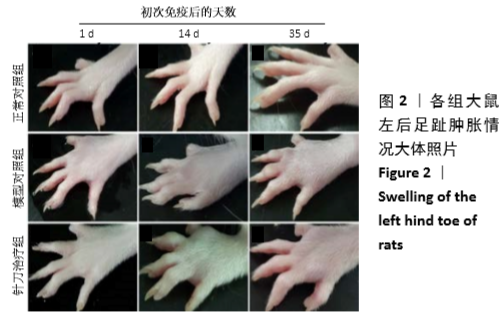
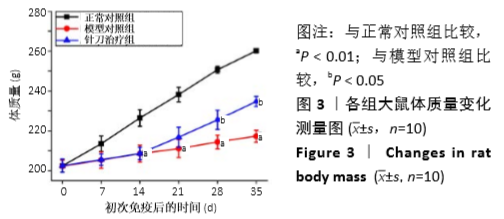
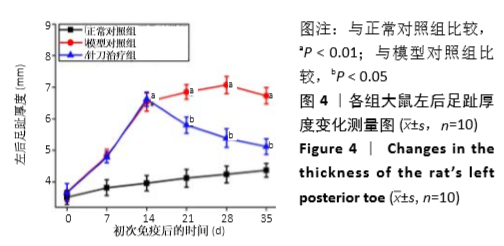
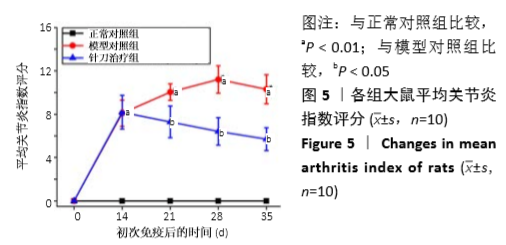
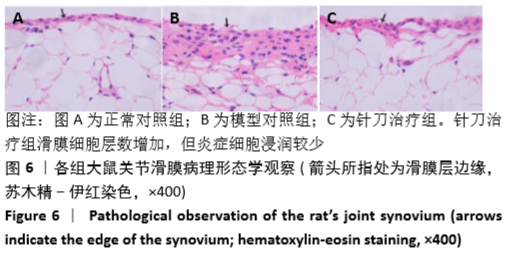
结果与结论:①与正常组相比,模型组左后足趾厚度及关节炎指数评分明显增加(P < 0.01,P < 0.01);与模型组相比,针刀组左后足趾厚度及关节炎指数评分减小(P < 0.05,P < 0.05);②病理形态上,模型组较正常组滑膜层数增厚,大量炎症细胞浸润,针刀组较模型组滑膜层数减少,炎症细胞浸润减轻;③各组间滑膜组织Bax mRNA表达水平比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);针刀组Bcl-2 mRNA、Bcl-2/Bax mRNA表达较模型组明显降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.01);④与模型组比较,针刀组Bcl-2/Bax荧光强度明显降低(P < 0.01);⑤结果表明,针刀治疗类风湿关节炎的机制可能与下调滑膜组织中Bcl-2表达,降低Bcl-2/Bax比值有关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6777-8616 (刘青)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: