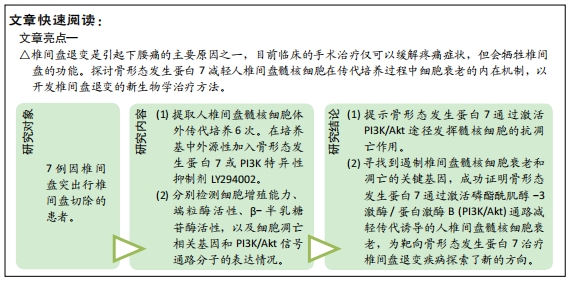
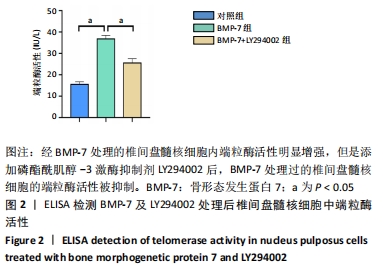
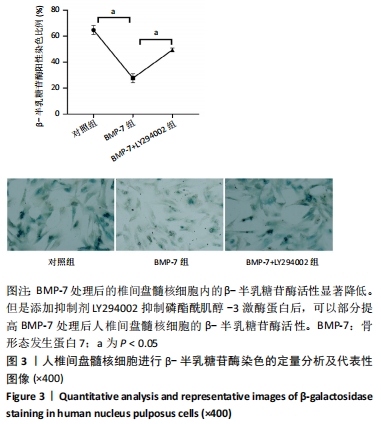
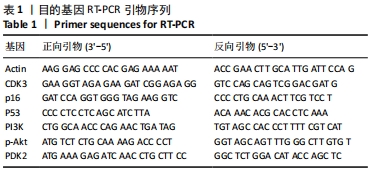
[1] 邱晨生, 邓念, 相宏飞, 等. 椎间盘退变相关危险因素的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(10):654-659.
[2] 陈敏, 赵凯. 椎间盘退变的机制及其治疗方法的研究进展[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2019,10(18):58-60.
[3] 余城墙, 张宇, 谢程欣, 等. 椎间盘退变分子生物学机制及再生治疗的优势与未来[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4889-4896.
[4] VADALA G, RUSSO F, De STROBEL F, et al. Novel stepwise model of intervertebral disc degeneration with intact annulus fibrosus to test regeneration strategies. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(9):2460-2468.
[5] 陈铭, 沈军. 椎间盘髓核退变再生修复研究和临床应用现状[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(5):774-780.
[6] ZHAO K, AN R, XIANG Q, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels regulate nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and pyroptosis via the NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021; 54(1):e12941.
[7] WANG W, DENG G, QIU Y, et al. Transplantation of allogenic nucleus pulposus cells attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting apoptosis and increasing migration. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(5):2553-2564.
[8] LIU J, YU J, JIANG W, et al. Targeting of CDKN1B by miR-222-3p may contribute to the development of intervertebral disc degeneration. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(4):728-735.
[9] MA K, CHEN S, LI Z, et al. Mechanisms of endogenous repair failure during intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(1):41-48.
[10] WU Q, MATHERS C, WANG EW, et al. TGF-beta Initiates beta-Catenin-Mediated CTGF Secretory Pathway in Old Bovine Nucleus Pulposus Cells: A Potential Mechanism for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. JBMR Plus. 2019;3(2):e10069.
[11] CHEN S, LIU S, MA K, et al. TGF-beta signaling in intervertebral disc health and disease. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(8):1109-1117.
[12] KROUWELS A, ILJAS JD, KRAGTEN A, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins for Nucleus Pulposus Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(8):2720.
[13] LI Z, LANG G, KARFELD-SULZER LS, et al. Heterodimeric BMP-2/7 for nucleus pulposus regeneration-In vitro and ex vivo studies. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(1):51-60.
[14] MA K, CHEN S, LI Z, et al. Mechanisms of endogenous repair failure during intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(1):41-48.
[15] De CICCO FL, CAMINO WG. Nucleus Pulposus Herniation. 2021.
[16] TAVAKOLI J, DIWAN AD, TIPPER JL. Elastic fibers: The missing key to improve engineering concepts for reconstruction of the Nucleus Pulposus in the intervertebral disc. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:407-416.
[17] MOHANTY S, DAHIA CL. Defects in intervertebral disc and spine during development, degeneration, and pain: New research directions for disc regeneration and therapy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2019;8(4): e343.
[18] TANG X, JING L, RICHARDSON WJ, et al. Identifying molecular phenotype of nucleus pulposus cells in human intervertebral disc with aging and degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(8):1316-1326.
[19] WU H, SHANG Y, YU J, et al. Regenerative potential of human nucleus pulposus resident stem/progenitor cells declines with ageing and intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(4):2193-2202.
[20] ZHAO R, LIU W, XIA T, et al. Disordered Mechanical Stress and Tissue Engineering Therapies in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(7):1151.
[21] GE J, CHENG X, YUAN C, et al. Syndecan-4 is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Suppressing JNK/p53 Pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(5):766-776.
[22] LEUNG VYL, ZHOU L, TAM WK, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -7 mediate the anabolic function of nucleus pulposus cells with discrete mechanisms. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(6):573-585.
[23] GU T, SHI Z, WANG C, et al. Human bone morphogenetic protein 7 transfected nucleus pulposus cells delay the degeneration of intervertebral disc in dogs. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(6):1311-1322.
[24] KIM JS, ELLMAN MB, AN HS, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 synergizes with bone morphogenetic protein 7-mediated anabolism in bovine intervertebral disc cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(12):3706-3715.
[25] WANG C, RUAN DK, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of adeno-associated virus-2-mediated human BMP-7 gene transfection on the phenotype of nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(6):838-845.
[26] WANG Z, HUTTON WC, YOON ST. The effect of capacitively coupled (CC) electrical stimulation on human disc nucleus pulposus cells and the relationship between CC and BMP-7. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(1):240-247.
[27] LI XC, WU YH, BAI XD, et al. BMP7-Based Functionalized Self-Assembling Peptides Protect Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Stem Cells From Apoptosis In Vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(19-20):1218-1228.
[28] CHAOFENG W, CHAO Z, DELI W, et al. Nucleus pulposus cells expressing hBMP7 can prevent the degeneration of allogenic IVD in a canine transplantation model. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(9):1366-1373.
[29] YANG P, TRONCONE L, AUGUR ZM, et al. The role of bone morphogenetic protein signaling in vascular calcification. Bone. 2020;141:115542.
[30] SAMPATH TK, VUKICEVIC S. Biology of bone morphogenetic protein in bone repair and regeneration: A role for autologous blood coagulum as carrier. Bone. 2020;141:115602.
[31] GONG C, PAN W, HU W, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-7 retards cell subculture-induced senescence of human nucleus pulposus cells through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3): BSR20182312.
[32] ZHOU X, TAO Y, LIANG C, et al. BMP3 Alone and Together with TGF-beta Promote the Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells into a Nucleus Pulposus-Like Phenotype. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):20344-20359.
[33] XIE Z, JIE Z, WANG G, et al. TGF-beta synergizes with ML264 to block IL-1beta-induced matrix degradation mediated by Kruppel-like factor 5 in the nucleus pulposus. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018; 1864(2): 579-589.
[34] TAN Y, YAO X, DAI Z, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 alleviated intervertebral disc degeneration through mediating the degradation of ECM and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(1):583-592.
[35] HUANG J, JIANG R, CHU X, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-23a-5p induces myocardial infarction by promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis through inhibited of PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020;38(8):1047-1055.
[36] TAO H, CHENG L, YANG R. Downregulation of miR-34a Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Rat Osteoarthritic Cartilage Cells by Activating PI3K/Akt Pathway. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:373-385.
[37] SUN K, LUO J, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4): 400-409.
|