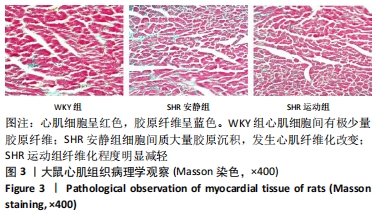
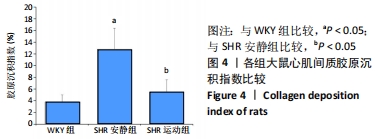
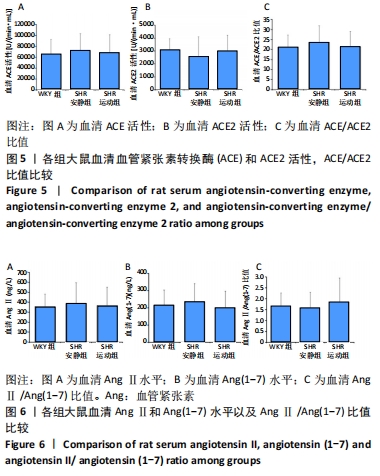
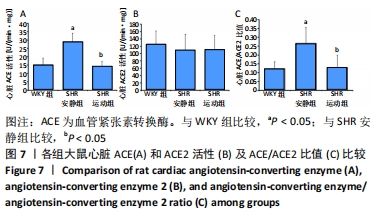
[1] TOMEK J, BUB G. Hypertension-induced remodelling: on the interactions of cardiac risk factors. J Physiol. 2017;595(12):4027-4036.
[2] TAKIMOTO-OHNISHI E, MURAKAMI K. Renin-angiotensin system research: from molecules to the whole body. J Physiol Sci. 2019;69(4):581-587.
[3] VARAGIC J, FROHLICH ED. Local cardiac renin-angiotensin system: hypertension and cardiac failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002;34(11):1435-1442.
[4] SANTOS R, OUDIT GY, VERANO-BRAGA T,et al. The renin-angiotensin system: going beyond the classical paradigms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019; 316(5):H958-970.
[5] SANTOS R, SAMPAIO WO, ALZAMORA AC, et al. The ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis of the renin-angiotensin system: Focus on angiotensin-(1-7). Physiol Rev. 2018;98(1):505-553.
[6] PAZ OCARANZA M, RIQUELME JA, GARCÍA L, et al. Counter-regulatory renin-angiotensin system in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(2): 116-129.
[7] BESSA A, JESUS ÉF, NUNES A, et al. Stimulation of the ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis in hypertensive pregnant rats attenuates cardiovascular dysfunction in adult male offspring. Hypertens Res. 2019;42(12):1883-1893.
[8] LEWINGTON S, CLARKE R, QIZILBASH N, et al. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360 (9349):1903-1913.
[9] LAURENT S. Antihypertensive drugs. Pharmacol Res. 2017;124:116-125.
[10] THOMPSON G, DAVISON GW, CRAWFORD J, et al. Exercise and inflammation in coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. J Sports Sci. 2020;38(7):814-826.
[11] JACOB S, KRENTZ AJ. Exercise prescription in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease: could less be more?. Cardiovasc Endocrinol Metab. 2020;9(1):1-2.
[12] TIPTON CM. The history of “Exercise Is Medicine” in ancient civilizations[J]. Adv Physiol Educ. 2014;38(2):109-117.
[13] CORNELISSEN VA, FAGARD RH. Effects of endurance training on blood pressure, blood pressure-regulating mechanisms, and cardiovascular risk factors. Hypertension. 2005;46(4):667-675.
[14] 袁国强, 秦永生, 彭朋. 有氧运动对自发性高血压大鼠心肌纤维化的影响及机制[J]. 天津医药,2020,48(2):100-104.
[15] 袁国强, 秦永生, 彭朋. 高强度间歇运动对自发性高血压模型大鼠病理性心脏肥大的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(23):3708-3715.
[16] 黄红梅, 胡宗祥, 刘昭强, 等. 长期高强度间歇训练加重自发性高血压大鼠心肌纤维化[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(8):615-625.
[17] 范朋琦, 秦永生, 彭朋. 不同运动方式对自发性高血压大鼠心脏重塑和运动能力的影响[J]. 现代预防医学,2018,45(23):4341-4345.
[18] 孟宪欣, 管泽毅, 葛吉生, 等. 间歇运动干预自发性高血压大鼠病理性心脏肥大:运动强度与健康效应的关系[J]. 体育科学,2019,39(6):73-82.
[19] MEDEIROS RF, GAIQUE TG, BENTO-BERNARDES T, et al. Aerobic training prevents oxidative profile and improves nitric oxide and vascular reactivity in rats with cardiometabolic alteration. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016;121(1): 289-298.
[20] CARMONA AK, SCHWAGER SL, JULIANO MA, et al. A continuous fluorescence resonance energy transfer angiotensin I-converting enzyme assay. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(4):1971-1976.
[21] ROSA RM, COLUCCI JA, YOKOTA R, et al. Alternative pathways for angiotensin II production as an important determinant of kidney damage in endotoxemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311(3):F496-504.
[22] SHENASA M, SHENASA H. Hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy, and sudden cardiac death. Int J Cardiol. 2017;237:60-63.
[23] OLDFIELD CJ, DUHAMEL TA, DHALLA NS. Mechanisms for the transition from physiological to pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;98(2):74-84.
[24] GEORGE K, WHYTE GP, GREEN DJ, et al. The endurance athletes heart: acute stress and chronic adaptation. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46 Suppl 1:i29-36.
[25] NADRUZ W. Myocardial remodeling in hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2015;29(1):1-6.
[26] MA ZG, YUAN YP, WU HM, et al. Cardiac fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(12):1645-1657.
[27] KYSELOVIČ J, LEDDY JJ. Cardiac fibrosis: The beneficial effects of exercise in cardiac fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;999:257-268.
[28] CHOI SY, CHANG HJ, CHOI SI, et al. Long-term exercise training attenuates age-related diastolic dysfunction: association of myocardial collagen cross-linking. J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(1):32-39.
[29] FILHO AG, FERREIRA AJ, SANTOS SH, et al. Selective increase of angiotensin(1-7) and its receptor in hearts of spontaneously hypertensive rats subjected to physical training. Exp Physiol. 2008;93(5):589-598.
[30] FERNANDES T, HASHIMOTO NY, MAGALHÃES FC, et al. Aerobic exercise training-induced left ventricular hypertrophy involves regulatory MicroRNAs, decreased angiotensin-converting enzyme-angiotensin ii, and synergistic regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-angiotensin (1-7). Hypertension. 2011;58(2):182-189.
[31] BOSNYAK S, JONES ES, CHRISTOPOULOS A, et al. Relative affinity of angiotensin peptides and novel ligands at AT1 and AT2 receptors. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;121(7):297-303.
[32] GOWRISANKAR YV, CLARK MA. Angiotensin II regulation of angiotensin-converting enzymes in spontaneously hypertensive rat primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem. 2016;138(1):74-85.
[33] PATEL VB, ZHONG JC, GRANT MB, et al. Role of the ACE2/Angiotensin 1-7 Axis of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Heart Failure. Circ Res. 2016;118(8): 1313-1326.
[34] WANG X, YE Y, GONG H, et al. The effects of different angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on the regulation of the ACE-AngII-AT1 and ACE2-Ang(1-7)-Mas axes in pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling in male mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;97:180-190.
[35] NI J, YANG F, HUANG XR, et al. Dual deficiency of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 and Mas receptor enhances angiotensin II-induced hypertension and hypertensive nephropathy. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(22):13093-13103.
[36] LIAO W, WU J. The ACE2/Ang (1-7)/MasR axis as an emerging target for antihypertensive peptides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(15):2572-2586.
[37] FRANTZ E, PRODEL E, BRAZ ID, et al. Modulation of the renin-angiotensin system in white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle: focus on exercise training. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132(14):1487-1507.
|