[1] MADER TH, GIBSON CR, PASS AF, et al. Optic disc edema, globe flattening, choroidal folds, and hyperopic shifts observed in astronauts after long-duration space flight. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(10):2058-2069.
[2] MAKAROV IA, VORONKOV YI, ASLANJAN MG. Ophthalmic Changes Associated with Long-Term Exposure to Microgravity. Fiziol Cheloveka. 2017;43(1):111-120.
[3] ANDERSON AP, SWAN JG, PHILLIPS SD, et al. Acute effects of changes to the gravitational vector on the eye. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016; 120(8):939-946.
[4] 赵军,胡莲娜,梁会泽,等.模拟失重状态对正常人远视力、近视力、近点、立体视觉及眼压的影响[J]. 眼科新进展,2011,31(7):642-644.
[5] 许欣,徐志明,刘国印,等.头低位卧床对眼内压、近视力、视野的影响及其中药防护[J].航天医学与医学工程,2002,15(6):419-422.
[6] TAIBBI G, KAPLOWITZ K, CROMWELL RL, et al. Effects of 30-day head-down bed rest on ocular structures and visual function in a healthy subject. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2013;84(2):148-154.
[7] SHINOJIMA A, IWASAKI K, AOKI K, et al. Subfoveal choroidal thickness and foveal retinal thickness during head-down tilt. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2012,83(4):388-393.
[8] CHAKRABORTY R, READ SA, COLLINS MJ. Diurnal variations in axial length, choroidal thickness, intraocular pressure, and ocular biometrics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(8):5121-5129.
[9] SINGH SR, RASHEED MA, GOUD A, et al. Diurnal variation in subfoveal and peripapillary choroidal vascularity index in healthy eyes. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2019;67(10):1667-1672.
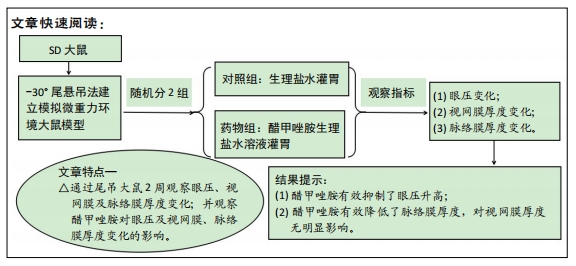
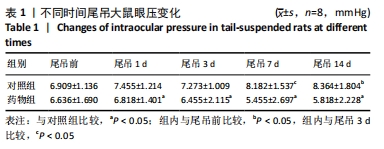
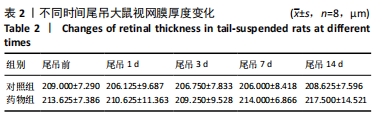
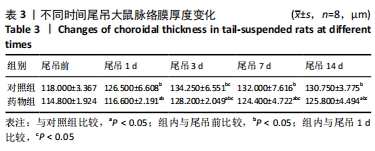
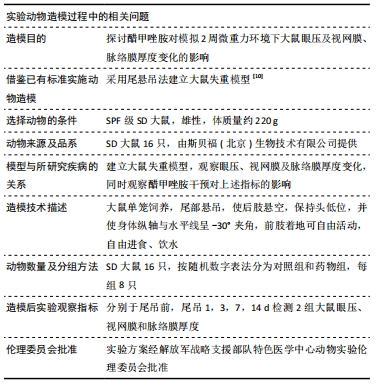
[10] 陈杰,马进,丁兆平,等.一种模拟长期失重影响的大鼠尾部悬吊模型[J].空间科学学报,1993,13(2):159-162.
[11] 杨振菲,朱思泉. 失重状态对眼部影响的研究进展[J].中华眼科杂志,2015,51(4):310-313.
[12] TAIBBI G, CROMWELL RL, KAPOOR KG, et al. The effect of microgravity on ocular structures and visual function: a review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2013;58(2):155-163.
[13] ZHANG LF,HARGENS AR.Spaceflight-Induced Intracranial Hypertension and Visual Impairment: Pathophysiology and Countermeasures. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(1):59-87.
[14] 孙伟,林少芬,李涛,等. FFA及OCT对STZ诱导的早期糖尿病大鼠视网膜的活体观察[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2014,32(4):318-323.
[15] BILL A, SPERBER GO. Control of retinal and choroidal blood flow. Eye (Lond).1990;4(Pt 2):319-325.
[16] MADER TH. Intraocular pressure in microgravity. J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;31(10):947-950.
[17] REINER A, FITZGERALD MEC, DEL MAR N, et al. Neural control of choroidal blood flow. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018;64:96-130.
[18] 袁菁,汪锐,胡维琨.小梁切除术联合醋甲唑胺片治疗青光眼的效果及对患者眼压、眼血流动力学的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2019, 35(8):1318-1321.
[19] PATEL N, PASS A, MASON S, et al. Optical Coherence Tomography Analysis of the Optic Nerve Head and Surrounding Structures in Long-Duration International Space Station Astronauts. JAMA Ophthalmol 2018;136(2):193-200.
[20] LAURIE SS, LEE SMC, MACIAS BR, et al. Optic Disc Edema and Choroidal Engorgement in Astronauts During Spaceflight and Individuals Exposed to Bed Rest. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;138(2):165-172.
[21] MACIAS BR, PATEL NB, GIBSON CR, et al. Association of Long-Duration Spaceflight With Anterior and Posterior Ocular Structure Changes in Astronauts and Their Recovery. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020;138(5):1-7.
[22] HUANG AS, STENGER MB, MACIAS BR. Gravitational Influence on Intraocular Pressure: Implications for Spaceflight and Disease. J Glaucoma. 2019;28(8):756-764.
[23] MACIAS BR, LIU JH, GRANDE-GUTIERREZ N, et al. Intraocular and intracranial pressures during head-down tilt with lower body negative pressure. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2015;86(1):3-7.
[24] ARORA N, MCLAREN JW, HODGE DO,et al. Effect of Body Position on Epsicleral Venous Pressure in Healthy Subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(12):5151-5156.
[25] DRAEGER J, SCHWARTZ R, GROENHOFF S, et al. Self tonometry during the German 1993 Spacelab D2 mission. Ophthalmologe. 1994;91(5): 697-699.
[26] DRAEGER J, SCHWARTZ R, GROENHOFF S, et al. Self-tonometry under microgravity conditions. Clin Investig. 1993;71(9):700-703.
[27] 陈小凤,潘学会,朱思泉.微重力环境对眼压和视力的影响及其机制研究进展[J]. 西南国防医药,2018,28(12):1290-1292.
[28] SMITH TJ, LEWIS J.Effect of inverted body position intraocular pressure.Am J Ophthalmol. 1985;99(5):617-618.
[29] ANDERSON AP, BABU G, SWAN JG, et al. Ocular changes over 60 min in supine and prone postures. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;123(2):415-423.
[30] 孟超,景筠,王佳伟. 颅内压增高伴原发性血小板增多症七例临床分析[J].中华神经科杂志,2017,50(12):922-926.
|