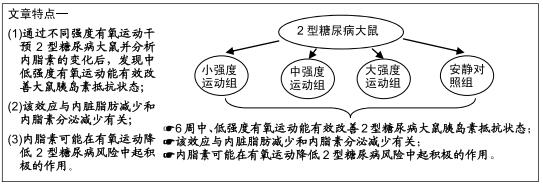
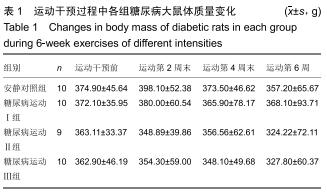
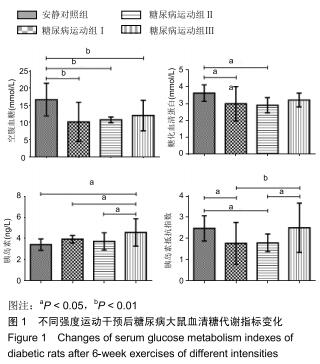
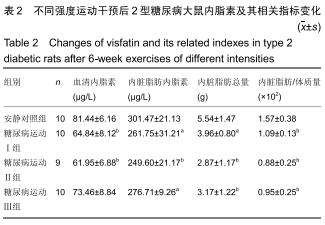
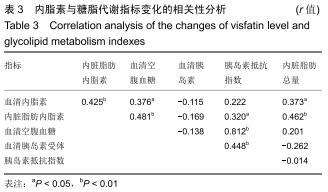
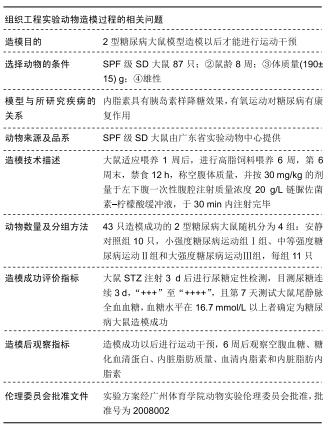
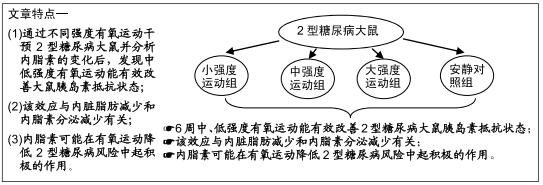
|
[1] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018; 44:38-50.
[2] ROMACHO T, ELSEN M, RÖHRBORN D, et al. Adipose tissue and its role in organ crosstalk. Acta Physiol. 2014;210(4):733-753.
[3] SOUNDARRAJAN M, DENG J, KWASNY M, et al. Activated brown adipose tissue and its relationship to adiposity and metabolic markers: an exploratory study. Adipocyte. 2020;9(1): 87-95.
[4] FUKUHARA A, MATSUDA M, NISHIZAWA M, et al. Visfatin: a protein secreted by visceral fat that mimics the effects of insulin. Science. 2005;307(5708):426-430.
[5] GOK DE, YAZICI M, UCKAYA G, et al. The role of visfatin in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol Invest. 2011;34(1):3-7.
[6] 余臣祖,张朝宁.实验性T2DM动物模型研究进展[J].医学综述,2006, 12(1):41-42.
[7] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.
[8] 俞静.内脏脂肪棕色化功能改变影响肥胖的分子机制研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2013.
[9] 唐丽丽,汤晓涵,李霞等.高糖和高脂饮食对小鼠肥胖和内脏脂肪的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2014,36(6):614-619.
[10] 孔小岑.糖皮质激素通过miR-27b调控白色脂肪棕色化功能的分子机理研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2013.
[11] HAFFNER SM, GONZALEZ C, MIETTINEN H, et al. A prospective analysis of the HOMA model: the Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes care. 1996;19(10):1138-1141.
[12] BRUCE CR, HAWLEY JA. Improvements in insulin resistance with aerobic exercise training: a lipocentric approach. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(7):1196-1201.
[13] IVY JL. Muscle insulin resistance amended with exercise training: role of GLUT4 expression. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36(7): 1207-1211.
[14] DOHM GL, SINHA MK, CARO JF. Insulin receptor binding and protein kinase activity in muscles of trained rats. Am J Physiol. 1987;252(2 Pt 1):E170-E175.
[15] KURYSZKO J, SŁAWUTA P, SAPIKOWSKI G. Secretory function of adipose tissue. Pol J Vet Sci. 2016;19(2):441-446.
[16] SULAIEVA O, CHERESHNEVA Y, KARTASHKINA N, et al. Secretory function of white adipose tissue and adipokines: biological effects and clinical significance (review). Georgian Med News. 2018;(274):116-124.
[17] CHEN MP, CHUNG FM, CHANG DM, et al. Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(1):295-299.
[18] DOGRU T, SONMEZ A, TASCI I, et al. Plasma visfatin levels in patients with newly diagnosed and untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;76(1):24-29.
[19] RAHMOUNI K, CORREIA MLG, HAYNES WG, et al. Obesity-associated hypertension: new insights into mechanisms. Hypertension. 2005;45(1):9-14.
[20] OLSZANECKA-GLINIANOWICZ M, KOCEŁAK P, NYLEC M, et al. Circulating visfatin level and visfatin/insulin ratio in obese women with metabolic syndrome. Arch Med Sci. 2012;8(2):214.
[21] KOWALSKA I, KARCZEWSKA-KUPCZEWSKA M, ADAMSKA A, et al. Serum visfatin is differentially regulated by insulin and free fatty acids in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(2): E293-E297.
[22] AUGUET T, TERRA X, PORRAS JA, et al. Plasma visfatin levels and gene expression in morbidly obese women with associated fatty liver disease. Clin Biochem. 2013;46(3):202-208.
[23] MATHSA TE, ISMAIL SV, SPEELMAN A, et al. Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue association with metabolic syndrome and its components in a South African population. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019;10(1016):76-78.
[24] NOURBAKHSH M, NOURBAKHSH M, GHOLINEJAD Z, et al. Visfatin in obese children and adolescents and its association with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2015;75(2):183-188.
[25] KAMIŃSKA A, KOPCZYŃSKA E, BRONISZ A, et al. An evaluation of visfatin levels in obese subjects. Endokrynol Polska. 2010; 61(2):169-173.
[26] USLU S, KEBAPÇI N, KARA M, et al. Relationship between adipocytokines and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4(1):113-120.
[27] STROMSDORFER KL, YAMAGUCHI S, YOON MJ, et al. NAMPT-mediated NAD+ biosynthesis in adipocytes regulates adipose tissue function and multi-organ insulin sensitivity in mice. Cell Rep. 2016;16(7):1851-1860.
[28] TRON'KO ND, ZAK KP. Obesity and diabetes mellitus. Lik Sprava. 2013;(8):3-21.
[29] BANERJEE S, TALUKDAR I, BANERJEE A, et al. Type II diabetes mellitus and obesity: common links, existing therapeutics and future developments. J Biosci. 2019;44(6):150.
[30] ROMACHO T, AZCUTIA V, VAZQUEZ-BELLA M, et al. Extracellular PBEF/NAMPT/visfatin activates pro-inflammatory signalling in human vascular smooth muscle cells through nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase activity. Diabetologia. 2009;52(11):2455-2463.
|