中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (23): 3648-3653.doi: 10.12307/2021.034
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
针刺干预大负荷运动损伤模型大鼠骨骼肌线粒体功能的动态变化
白胜超1,高 扬2,王 博3,李俊平2,王瑞元2
- 1南京理工大学体育部,江苏省南京市 210094;北京体育大学,2运动人体科学学院,3运动医学与康复学院,北京市 100084
Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury
Bai Shengchao1, Gao Yang2, Wang Bo3, Li Junping2, Wang Ruiyuan2
- 1Department of Sports, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China; 2School of Sports Human Sciences, 3School of Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
摘要:
文题释义:
大负荷运动损伤:机体长时间进行大负荷运动或是承受不适应的运动负荷后,出现骨骼肌超微结构改变、肌肉僵硬、收缩能力下降等现象。
左室射血分数:为目前评估心功能的主要指标,其计算方法为:(左室舒张末容积-左室收缩末容积)/左室舒张末容积×100%,正常值>50%,射血分数下降提示心脏供血不能满足全身代谢需要,表现为心功能下降,主要为冠心病引起,因此射血分数的提高提示心功能改善。
背景:一次大负荷运动后骨骼肌会出现损伤并导致线粒体功能下降,针刺作为重要的治疗措施,在损伤修复中应当发挥一定的作用。
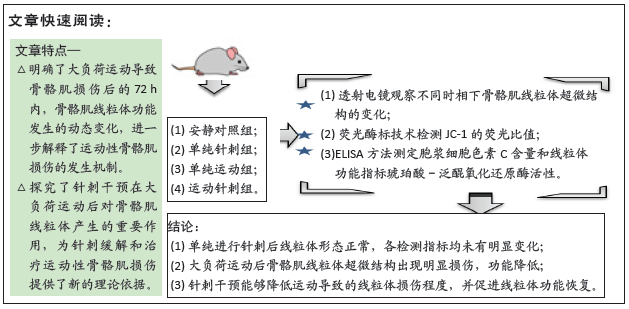
目的:观察一次大负荷运动及针刺干预后不同时相下骨骼肌线粒体的损伤变化,进一步探究针刺在防治运动性骨骼肌损伤中的作用。
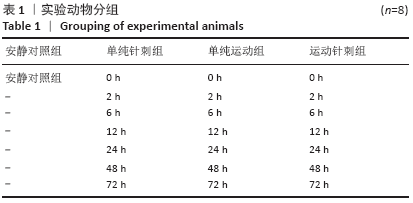
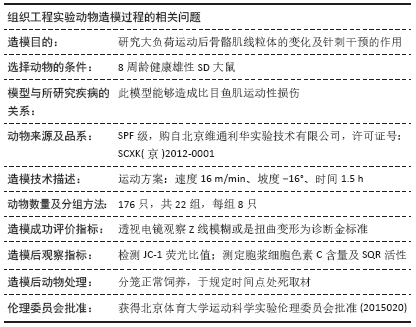
方法:雄性SD大鼠随机分为安静对照组、单纯针刺组、单纯运动组和运动针刺组,单纯运动组、运动针刺组进行一次性下坡跑离心运动,单纯针刺组、运动针刺组进行针刺干预。单纯针刺组、单纯运动组、运动针刺组又按干预后取材的时相点划分为0,2,6,12,24,48,72 h相组。透射电镜观察不同时相下骨骼肌线粒体超微结构的变化,荧光酶标技术检测JC-1的荧光比值,ELISA法测定胞浆细胞色素C含量和线粒体功能指标琥珀酸-泛醌氧化还原酶活性。
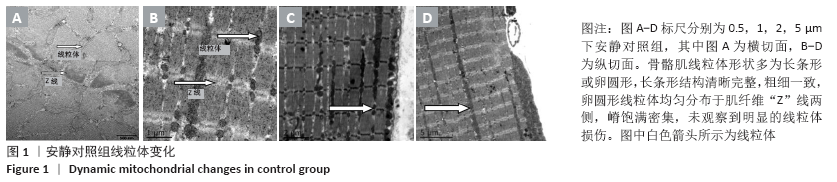
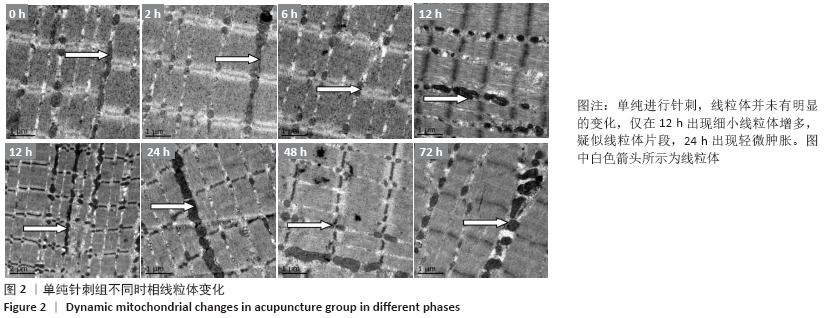
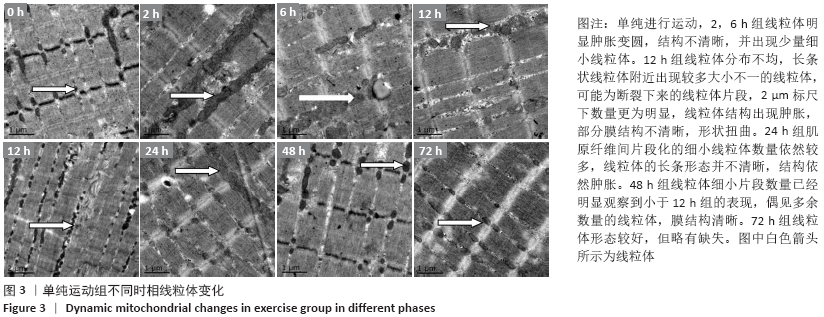
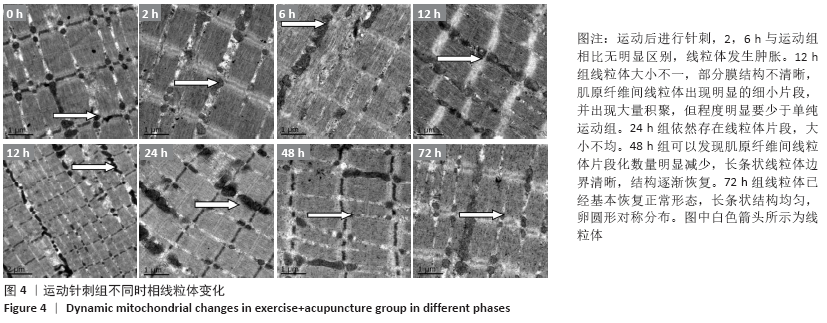
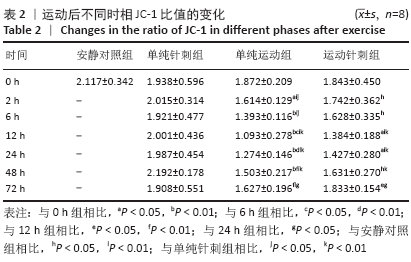
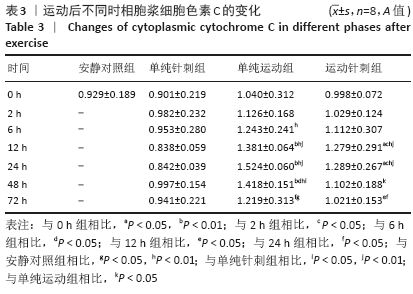
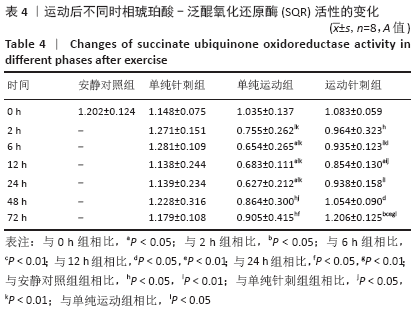
结果与结论:①运动后线粒体超微结构出现明显损伤,在12-24 h时间段损伤最为严重,胞浆细胞色素C含量升高(P < 0.05),JC-1比值、琥珀酸-泛醌氧化还原酶活性均下降(P < 0.05);②单纯进行针刺后线粒体形态正常,各检测指标均未有明显变化(P > 0.05);③针刺干预使运动后大鼠骨骼肌线粒体超微结构损伤下降,并且胞浆细胞色素C含量降低(P < 0.05),JC-1比值、琥珀酸-泛醌氧化还原酶活性均有所升高(P < 0.05);④提示一次离心运动后线粒体出现不同程度损伤并呈时相性变化,在12-24 h时间段损伤最为严重;单纯进行针刺并未引起明显的骨骼肌线粒体损伤;针刺干预可有效改善运动引起的线粒体损伤情况,可能促进运动后线粒体的功能恢复。
中图分类号: