[1] 刘力生.高血压慢性病管理与展望[J].中华高血压杂志,2019, 27(3):209-210.
[2] 陈伟伟.高血压、高胆固醇和高血糖常常相伴相随,实施“三高共管”是综合风险控制的有效策略,但在基层医院实施可行吗?该如何做?[J].中华高血压杂志,2017,25(10):908-912.
[3] 何秉贤.二甲双胍在高血压防治中应用的现代观点[J].中华高血压杂志,2018,26(6):508-509.
[4] 严心,陈晓平.高血压前期人群心血管病及靶器官损害的研究进展[J].中华高血压杂志,2019,27(5):483-488.
[5] 李杨,郭悦婷,王兵,等.加味地黄汤治疗阴虚阳亢型高血压的疗效及对血脂影响[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2019,33(4):54-57.
[6] 潘兴寿,梁烨,曾德创,等.野芭蕉多糖对自发性高血压大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖的影响及其与胆固醇调节元件结合蛋白表达的关系[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(7):3026-3030.
[7] 韩聪,姜月华,李伟.黄芪-丹参药对改善高血压肾损害的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(12):214-220.
[8] WU Y, QIAN Z, FU S, et al. IcarisideII improves left ventricular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats by inhibiting the ASK1-JNK/p38 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;819:68-79.
[9] RANDRIAMBOAVONJY JI, RIO M, PACAUD P, et al. Moringa oleifera Seeds Attenuate Vascular Oxidative and Nitrosative Stresses in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017; 2017:4129459.
[10] WANG X, LI G, SHEN W. Protective effects of D-Limonene against transient cerebral ischemia in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):699-706.
[11] 罗佳,施丽红,李慧兰,等.肾素-血管紧张素阻滞剂与钙通道阻滞剂长期治疗高血压合并糖尿病患者的疗效和安全性的比较[J].中国医院药学杂志,2019,39(8):841-847.
[12] THABIT S, HANDOUSSA H, ROXO M, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant and neuroprotective activities of Cassia fistula (L.) using the Caenorhabditis elegans model. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5159.
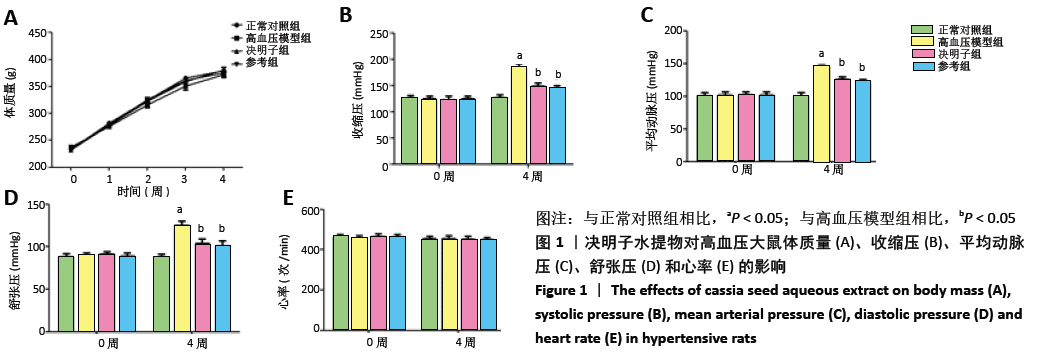
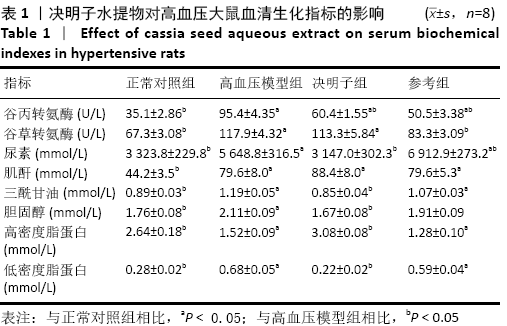
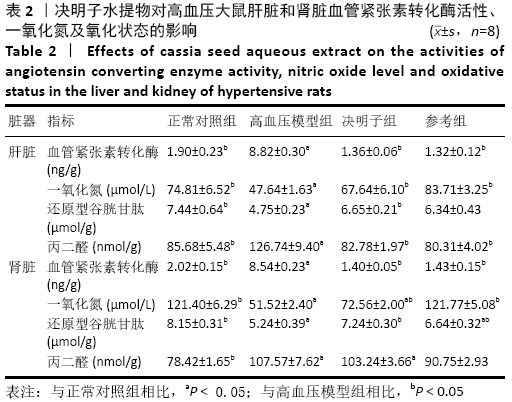
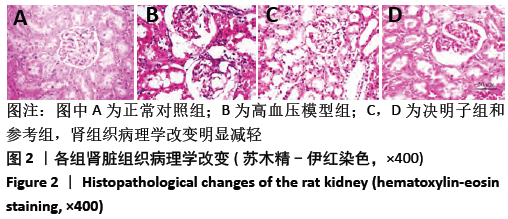
[13] 潘正军,陆祈,潘丽,等.决明子水提液对高血压小鼠血压血脂及肾脏结构的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2010,16(13):203-206.
[14] 许鹏飞,孙学斌,黄尹琦,等.决明子降脂有效成分的研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(1):150-153.
[15] 李艳文,王婷,许蓝蓝,等.决明子水提物对高血压大鼠RAAS系统的调控机制研究[J].医学动物防制,2019,35(8):774-776.
[16] MAJITHIYA JB, PARMAR AN, TRIVEDI CJ, et al. Effect of pioglitazone on L-NAME induced hypertension in diabetic rats. Vascul Pharmacol. 2005;43(4):260-266.
[17] 徐梦丹,戴秋艳,刘少稳.N-硝基-L-精氨酸甲酯诱导的高血压大鼠胸主动脉血管紧张素转换酶2和血管紧张素转换酶的表达[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2012,32(3):269-273.
[18] ÖZEN N, NASIRCILAR ÜLKER S, ÜLKER P, et al. Effect of 20-HETE inhibition on L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018;40(3):292-302.
[19] MOHEBBATI R, BAVARSAD K, RAHIMI M, et al. Protective effects of long-term administration of Ziziphus jujuba fruit extract on cardiovascular responses in L-NAME hypertensive rats. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2018; 8(2):143-151.
[20] BILANDA DC, DZEUFIET PDD, KOUAKEP L, et al. Bidens pilosa Ethylene acetate extract can protect against L-NAME-induced hypertension on rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):479.
[21] 邓华菲, 李坚, 周琴, 等. PI3K/Akt/eNOS信号通路在葛根素抑制ox-LDL诱导的血管内皮细胞组织因子表达中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(7):1214-1218.
[22] BULBUL T, AKOSMAN MS, YILMAZ O, et al. Supplementary dietary nitric oxide donor (sodium nitroprusside) or inhibitor (NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester) depressed growth performance and ovarian primordial and primary follicles in Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) in a dose-dependent manner. Br Poult Sci. 2015;56(1):113-120.
[23] GHASEMI M, NEMATBAKHSH M, DANESHMAND F, et al. Role of nitric oxide in kidney and liver (as distance organ) function in bilateral renal ischemia-reperfusion: Effect of L-Arginine and NG-nitro-L-Arginine methyl ester. Adv Biomed Res. 2015;4:233.
[24] NTCHAPDA F, BARAMA J, KEMETA AZAMBOU DR, et al. Diuretic and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of leaves of Cassia occidentalis (Linn.) in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015;8(9):685-693.
[25] 陈顺煌,王勇,陈晓洋,等.高血压患者血清血管紧张素转化酶水平与心房颤动的关系[J].山东医药,2017,57(1):54-56.
[26] TYRANKIEWICZ U, OLKOWICZ M, SKÓRKA T, et al. Activation pattern of ACE2/Ang-(1-7) and ACE/Ang II pathway in course of heart failure assessed by multiparametric MRI in vivo in Tgαq*44 mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2018;124(1):52-65.
[27] 彭雯雯,刘国英,潘燕霞,等. ACE2基因过表达减轻血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的神经细胞氧化应激[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2019,35(6): 1081-1088.
[28] MAJID DSA,练桂丽,叶鹏.过氧亚硝基阴离子对肾功能的调节及其在盐敏感性高血压中的病理生理学意义[J]. 中华高血压杂志, 2017,25(11):1014-1018.
[29] 吕林林,安姿旖,梁家健,等.丹参多酚酸盐对过氧化氢诱导人内皮细胞EA.hy926氧化应激损伤的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(5): 865-872.
[30] 林忠伟,王卓,喻婵,等.赤芍总苷对高血压大鼠血管重构基质金属蛋白酶9、金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1和血管壁氧化应激的干预作用[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2018,26(8):774-778.
[31] SONODA K, OHTAKE K, UCHIDA H, et al. Dietary nitrite supplementation attenuates cardiac remodeling in l-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Nitric Oxide. 2017;67:1-9.
[32] SHAMARDL HA, EL-ASHMONY SM, KAMEL HF, et al. Potential Cardiovascular and Renal Protective Effects of Vitamin D and Coenzyme Q10 in l-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354(2): 190-198.
[33] 吴宿慧,刘亚敏,吴宿慧,等.基于自由基学说研究决明子水煎液对小鼠静止代谢率和抗氧化活性的影响[J].中成药,2015,37(6): 1343-1347.
[34] FADEL PJ. Nitric Oxide and Cardiovascular Regulation: Beyond the Endothelium. Hypertension. 2017;69(5):778-779.
[35] 任川,陈少敏,祖凌云,等.高血压患者血管生成素2与血管内皮因子及血管舒张功能的关系分析[J].中华医学杂志,2019,99(12): 934-938.
[36] 邱秀琴,李萍.四氢生物蝶呤与心血管保护的研究进展[J].中华心血管病杂志,2018,46(3):247-250.
[37] 张惟,姜鉴洪,陈松,等.精氨酸酶抑制剂对体外高糖培养的恒河猴视网膜微血管内皮细胞的保护作用[J].中华眼底病杂志,2017, 33(3):281-285.
[38] AMARAL TAS, OGNIBENE DT, CARVALHO LCRM, et al. Differential responses of mesenteric arterial bed to vasoactive substances in L-NAME-induced preeclampsia: Role of oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018;40(2):126-135.
[39] 李园园,徐文清.诱导型一氧化氮合酶抑制剂的研究进展[J].中国药物化学杂志,2017,27(6):477-489.
[40] CERON CS, DO VALE GT, SIMPLICIO JA, et al. Chronic ethanol consumption increases vascular oxidative stress and the mortality induced by sub-lethal sepsis: Potential role of iNOS. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;825:39-47.
[41] DU L, HE F, KUANG L, et al. eNOS/iNOS and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in the placentas of patients with preeclampsia. J Hum Hypertens. 2017;31(1):49-55.
|
 文题释义:
文题释义: