中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1699-1704.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3082
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
刺山柑总生物碱干预椎间盘退变模型大鼠髓核细胞的增殖与凋亡
刘志刚,郭庆功,陈景涛
- 河南大学第一附属医院骨科,河南省开封市 475001
Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model
Liu Zhigang, Guo Qinggong, Chen Jingtao
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, Henan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
椎间盘退变:是指椎间盘组织由于老龄化、长期单一机械应力造成的椎间盘组织退行性病变,一般表现为神经性疼痛及椎间盘突出等症状,其病理基础一般来自于椎间盘组织长期炎症、髓核细胞的衰老、凋亡、生长活性降低,以及胶原蛋白表达水平下降导致的细胞外基质合成减少等。
Ⅱ型胶原蛋白:胶原蛋白是结缔组织的主要成分,可分为Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ等型。Ⅱ型胶原蛋白主要由软骨组织产生,其形成的胶原蛋白纤维有很高的机械强度,用于组成软骨组织的基质部分。胶原纤维组成的软骨基质在缓解骨骼应力、骨骼摩擦中发挥重要作用,当Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达过低时会导致软骨基质退变及一系列相关疾病。
背景:刺山柑总生物碱在细胞生长、胞外基质合成上有一定效用,而髓核细胞的老化、凋亡是椎间盘退变的主要病理基础之一,因此推测刺山柑总生物碱可能通过髓核细胞对椎间盘退变有一定影响。
目的:探讨刺山柑总生物碱对椎间盘退变大鼠模型及髓核细胞的影响。
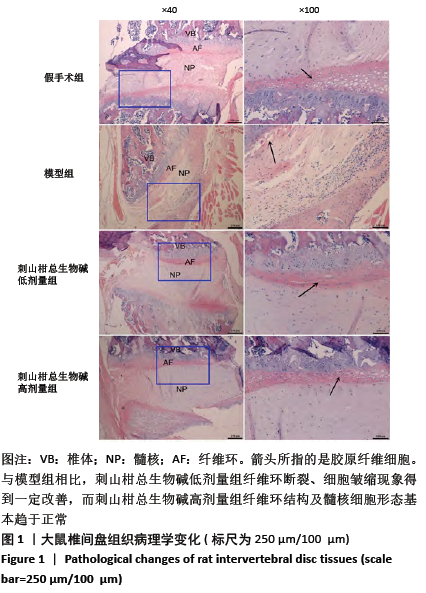
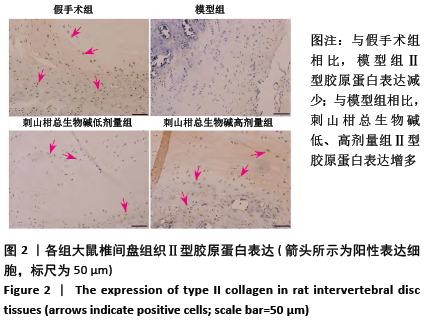
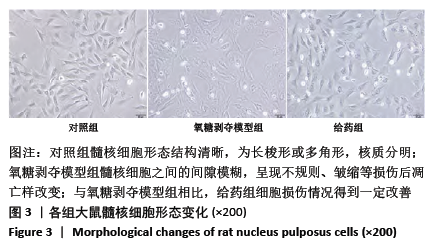
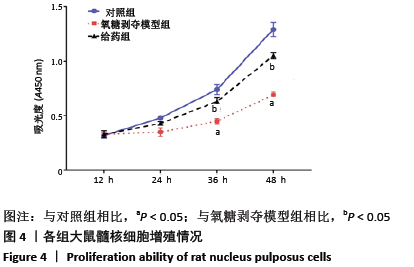
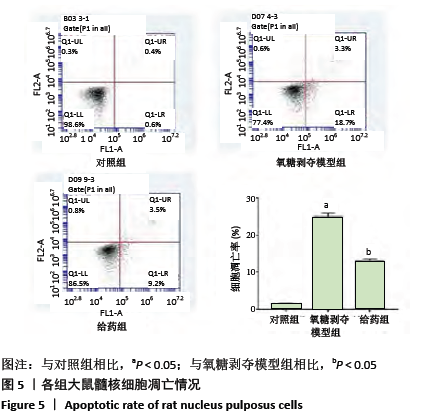
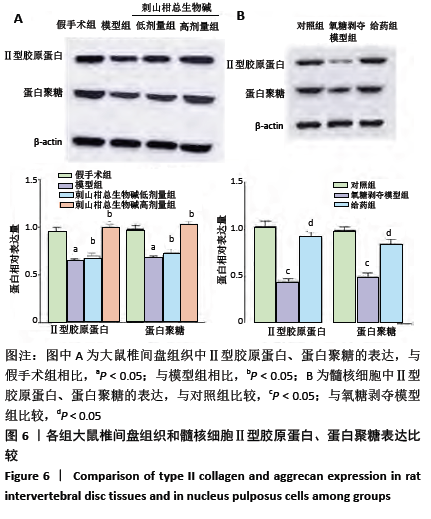
方法:①32只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、刺山柑总生物碱低剂量组和刺山柑总生物碱高剂量组,每组8只,后3组构建大鼠椎间盘退变模型,假手术组进行假手术对照。造模成功后,刺山柑总生物碱低、高剂量组大鼠分别灌胃刺山柑总生物碱225 mg/kg和 450 mg/kg,1次/d,连续4周。给药结束后苏木精-伊红染色观察椎间盘组织病理形态变化,免疫组化观察Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的表达,Western blot检测Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖的表达。②分离培养2只SD大鼠椎间盘髓核细胞并分为对照组、氧糖剥夺模型组和给药组,其中氧糖剥夺模型组髓核细胞接种于无糖无血清的DMEM培养基中培养,给药组在造模基础上,添加10 mg/L刺山柑总生物碱浓缩液。培养24 h采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖情况,培养48 h采用流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡情况,培养48 h采用Western blot检测Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖的表达。
结果与结论:①与假手术组相比,模型组大鼠椎间盘组织出现纤维环裂隙、髓核细胞聚集、皱缩,而刺山柑总生物碱低、高剂量组相较于模型组都有改善;②模型组椎间盘组织Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖表达显著低于假手术组,而刺山柑总生物碱低、高剂量组Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖表达均高于模型组(P < 0.05);③与对照组相比,氧糖剥夺模型组髓核细胞表现为形态不规则和凋亡状态,给药组细胞形态相较于氧糖剥夺模型组有所改善;④与对照组相比,氧糖剥夺模型组髓核细胞增殖缓慢,凋亡率升高,Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖表达降低(P < 0.05);与氧糖剥夺模型组相比,给药组髓核细胞增殖加快、凋亡率下降,Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白聚糖表达升高(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,刺山柑总生物碱可通过促进髓核细胞增殖并抑制其凋亡和基质降解来改善椎间盘退变。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2526-1875 (刘志刚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: