中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1693-1698.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3075
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧和抗阻运动干预2型糖尿病模型大鼠周围神经内质网应激相关蛋白的表达
税晓平1,2,3,李春莹4,曹艳霞1,苏全生3
- 1四川中医药高等专科学校,四川省绵阳市 621000;2绵阳市骨科医院,四川省绵阳市 621000;3成都体育学院运动医学与健康学院,四川省成都市 610041;4绵阳市中医医院,四川省绵阳市 621000
Effects of aerobic and resistance exercises on endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins in diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats
Shui Xiaoping1, 2, 3, Li Chunying4, Cao Yanxia1, Su Quansheng3
- 1Sichaun College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Mianyang Osteological Hospital, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China; 3College of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 4Mianyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
 文题释义:
文题释义:
糖尿病周围神经病变:周围神经病变是糖尿病最常见的并发症之一,临床表现为双侧肢体远端对称性麻木和疼痛,运动和感觉神经传导速度下降,痛阈下降。
内质网应激:内质网对各种刺激极为敏感,氧化应激、葡萄糖缺乏和缺氧等刺激将会引起内质网应激。过度的内质网应激将通过PERK/ eIF-2a / CHOP途径、IRE-1/JNK途径和Caspase-12途径介导细胞凋亡。Grp78是内质网应激的标志性蛋白,Chop是PERK信号通路中重要的促凋亡蛋白,Caspase-12是内质网应激介导凋亡途径中的特异蛋白。
背景:研究提示内质网应激参与了糖尿病周围神经病变过程,改善内质网应激状态可减轻糖尿病周围神经病变程度。而运动是否对糖尿病周围神经中内质网应激有积极干预作用,目前少见文献报道。
目的:观察有氧和抗阻运动对2型糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经中内质网应激信号通路关键蛋白Grp78、Chop及Caspase-12表达的影响。
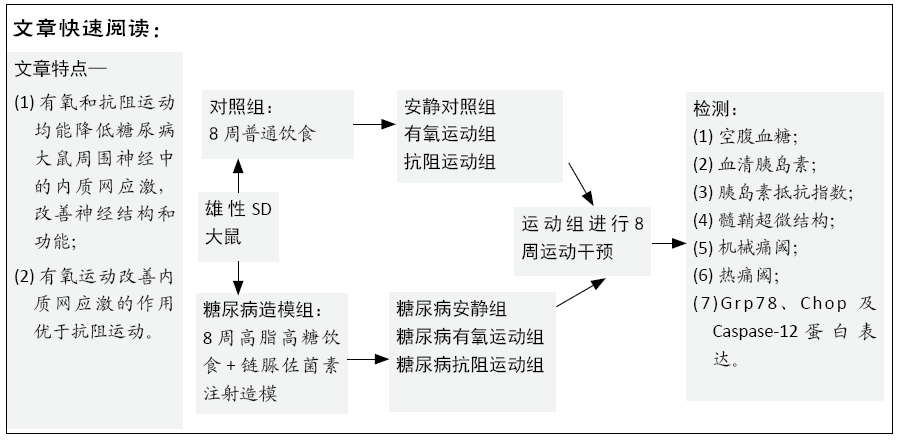
方法:60只SD雄性大鼠分为普通饲料喂养组(n=24)和糖尿病造模组(n=36)。糖尿病造模组采用高脂高糖饲料喂养8周+链脲佐菌素注射建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型。造模结束后,对照组随机分为安静对照组、有氧运动组、抗阻运动组;糖尿病模型大鼠随机分为糖尿病安静组、糖尿病有氧运动组和糖尿病抗阻运动组。各运动组分别进行8周有氧和抗阻运动,各安静组不进行运动干预。8周运动结束后测试各组大鼠空腹血糖、胰岛素、计算稳态胰岛素抵抗指数、测试机械痛阈和热痛阈;透射电镜观察坐骨神经超微结构变化;Western blot检测坐骨神经中Grp78、Chop及Caspase-12的表达。实验方案经成都体育学院动物实验伦理委员会批准(备案批准号为2018024A)。
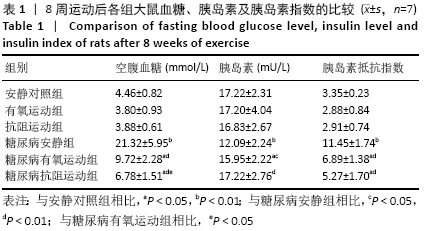
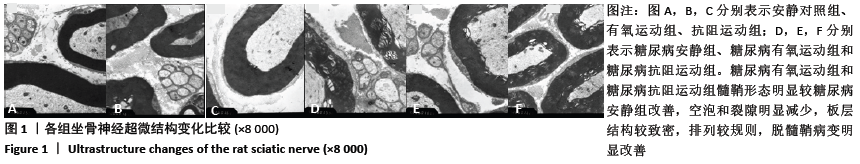
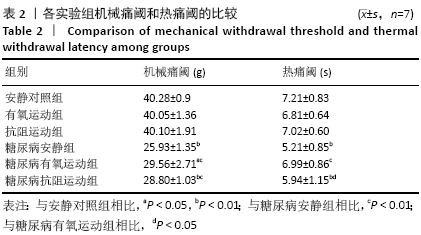
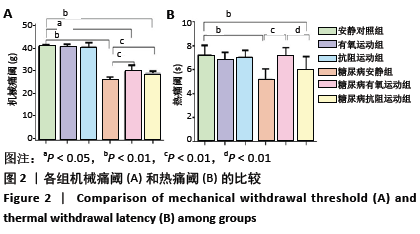
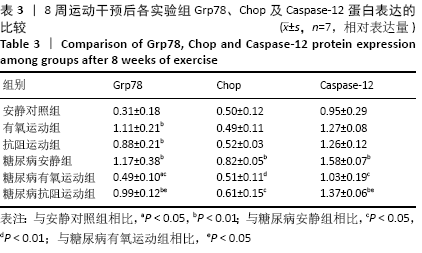
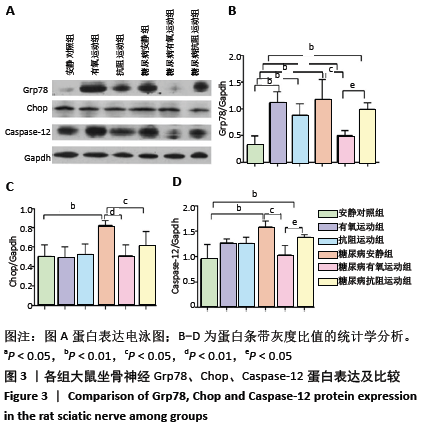
结果与结论:①8周运动结束后,与安静对照组比较,糖尿病各组大鼠空腹血糖和稳态胰岛素抵抗指数显著升高(P < 0.01);与糖尿病安静组比较,2个糖尿病运动组大鼠的空腹血糖与稳态胰岛素抵抗指数均显著降低(P < 0.01),糖尿病抗阻运动组空腹血糖显著低于糖尿病有氧运动组(P < 0.05);②与安静对照组比较,糖尿病各组大鼠坐骨神经结构表现为髓鞘排列紊乱疏松,板层分离和皱缩等典型脱髓鞘改变;与糖尿病安静组比较,2个糖尿病运动组大鼠坐骨神经髓鞘结构较紧密,板层分离程度减轻;③与安静对照组比较,糖尿病安静组和糖尿病抗阻运动组中的机械痛阈与热痛阈均出现显著降低(P < 0.01),糖尿病有氧运动组大鼠热痛阈显著高于糖尿病抗阻运动组(P < 0.05);④与安静对照组比较,糖尿病安静组Grp78、Chop及Caspase-12蛋白表达均明显增加(P < 0.01);与糖尿病安静组比较,糖尿病有氧运动组Grp78、Chop和Caspase-12蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.01;P < 0.05),糖尿病抗阻运动组Grp78和Caspase-12蛋白表达明显高于糖尿病有氧运动组(P < 0.05);⑤结果说明,糖尿病大鼠周围神经中出现内质网应激,导致周围神经出现脱髓鞘改变,机械痛阈和热痛阈下降。有氧和抗阻运动均能降低糖尿病大鼠周围神经中的内质网应激,改善神经结构和功能,且有氧运动改善内质网应激的作用优于抗阻运动。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9106-0919 (税晓平)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: