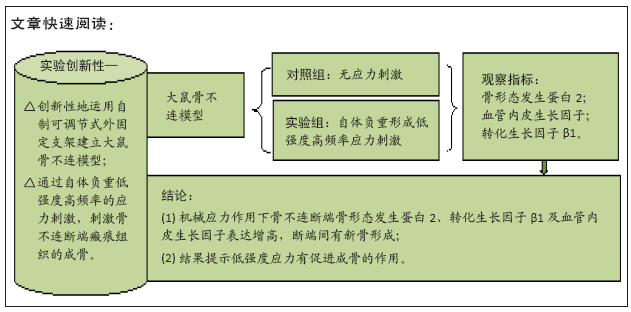
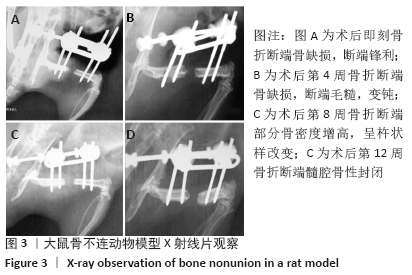
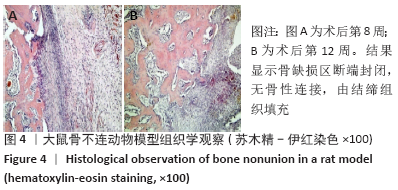
[1] NELSON FR, BRIGHTON CT, RYABY J, et al. Use of physical forces in bone healing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(5):344-354.
[2] 韩昕光, 毕郑钢, 王东奎, 等. 骨不连接区成骨活性的实验研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(1):45-50.
[3] REED AA, JOYNER CJ, BROWNLOW HC, et al. Human atrophic fracture non-unions are not avascular. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(3):593-599.
[4] SIGURDSEN U, REIKERAS O, UTVAG SE. The influence of compression on the healing of experimental tibial fractures. Injury.2011;42(10):1152-1156.
[5] SANTOS A, BAKKER AD, WILLEMS HM, et al. Mechanical loading stimulates BMP7, but not BMP2, production by osteocytes. Calcif Tissue Int. 2011; 89(4):318-326.
[6] PALOMARES KT, GLEASON RE, MASON ZD, et al. Mechanical stimulation alters tissue differentiation and molecular expression during bone healing. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(9):1123-1132.
[7] SCHWARZ C, WULSTEN D, ELLINGHAUS A, et al. Mechanical load modulates the stimulatory effect of BMP2 in a rat nonunion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(1-2):247-254.
[8] BOERCKEL JD, UHRIG BA, WILLETT NJ, et al. Mechanical regulation of vascular growth and tissue regeneration in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(37):E674-680.
[9] 赵震宇, 邵林, 刘建宇, 等. 新型外固定器制作大鼠负重骨节段性骨缺损模型的实验研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(12):1160-1163.
[10] HUANG G, LIU G, ZHANG F, et al. Combination of heel-strike like mechanical loading with deproteinized cancellous bone scaffold implantation to repair segmental bone defects in rabbits. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(9):871-879.
[11] Yang H, Embry RE, Main RP. Effects of loading duration and short rest insertion on cancellous and cortical bone adaptation in the mouse tibia. PLoS One.2017;12(1):e0169519
[12] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283
[13] 梁军,钱洁,王惠芳,等.不同强度的主动运动对大鼠膝关节软骨的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2012,27(1):8-11.
[14] JOHNSON KD, FRIERSON KE, KELLER TS, et al. Porous ceramics as bone graft substitutes in long bone defects: a biomechanical, histological, and radiographic analysis. J Orthop Res. 1996;14(3):351-369.
[15] CHAROENPANICH A, WALL ME, TUCKER CJ, et al. Cyclic tensile strain enhances osteogenesis and angiogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells from osteoporotic donors. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(1-2):67-78.
[16] HU M, QIN YX. Dynamic fluid flow stimulation on cortical bone and alterations of the gene expressions of osteogenic growth factors and transcription factors in a rat functional disuse model.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;545:154-161.
[17] JIANG Y, WANG Y, TANG G. Cyclic tensile strain promotes the osteogenic differentiation of a bone marrow stromal cell and vascular endothelial cell co-culture system. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016;607:37-43.
[18] CLAES L, BLAKYTNY R, BESSE J, et al. Late dynamization by reduced fixation stiffness enhances fracture healing in a rat femoral osteotomy model. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(3):169-174.
[19] GARDNER MJ, VAN DER MEULEN MC, DEMETRAKOPOULOS D, et al. In vivo cyclic axial compression affects bone healing in the mouse tibia. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(8):1679-1686.
[20] ZHAO F, VAUGHAN TJ, MCNAMARA LM. Quantification of fluid shear stress in bone tissue engineering scaffolds with spherical and cubical pore architectures. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2016;15(3):561-577.
[21] MCDERMOTT AM, HERBERG S, MASON DE, et al. Recapitulating bone development through engineered mesenchymal condensations and mechanical cues for tissue regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(495).
[22] LEE S, SUZUKI T, IZAWA H, et al. The Influence of the Type of Continuous Exercise Stress Applied during Growth Periods on Bone Metabolism and Osteogenesis. J Bone Metab. 2016;23(3):157-164.
[23] WANG L, HSU HY, LI X, et al. Effects of Frequency and Acceleration Amplitude on Osteoblast Mechanical Vibration Responses: A Finite Element Study. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2735091.
[24] 查丁制. 低强度高频率振动对成骨细胞生物学特性的影响及机制[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2011.
[25] EINHORN TA,GERSTENFELD LC.Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45-54.
[26] NAUTH A, GIANNOUDIS PV, EINHORN TA, et al. Growth factors: beyond bone morphogenetic proteins. J Orthop Trauma.2010;24(9):543-546.
[27] STEINBRECH DS, MEHRARA BJ, SAADEH PB, et al. Hypoxia regulates VEGF expression and cellular proliferation by osteoblasts in vitro. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;104(3):738-747.
[28] KERAMARIS NC, CALORI GM, NIKOLAOU VS, et al. Fracture vascularity and bone healing: a systematic review of the role of VEGF. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 2:S45-557.
[29] SENEL K, BAYKAL T, SEFEROGLU B, et al. Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor concentrations in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Arch Med Sci. 2013;9(4):709-712.
[30] BALTZER AW, LATTERMANN C, WHALEN JD, et al. Genetic enhancement of fracture repair: healing of an experimental segmental defect by adenoviral transfer of the BMP-2 gene. Gene Ther. 2000;7(9):734-739.
[31] MIYAZAKI M, MORISHITA Y, HE W, et al. A porcine collagen-derived matrix as a carrier for recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 enhances spinal fusion in rats. Spine J. 2009;9(1):22-30.
[32] KHAN SN, BOSTROM MP, LANE JM. Bone growth factors. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000;31(3):375-388.
[33] ECKARDT H, CHRISTENSEN KS, LIND M, et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 enhances bone healing in an experimental model of fractures at risk of non-union. Injury. 2005;36(4):489-994.
[34] MCBRIDE-GAGYI SH, MCKENZIE JA, BUETTMANN EG, et al. Bmp2 conditional knockout in osteoblasts and endothelial cells does not impair bone formation after injury or mechanical loading in adult mice. Bone. 2015;81:533-543.
[35] PATIL AS, SABLE RB, KOTHARI RM. An update on transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β): sources, types, functions and clinical applicability for cartilage/bone healing. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(12):3094-3103.
[36] CARTER DR, BLENMAN PR, BEAUPRÉ GS. Correlations between mechanical stress history and tissue differentiation in initial fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 1988;6(5):736-748.
|