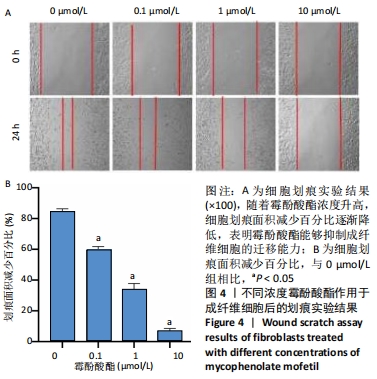
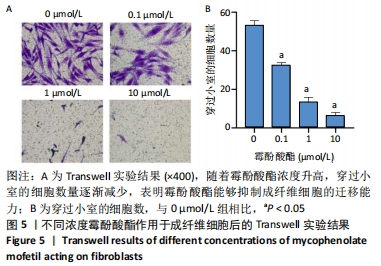
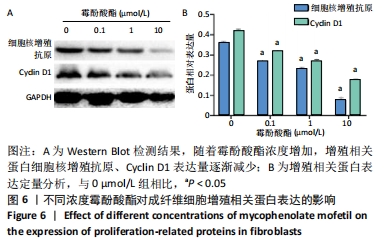
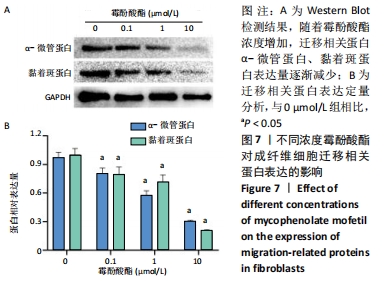
[1] KONG L, SHANG XF, ZHANG WZ, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy and microsurgical laminotomy : A prospective, randomized controlled trial of patients with lumbar disc herniation and lateral recess stenosis. Orthopade. 2019;48(2):157-164.
[2] SUN F, LIANG Q, YAN M, et al. Unilateral Laminectomy by Endoscopy in Central Lumbar Canal Spinal Stenosis: Technical Note and Early Outcomes. Spine. 2020;45(14):E871-E877.
[3] AVELLANAL M, DIAZ-REGANON G, ORTS A, et al. Transforaminal Epiduroscopy in Patients with Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. Pain Physician. 2019;22(1):89-95.
[4] ROGERSON A, AIDLEN J, JENIS LG. Persistent radiculopathy after surgical treatment for lumbar disc herniation: causes and treatment options. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):969-973.
[5] SOBTI S, GROVER A, JOHN BPS, et al. Prospective Randomized Comparative Study to Evaluate Epidural Fibrosis and Surgical Outcome in Patients Undergoing Lumbar Laminectomy with Epidural Autologous Free Fat Graft or Gelfoam: A Preliminary Study. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2018;8(2):71-75.
[6] DAI J, SUN Y, CHEN D, et al. Negative regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis regulates fibroblast proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy play a vital role in triptolide-induced epidural fibrosis reduction. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;864:172724.
[7] KIKUCHI K, SETOYAMA K, TERASHI T, et al. Application of a Novel Anti-Adhesive Membrane, E8002, in a Rat Laminectomy Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5):1513.
[8] ZENG L, SUN Y, LI X, et al. 10‑Hydroxycamptothecin induces apoptosis in human fibroblasts by regulating miRNA‑23b‑3p expression. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):2680-2686.
[9] ANDERSON KD, BRYDEN AM, MOYNAHAN M. Risk-benefit value of upper extremity function by an implanted electrical stimulation device targeting chronic cervical spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2019;5(1):68.
[10] TACCOLA G, BARBER S, HORNER PJ, et al. Complications of epidural spinal stimulation: lessons from the past and alternatives for the future. Spinal cord. 2020;58(10):1049-1059.
[11] 李杨.吡非尼酮抑制大鼠皮肤切口瘢痕形成的实验研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2019.
[12] 佟格霏.A型肉毒毒素抑制增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞生物学功能的实验研究[D].大连:大连医科大学,2019.
[13] 杨春兰.霉酚酸酯在肾移植中的治疗药物监测研究及基因多态性的影响[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2017.
[14] MORATH C, SCHWENGER V, BEIMLER J, et al. Antifibrotic actions of mycophenolic acid. Clin Transplant. 2006;20:25-29.
[15] ZHANG C, CHAN CCY, CHEUNG KF, et al. Effect of mycophenolate and rapamycin on renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis. Clin Sci. 2019; 133(15):1721-1744.
[16] 朱忠华,张春,邓安国,等.霉酚酸酯抑制大鼠肾间质纤维化的研究[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2002,18(4):61-63.
[17] 周晓霜.根据细胞周期联合使用他克莫司和霉酚酸酯治疗系膜增生性肾病的实验研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2015.
[18] XIE F, LI X, SUN K, et al. An experimental study on drugs for improving blood circulation and removing blood stasis in treating mild chronic hepatic damage. J Tradit Chin Med. 2001;21(3):225-231.
[19] KNAPP S, BERTELMANN E, HARTMANN C, et al. Intraocular availability of topically applied mycophenolate mofetil in rabbits. Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics. 2003;19(2):181-192.
[20] XIONG G, CHEN H, WAN Q, et al. Emodin promotes fibroblast apoptosis and prevents epidural fibrosis through PERK pathway in rats. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):319.
[21] ISMAILOGLU O, KIZILAY Z, CETIN NK, et al. Effect of Curcumin on the Formation of Epidural Fibrosis in an Experimental Laminectomy Model in Rats. Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29(3):440-444.
[22] VEDIAPPAN RS, MASCARENHAS A, NGUYEN-HOANG A, et al. Prevention of peridural adhesions in spinal surgery: Assessing safety and efficacy of Chitogel with Deferiprone in a sheep model. J Clin Neurosci. 2020; 72:378-385.
[23] ERDOGAN B, IS M, AKER FV, et al. Preventative effect of diclofenac sodium and/or diltiazem in rats with epidural fibrosis. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2019;120(11):813-818.
[24] KESER N, IS M, CEMAN D, et al. Locally Used Antibiotics for Spinal Infection Prophylaxis and Their Effects on Epidural Fibrosis: an Experimental Laminectomy Study in Rats Using Rifamycin and Gentamycin. Inflammation. 2019;42(2):714-720.
[25] WU Y, LIU D, ZHOU Q, et al. Effect of surface microstructure on the anti-fibrosis/adhesion of hydroxyapatite ceramics in spinal repair of rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res. Part B, Applied biomaterials. 2019;107(8):2629-2637.
[26] ALBIÑANA-CUNNINGHAM JN, RIPALDA-CEMBORÁIN P, LABIANO T, et al. Mechanical barriers and transforming growth factor beta inhibitor on epidural fibrosis in a rabbit laminectomy model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):72.
[27] YANG L, GAO Q, LV F, et al. miR‑519d‑3p promotes TGFβ/Smad mediated postoperative epidural scar formation via suppression of BAMBI. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3901-3909.
[28] PIYASIRIDEJ S, TOWNAMCHAI N, UDOMKARNJANANUN S, et al. Plasmapheresis Reduces Mycophenolic Acid Concentration: A Study of Full AUC(0-12) in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J Clin Med. 2019;8(12): 2084.
[29] DUARTE AC, SANTOS MJ, CORDEIRO A. Anti-fibrotic nintedanib-a new opportunity for systemic sclerosis patients? Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(4):1123-1127.
[30] SCHEEL PJ JR, FEELEY N, SOZIO SM. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis: a case series. Ann Intern Med. 2011;154(1):31-36.
[31] YUNG S, ZHANG Q, CHAU MK, et al. Distinct effects of mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide on renal fibrosis in NZBWF1/J mice. Autoimmunity. 2015;48(7):471-487.
[32] WANG QJ, ZHANG AL, KANG ZQ, et al. Exogenous IL-19 mediates downregulation of TGF-β through Erk and p38 pathway to inhibit epidural fibrosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(17):7184-7190.
[33] BAGCI G, YÜCEL I, DURANOGLU Y. The effect of cyclosporin A on cultured rabbit subconjunctival fibroblast proliferation. Ophthalmologica. 1999;213(2):114-119.
[34] YILDIZ KH, GEZEN F, IS M, et al. Mitomycin C, 5-fluorouracil, and cyclosporin A prevent epidural fibrosis in an experimental laminectomy model. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9):1525-1530.
[35] 戴纪杭.羟基喜树碱通过调控NOXA表达预防椎板切除术后硬膜外瘢痕粘连的研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2017.
[36] LI X, WANG S, DAI J, et al. Homoharringtonine prevents surgery-induced epidural fibrosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;815:437-445.
|