中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (8): 1187-1193.doi: 10.12307/2022.222
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
采用复合因素建立内热消渴小鼠模型的特点分析
吕依妍,李寒冰,马晓庆,张 晗,张宇航,李根林
- 河南中医药大学,河南省仲景方药健康衰老产业工程研究中心,河南省郑州市 450046
Establishment and characteristic analysis of interior heat and diabetes mouse model using compound factors
Lü Yiyan, Li Hanbing, Ma Xiaoqing, Zhang Han, Zhang Yuhang, Li Genlin
- Henan Zhongjing Prescription Health and Aging Industry Engineering Research Center, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
动物造模:常规的西医动物造模,基于明确、特异的病理损害变化,重复性好,应用广泛,如将链脲佐菌素通过腹腔注射进入模型动物体内建立相关糖尿病模型就是其中之一。但这种方法运用现代医学技术测得的实验室理化指标虽然明确可靠,但缺乏中医辨证论治的思想,常规造模动物的病理状态缺少些中医辨证特点。
内热:不是单纯的燥热,或也可为湿热、痰热、郁热及情志之火、脏腑之火等,《素问 阴阳应象大论》中指出“燥胜则干”,典型的消渴病所表现出的烦热口渴、多饮、多尿、便干、舌红苔黄而燥等属于燥热之象。而当今消渴病多数为2型糖尿病,因生活方式的改变、自然与社会环境的变化以及医学技术的进步,典型症状不甚多见,但内热病因仍存在且贯穿病程始终。
背景:糖尿病属于中医“消渴”范畴,根据该病的发展进程及临床表现往往有不同的证候表现,多数情况下早期表现以热盛为主称之为热盛型消渴,中晚期以气阴两虚证候为主称之为气阴两虚型消渴。
目的:采用复合方法,制备体现中医症候特点的内热消渴小鼠模型,为研究消渴病的演变规律及相关药物研究奠定基础。
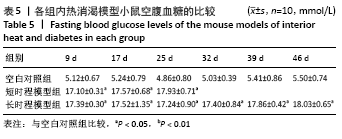
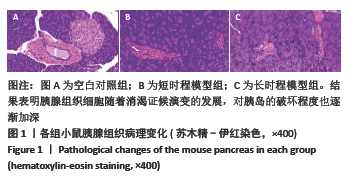
方法:30只ICR小鼠随机分为空白对照组、短时程模型组和长时程模型组,短时程模型组连续5 d腹腔注射40 mg/kg链脲佐菌素,然后继续灌服20 g/kg温热药14 d建立内热消渴动物模型;长时程模型组是在短时程模型的基础上继续灌服同剂量温热药21 d。测定各组小鼠造模后体质量、空腹血糖、饮水量、摄食量、尿量、血清胰岛素水平;计算胰岛素抵抗指数、胰岛素敏感指数;测定肝、肾组织中线粒体呼吸链复合物Ⅲ、Ⅴ的活性;苏木精-伊红染色检测小鼠胰腺病理变化。实验经河南省中医药大学动物伦理委员会批准,动物伦理批件号:DWLL202003270。
结果与结论:①与空白组相比,短时程模型组和长时程模型组的小鼠均表现出多饮多食多尿、体质量降低、肛温升高等消渴病的典型症状(P < 0.05),空腹胰岛素及胰岛素抵抗指数水平显著升高,胰岛素敏感指数水平显著降低(P < 0.05),肝肾组织中线粒体呼吸链复合物Ⅲ和Ⅴ的活性升高(P < 0.05);胰腺病理观察发现短时程模型组和长时程模型组小鼠的胰腺组织有不同程度的损害;②与短时程模型组相比,长时程模型组多饮多食多尿、体质量增长缓慢、肛温随着病情发展有明显降低(P < 0.05);空腹胰岛素及胰岛素抵抗指数明显升高,胰岛素敏感指数明显降低(P < 0.05);肝肾组织中线粒体呼吸链复合物Ⅲ和Ⅴ的活性显著降低(P < 0.05);病理观察随着病情的发展胰岛功能进一步损伤和破坏;③结果表明,“链脲佐菌素+温热药”复合因素造模,可完善内热消渴的病证结合模型,且模型存在着证候演变规律:短时程模型表现出热盛型消渴,长时程模型表现出气阴两虚型消渴。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8153-7325 (吕依妍)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: