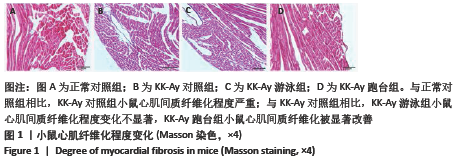
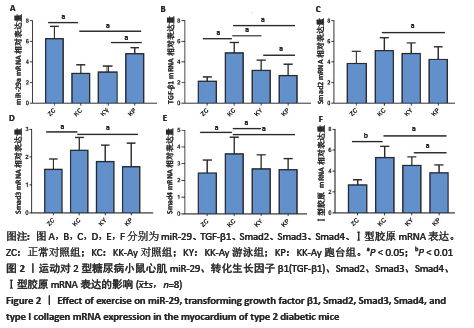
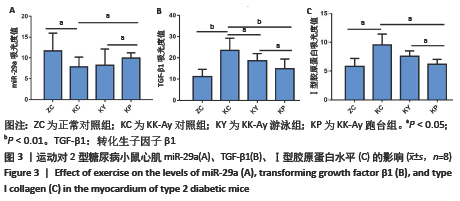
[1] LIU MJ, LI Y, LIANG B, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial fibrosis in diabetic rats through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):1867-1876.
[2] ZOLTAN VV, ZOLTAN G, LUCAS L, et al. Interplay of oxidative, nitrosative/ nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(2):232-242.
[3] TIAN JF, ZHAO YK, LIU YF, et al. Roles and mechanisms of herbal medicine for diabetic cardiomyopathy: current status and perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;23(11):8214-8221.
[4] WANG J, WANG YL, WANG Y, et al. Transforming growth factor β-regulated microRNA-29a promotes angiogenesis through targeting the phosphatase and tensin homolog in endothelium.J Biol Chem. 2013;288(5):10418-10426.
[5] DENG Z, HE Y, YANG X, et al. MicroRNA-29:a crucial player in fibrotic disease. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017;21:285-294.
[6] XURDE MC, VICTOR F, EDUARDO O, et al. The microRNA-29/PGC1α regulatory axis is critical for metabolic control of cardiac function. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(10):e2006247.
[7] 王灵纳,康福新.吡格列酮通过抑制炎症反应和TGF-β1/Smad3 信号通路抗2 型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化的研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2020,43(9):1754-1757.
[8] 曾奇虎,翁静飞,李小林,等.外源性硫化氢对2 型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化及TGF-β1 /Smads 信号通路的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020,36(6):653-657.
[9] 吴倩.气体信号分子SO2调控TGF β-Smad2/3通路调节自噬改善2型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化[D]. 衡阳:南华大学,2020.
[10] 李丹,王世强,艳群,等. 运动抑制转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路对糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化影响的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 2018,26(9):780-786.
[11] 明文娟. 抗阻运动伴二甲双胍干预对2型糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化的影响研究[D].南京:南京体育学院,2018.
[12] PLOUG T, STALLKNECHT BM, PEDERSEN O, et al. Effect of endurance training on glucose transport capacity and glucose transporter expression in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990;259(6 Pt 1):E778.
[13] 杨道宁,李丽.运动性疲劳动物模型制备的研究进展[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2011,30(3):80-85+89.
[14] BEDFORD TG, TIPTON CM, WILSON NC, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;47(6): 1278-1283.
[15] WANG L, DI LJ, CONSTANCE T. Erythropoietin, a novel versatile player regulating energy metabolism beyond the erythroid system. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(8):921- 939.
[16] 陈园园.芦丁对大鼠2型糖尿病心肌纤维化的保护作用及机理的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2014.
[17] LI CG, ZHANG J, XUE M, et al. SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(8):15.
[18] RAN Q, WANG J, WANG L, et al. Rhizoma coptidis as a potential treatment agent for type 2 diabetes mellitus and the underlying mechanisms: A review. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10(4):805.
[19] ZHOU H, LI YJ, WANG M, et al. Involvement of RhoA/ROCK in myocardial fibrosis in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2011;32(8):999-1008.
[20] 候改霞,肖国强.运动训练对糖尿病大鼠心肌纤维化的改善作用及其可能机制[J].体育学刊,2013,20(2):56-60.
[21] ZHAO J, RANDIVE R, STEWART JA. Molecular mechanisms of AGE/RAGE -mediated fibrosis in the diabetic heart. World J Diabetes. 2014;5(6): 860-867.
[22] HIRAKAWA H, ZEMPO H, OGAWA M, et al. A DPP-4 inhibitor suppresses fibrosis and inflammation on experimental autoimmune myocarditis in mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119360.
[23] ZHANG T, LI XW, LI Y, et al. Inhibition of TGF-β-Smad signaling attenuates hyperoxia-induced brain damage in newborn rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(10):3772-3781.
[24] CHEVAUN DM, JENNY GP, WILLIAM PS. The relevance of the TGF-β paradox to EMT-MET programs. Cancer Lett. 2013;341(1):10-12.
[25] VARUN N, RAHUL R, AARON TP, et al. MiR-125b is critical for fibroblast-to- myofibroblast transition and cardiac fibrosis. Circulation. 2016;133(3):291-301.
[26] LU F, ANDRIS HE, MOORE XL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for diffuse myocardial fibrosis in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Transl Med. 2015;13(4):314-324.
[27] ZHANG Y, HUANG XR, WEI LH, et al. miR-29b as a Therapeutic agent for angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting TGF-β/Smad3 signaling. Mol Ther. 2014;22(5):974-985.
[28] JAMES D, JOSSELYN EG, JAYASREE S, et al. The microRNA-29 family dictates the balance between homeostatic and pathological glucose handling in diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 2016;65(1):53-61.
[29] AMANDA F, PRADEEP S. miR-590-5p, miR-219-5p, miR-15b and miR-628- 5p are commonly regulated by IL-3, GM-CSF and G-CSF in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2012;36(3):334-341.
[30] WU H, KONG LL, ZHOU SS, et al. The role of microRNAs in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2014;9(2):14-18.
[31] 王世强,常芸,李丹,等.运动性心肌纤维化的发生特征、可能机制和消退逆转[J].体育科学,2018,38(11):81-91.
[32] ZHU JN, CHEN R, FU YH, et al. Smad3 inactivation and miR-29b upregulation mediate the effect of carvedilol on attenuating the acute myocardium infarction- induced myocardial fibrosis in rat. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75557.
[33] 周曼萍. TGF-β1/Smad2、3信号通路和miR-29a与宫腔粘连相关性的研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2014.
[34] 鲍丽颖,王佩云.不同形式的运动对生长期大鼠下肢骨纵向生长的影响[J]. 天津体育学院学报,2003,18(3):63-65.
[35] GUADALUPE V, OH DJ, KANG MH, et al. Coordinated Regulation of Extracellular Matrix Synthesis by the MicroRNA-29 Family in the Trabecular Meshwork. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(6):3391-3397.
[36] XI Y, LIU HJ, ZHAO YQ, et al. Comparative analysis of longissimus muscle miRNAomes reveal microRNAs associated with differential regulation of muscle fiber development between Tongcheng and Yorkshire pigs. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0200445.
[37] 贾单单.间歇运动激活心梗大鼠骨骼肌和心肌LIF-LIFR-STAT3信号通路改善心功能[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学,2016.
[38] 黄明,丁同英,张晓玲,等. 跑台运动与负重游泳致大鼠力竭性疲劳时心肌骨骼肌组织学变化特征观察[J]. 成都体育学院学报,1996, 11(4):54-57.
|