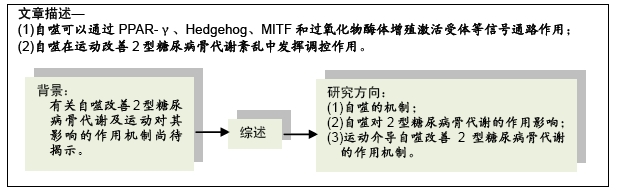
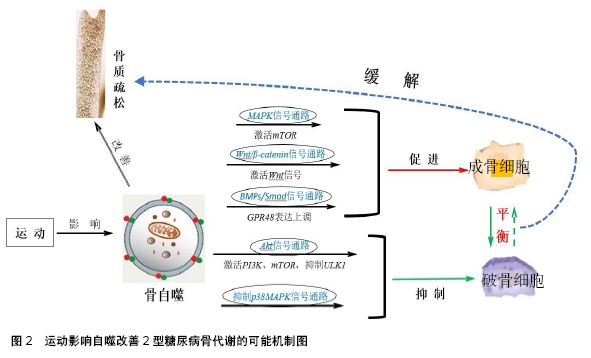
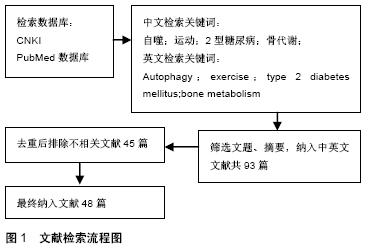
[1] KAYVAN Z, CASSIE JL, ALISONL MC, et al. SIRT1 is a positive regulator of in vivo bone mass and a therapeutic target for osteoporosis. PLoS One.2017;12(9): e0185236.1528.
[2] 谭伟源,陈军平,宋若愚,等.2型糖尿病性骨质疏松大鼠ADSCs成骨能力的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019, 25(9):1201-1205+1211.
[3] 张玲莉,林小晶,郭健民,等.有氧运动对2型糖尿病大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(3):254-260.
[4] 江洪.不同运动强度干预2型糖尿病模型大鼠的骨密度变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(27):3963-3969.
[5] HE Q, SHA S, SUN L, et al. GLP-1 analogue improves hepatic lipid accumulation by inducing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2016; 476(4):196-203.
[6] HU XK, YIN XH, ZHANG HQ, et al.Liraglutide attenuates the osteoblastic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by modulating AMPK/mTOR signaling.Mol Med Rep. 2016; 14(4):3662-3668.
[7] 王雨晴,李艳波.自噬与2型糖尿病关系研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016,30(11):1041-1043.
[8] WATADA H, FUJITANI Y. Autophary in pancreatic beta cells and its implication in diabetes.Mol Endocrionol. 2015;29(3): 338-348.
[9] 曾祥琴,胡肇衡.糖尿病与骨质疏松的关系[J].新疆医学,2007, 37(1):119-121.
[10] 应大文,刘芳.糖尿病与骨质疏松的相关性研究进展[J].实用预防医学,2015,22(10):1275-1278.
[11] YAN HM, GUO J, AN Y, et al. Research progress in molecular signaling pathways on the pathogenesis of osteoporosis.Chin J Osteoporos.2016;22(10): 1336-1340.
[12] WANG XF, SUN FQ, YE BL, et al. Research progress in the relationship between osteoclasts and osteoporosis.Chin J Osteoporos.2015;21(11):1420-1424.
[13] YANG L, LI P, FU S, et al. Defective hepatic autophagy inobesity promotes ER stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab.2010;11(6):467-478.
[14] MAHMOUD AB, ELGHERIANY AA, ABDEL SHAKOR ABM. Hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia induced hepatocellular autophagy in male mice.Egypt Acad J Biol Sci Hisol.2015; 6(1):1.
[15] 范梦琳,吴剑男,姜宏卫.自噬与胰岛素抵抗关系的研究进展[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2017,35(5):519-522.
[16] SAINTPASTOU TC, GASQUE P. Bone responses in health and infectious diseases: A focus on osteoblasts. J Infect. 2017;75(4):281-292.
[17] NOLLET M, SANTUCCI-DARMANIN S, BREUIL V, et al. Autophogy in osteoblasts is involved in mineralization and bone homeostasis.Autophagy.2014;10(11): 1965-1977.
[18] 杨康,陈祥和,赵仁清,等.运动调控骨自噬中长链非编码RNA的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(31):5065-5071.
[19] 张平.Insulin-TGF-β1-SATB2通路调控BMSCs自噬影响2型糖尿病颌骨再生修复的研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2018.
[20] WHITEHOUSE CA, WATERS S, MARCHBANK K, et al. Neighbor of Brca1 gene (Nbr1) functions as a negative regulator of postnatal osteoblastic bone formation and p38 MAPK activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2010;107(29): 12913.
[21] BARTOLOMÉ A, LÓPEZ-HERRADÓN A, PORTAL-NÚ, et al. Autophagy impairment aggravates the inhibitory effects of high glucose on osteoblast viability and function.Biochem J.2013;455(3):329-337.
[22] DAI W, JIANG L, YUAN EL, et al. Prevention of glucocorticoid induced bone changes with beta-ecdysone.Bone.2015; 74(5): 48-57.
[23] 陈祥和,李世昌,孙朋,等.游泳和下坡跑通过CN/NFAT信号途径对2型糖尿病小鼠骨吸收代谢的影响[J].中国体育科技,2018, 54(4):113-119+145.
[24] DESELM CJ, MILLER BC, ZOU W, et al. Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption.Dev Cell.2011;21(5):966-974.
[25] ZHU YB, JIA GL, LU JH, et al. The relationship between autophagy activation in spinal cord and type 2 diabetic neuropathic pain in rats.Acta Physiologica Sinica.2018; 34(4):318-323.
[26] 张路遥.能量代谢分子SIRT1在运动改善2型糖尿病骨代谢中的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(2):276-281.
[27] HOCKING LJ, WHITEHOUSE C, HELFRICH MH. Autophagy: a new player in skeletal maintenance.J Bone Miner Res.2012; 27(7):1439-1447.
[28] 张娜娜.不同方式运动对2型糖尿病小鼠骨形成代谢和骨髓间充质干细胞分化的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2016.
[29] 徐会金. 运动通过p38MAPK信号通路对2型糖尿病小鼠骨代谢的影响[D].上海:华东师范大学,2016.
[30] ZHAO H, XIONG J, ONAL M, et al. Osteocyte autophagy declines with age in mice and suppression of autophagy decreases bone mass.J Bone Min Res.2012;26(5):1039.
[31] 刘刚.自噬对镉致大鼠肾小管上皮细胞凋亡的影响及其调控机制[D].扬州:扬州大学,2017.
[32] GÓMEZ-PUERTO MC, VERHAGEN LP, BRAAT AK, et al. Activation of autophagy by FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic differentiation.Autophagy. 2016;12(10):1804-1816.
[33] 赵常红,李世昌,孙朋.不同运动对生长期大鼠Wnt/β-catenin信号及软骨内成骨的影响[J].天津体育学院学报,2019,34(3): 238-242+263.
[34] LIU S, ZHOU PU, ZHANG Y. Abnormal expression of key genes and proteins in the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway of articular cartilage in a rat model of exercise-induced osteoarthritis.Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):1999-2006.
[35] XI C, LIHUI L, JIANMIN G, et al. Treadmill running exercise prevents senile osteoporosis and upregulates the Wnt signaling pathway in SAMP6 mice.Oncotarget. 2016;7(44): 71072-71086.
[36] YASUHARA R, OHTA Y, YUASA T, et al. Roles of β-catenin signaling in phenotypic expression and proliferation of articular cartilage superficial zone cells.Lab Invest. 2011; 91(12):1739-1752.
[37] PASOLD J, OSTERBERG A, PETERS K, et al. Reduced expression of Sfrp1 during chondrogenesis and in articular chondrocytes correlates with osteoarthritis in STR/ort mice. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(5):649-659.
[38] 陈祥和,彭海霞,李世昌,等.不同运动方式对II型糖尿病小鼠骨形成及BMPs/Smad途径相关分子表达的影响[J].北京体育大学学报, 2017,40(5): 51-58.
[39] DIBBLE CC, MANNING BD. Signal integration by mTORC1co-ordinates nutrient input with biosynthetic output. Nat Cell Biol.2013;15(6):555.
[40] KIM J, KUNDU M, VIOLLET B, et al. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol.2011;13(2):132-141.
[41] INOKI K, OUYANG H, ZHU T, et al. TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via acoordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth.Cell.2006;126(5):955-968.
[42] GWINN DM, SHACKELFORD DB, EGAN DF, et al. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell.2008;30(2):214-226.
[43] ENGIN F, NGUYEN T, YERMALOVICH A, et al. Aberrant islet unfolded protein response in type 2 diabetes.Sci Reports. 2014;11(4):4054.
[44] IMPSON KA, MAVROS Y, KAY S, et al. Graded resistanceexercise and type 2 diabetes in older adults(the GRREAT2DO study):methods and baseling cohort characteristics of a randomized controlled trial.Trials.2015; 16(2):512-525.
[45] CHEN KH, SENGUPTA A, NAYAK RC, et al. p62 isrequired for stem cell/progenitor retention through inhibtion of IKK/NF-kappaB/Ccl4 signaling at the bone marrow macrophage-osteoblast-niche.Cell Rep.2014;9(6):2084.
[46] 朱子东,张海英,高静,等.肥胖儿童短期强化治疗前后生化及骨代谢相关指标的变化[J].中国医药指南, 2013, 11(36):143-144.
[47] WOHLGEMUTH SE, SEO AY, MARZETTI E, et al. Skeletal muscle autophagy and apoptosis during aging:effects of calorie restriction and life-long exercise.Exp Gerontol.2010; 45(2):138.
[48] CHEN K, YANG YH, JIANG SD, et al. Decreased activity of osteocyte autophagy with aging may contribute to the bone loss in senile population.Histochem Cell Biol.2014;14(3):285.
|