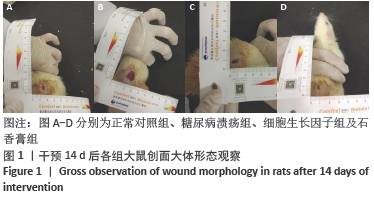
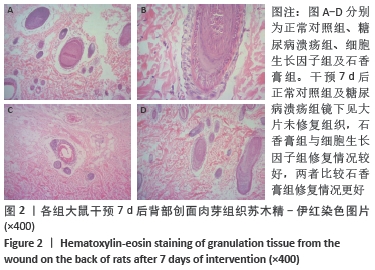
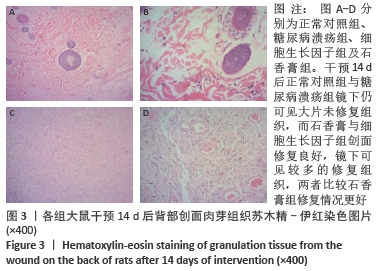
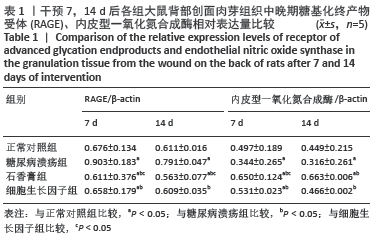
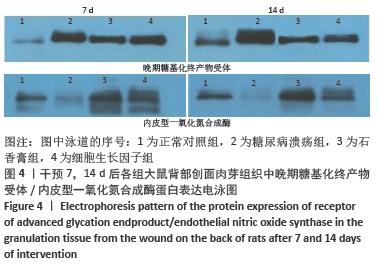
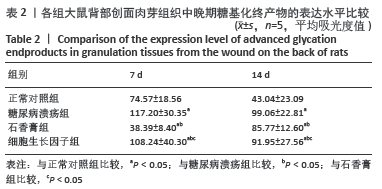
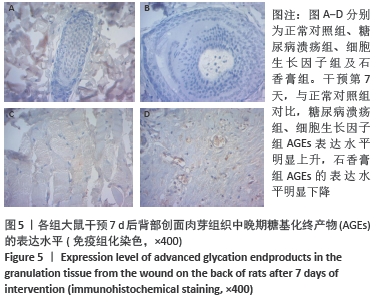
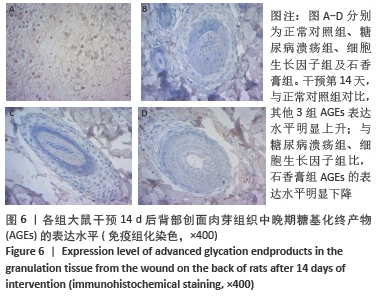
[1] JAWORSKI M, PANCZYK M, SLIWCZYRISKI A, et al. Severe depressive episode with psychotic symptoms and type 2 diabetes: a 2010-2017 longitudinal study. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:1760-1768.
[2] ADU MD, MALABU UH, MALAU-ADULI AEO, et al. Enablers and barriers to effective diabetes self-management: a multi-national investigation. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0217771.
[3] INFANTE-GARCIA C, GARCIA-ALLOZA M. Review of the effect of natural compounds and extracts on neurodegeration in Animal models of diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:E2533.
[4] YANG WY. Epidemiology and trends in diabetes in China (in Chinese). Sci Sin Vitae. 2018;48:812-819.
[5] CUNNION KM, KRISHNA NK, PALLERA HK, et al. Complement activation and STAT4 expression are associated with early inflammation in diabetic wounds. PloS One. 2017;12(1):e0170500.
[6] WOZNIAK SE, GEE LL, WACHTEL MS, et al. Adipose Tissue: The New Endocrine Organ A Review Article. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54(9): 1847-1856.
[7] SCHAFER M, WERNER S. Oxidative stress in normal and impaired wound repair. Pharmacol Res. 2008;58:165-167.
[8] KOENEN P,SPANHOLTZ TA,MAEGELE M, et al. Acute and chronic wound fluids inversely influence adi- pose-derived stem cell function: molecular insights into impaired wound healing. Int Wound J. 2015;12(1):10-16.
[9] BOLLA SR,MOHAMMED AL-SUBAIE A,YOUSUF AL-JINDAN R. In vitro wound healing potency of metha- nolic leaf extract of Aristolochia saccata is possibly media- ted by its stimulatory effect on collagen-1 expression. Heliyon. 2019;5(5): e01648.
[10] 凌一鸣,费冀,张开伟,等. 石香膏对糖尿病慢性难愈合创面模型大鼠创面组织血管内皮细胞黏附分子1、核因子κB p65 表达的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2020, 61(7): 619-625.
[11] WAUTIER MP, GUILLAUSSEAU PJ, WAUTIER JL. Activation of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and consequences on health. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11(4):305-309.
[12] 李文华,刘筱,周雯婷,等. 糖尿病溃疡动物模型的研究进展[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2018,34(8):246-248.
[13] 卓燊,乔雪,陈君,等. 复方愈疡散治疗糖尿病慢性难愈性创面的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(4):115-119.
[14] 陆少君,曾伟斌,臧林泉. 2 型糖尿病大鼠模型制备实验研究[J]. 广东药科大学学报,2017,33(5):624-628
[15] 凌一鸣,费冀,张开伟,等. 中药石香膏对糖尿病大鼠糖尿病溃疡 RAGE/NF-κBp65/eNOS mRNA表达影响的研究[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志,2019,25(7): 913-917.
[16] 吴允波,胡铁山,程仕萍,等. 解毒祛腐煨脓生肌法治疗蛇伤后溃疡的临床研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2018,29(6):1382-1384.
[17] 韩璐,孙甲友,周丽,等. 没药化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药,2015,11(3):38-42.
[18] 周灵君,张丽,丁安伟. 炉甘石敛口生肌的药效学研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2013,24(4):333-337.
[19] 尚坤,李敬文,常美月,等. 冰片化学成分及药理作用研究[J]. 吉林中医药, 2018,38(1):93-95.
[20] KANG R, CHEN R, XIE M, et al. The receptor for advanced glycation end products activates the AIM2 inflammasome in acute pancreatitis. Immunol. 2016;196(10): 4331-4337.
[21] ZHANG J, YAN J. Protective effect of ginkgolic acid in attenuating LDL induced inflammation human peripheral blood mononuclear cells via altering the NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;8(10):1241-1252.
[22] CONG L, YANG S, ZHANG Y, et al. DFMG attenuates the activation of macrophages induced by co-culture with LPC-injured HUVE-12 cells via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(5):2619-2628.
[23] IWAKIRI Y. S-nitrosylation of proteins: a new insight into endothelial cell function regulated by eNOS-devived NO. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25(2):95-101.
[24] Chen Z, DS Oliveira S, Zimnicka AM. Reciprocal Regulation of eNOS and Caveolin-1 Functions in Endothelial Cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2018;29(10):1190-1202.
[25] Papapetropoulos A, Carcina-Cardena G, Madri JA, et al. Nitric oxide production contributes to the angiogenic properties of vascular endothelial growth factor in humanendothelial cells. Clin Invest. 1997;100:3131-3139.
[26] SCHIEKOFER S, ANDRASSY M, CHEN J, et al. Acute hyperglycemia causesintracellular formation of CML,and activation of ras,p42/p44MAPK,and nuclear factor-kB in PBMCs. Diabetes. 2003;52:621-633.
[27] 宋涛,吴树金,刘玉晖,等.Cariporide对糖基化终末产物所致血管内皮损伤的保护作用[J]中南药学,2007,5(5):429-432.
[28] BIERHAUS A, HUMPERT PM, MORCOS M, et al. Understanding RAGE,the receptor for advanced glycation end products. Mol Med. 2005;83(11):876-886.
[29] IWAKIRI Y. S-nitrosylation of proteins: a new insight into endothelial cell function regulated by eNOS-devived NO. Nitric Oxide. 2011;25(2):95-101.
[30] CHEN Z, DS OLIVEIRA S, ZIMNICKA AM. Reciprocal Regulation of eNOS and Caveolin -1 Functions in Endothelial Cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2018;29(10):1190-1202.
|