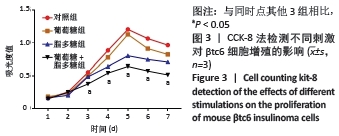
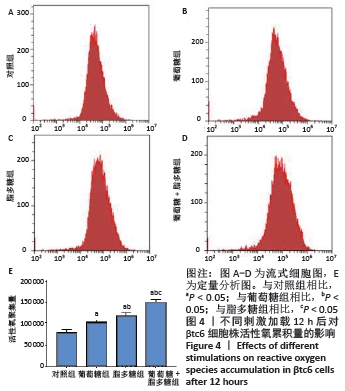
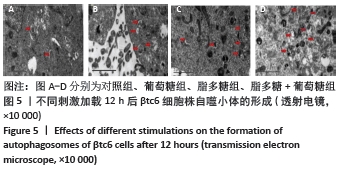
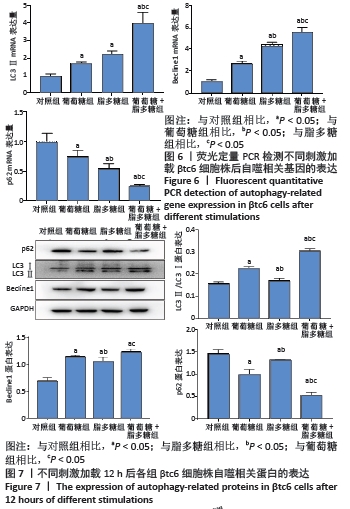
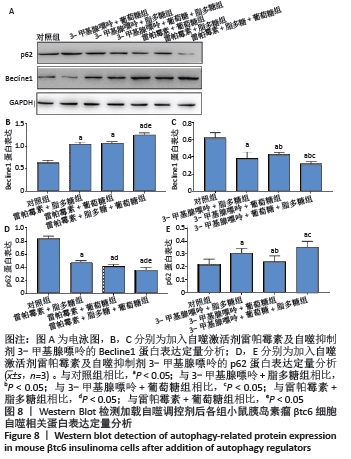
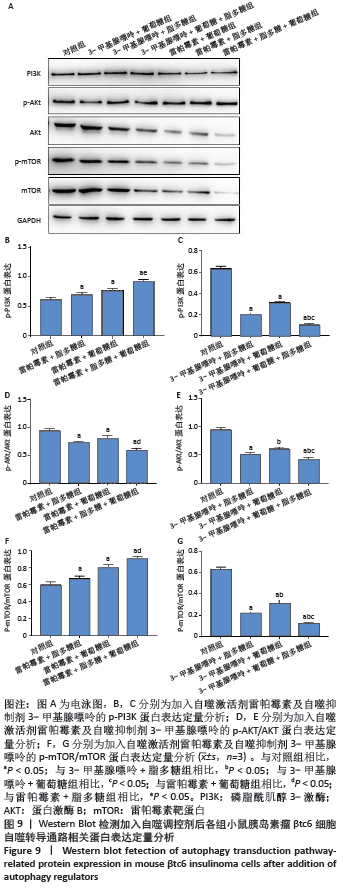
|
[1] 刘尔黎,钟雯怡,刘增一,等. 2型糖尿病伴牙周炎牙周膜干细胞成牙骨质分化能力的研究[J]. 遵义医科大学学报,2020,43(5):51-57.
[2] 杨琨,崔晓霞,邓超,等. 糖基化终末产物对人牙周膜干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化能力影响的比较研究[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2013,23(6):366-370.
[3] LIU Q , HU CH , ZHOU CH , et al. DKK1 rescues osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from periodontal ligaments of patients with diabetes mellitus induced periodontitis. Sci Rep. 2015;5(1):13142.
[4] TANG Y , LIU J , YAN Y , et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin-D3 promotes neutrophil apoptosis in periodontitis with type 2 diabetes mellitus patients via the p38/MAPK pathway. Medicine. 2018;97(52):e13903.
[5] YANG K, WANG Y, JU Y, et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor regulates differential mineralization of rat ectomesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. Cell Prolif. 2017; 50(1):e12290.
[6] KHAN MJ, AHMAD A, KHAN MA, et al. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Induces Apoptosis in Human Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells Through Reactive Oxygen Species and DNA Degradation. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021;199(6):2172-2181.
[7] GIACOPPO S, POLLASTRO F, GRASSI G,et al. Target regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway bycannabidiol in treatment of experimental multiple sclerosis. Fitoterapia. 2017;116:77-84.
[8] CLARIMUNDO VS, FARINON M, PEDÓ RT, et al. Gastrin-releasing peptide and its receptor increase arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes invasiveness through activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Peptides. 2017;95:57-61.
[9] LU XL,ZHAO CH,YAO XL,et al. Quercetin attenuates high fructose feeding-induced atherosclerosis bysuppressing inflammation and apoptosis via ROS-regulated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;85:658-671.
[10] SU R , JIN X , ZHANG W , et al. Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages via oxidative stress-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere. 2017;167:444-453.
[11] HUANG C, WANG HY, WANG ME, et al. Kisspeptin-Activated Autophagy Independently Suppresses Non-Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic β-Cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17451.
[12] NIU B , LIU L , SU H , et al. Role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signal transduction pathway in insulin secretion by β-TC6 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(5):4451-4454.
[13] 肖潇. 阿托伐他汀对脂多糖诱导小鼠胰岛β细胞活力与胰岛素分泌的影响[D]. 长沙:湖南师范大学,2017.
[14] ZHOU CC, XU RS, WU ZP, et al. Osteogenesis, Osteoclastogenesis and their Crosstalk in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Periodontitis in Mice. Chin J Dent Res. 2021;24(1):33-39.
[15] 林玉玲,刘琳,籍胤玺,等. 2型糖尿病合并牙周炎患者龈沟液中炎症因子,瘦素和脂多糖水平的变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2016,24(9): 815-819.
[16] 许霖水, 李强. 内毒素血症大鼠胰岛β-细胞功能损害的研究[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2002,9(6):395-397.
[17] SUN X, XIAO Y, WANG B, et al. Associations of pancreatic beta-cell function and insulin resistance with microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110(3):e22-26.
[18] VELA-GUAJARDO JE , GARZA-GONZÁLEZ S, GARCÍA N. Glucolipotoxicity-induced oxidative stress is related to mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis of pancreatic β-cell. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2021;17(5):e031120187541.
[19] ZHOU Y, LI W, ZHOU J, et al. Lipotoxicity reduces β cell survival through islet stellate cell activation regulated by lipid metabolism-related molecules. Exp Cell Res. 2019;380(1):1-8.
[20] JIA L, WANG X, MING Z, et al. Lipopolysaccharide from Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes autophagy of human gingival fibroblasts through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Life Ences. 2018;211:133-139.
[21] BOSI E, MARSELLI L, LUCA CD, et al. Integration of single-cell datasets reveals novel transcriptomic signatures of β-cells in human type 2 diabetes. NAR Genomi Bioinform. 2020;2(4):lqaa097.
[22] HUANG C, WANG HY, WANG ME, et al. Kisspeptin-Activated Autophagy Independently Suppresses Non-Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion from Pancreatic β-Cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17451.
[23] KHAN MA, JAIN VK, RIZWANULLAH M, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer: a review on drug discovery and future challenges. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(11):2181-2191.
[24] LIU YY , SUN C , XUE FS , et al. Effect of Autophagy Inhibition on the Protection of Ischemia Preconditioning against Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats. Chin Med J. 2018;131(14):1702-1709
[25] CHEN Z, YANG L, LIU Y, et al. LY294002 and Rapamycin promote coxsackievirus-induced cytopathic effect and apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;385(1-2): 169-177.
[26] KIM KY, PARK KI, KIM SH, et al. Inhibition of Autophagy Promotes Salinomycin-Induced Apoptosis via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/p38 MAPK-Dependent Signaling in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5):1088.
|