中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4147-4152.doi: 10.12307/2022.816
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
补肾健脾活血方干预骨质疏松模型大鼠骨代谢、氧化应激及自噬的变化
米健国1,乔荣勤2,刘少津3
- 1广东江门中医药职业学院,广东省江门市 529000;2广州中医药大学第三附属医院,广东省广州市 510240;3广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510405
Bushen Jianpi Huoxue Recipe improves bone metabolism, oxidative stress, and autophagy in osteoporotic rats
Mi Jianguo1, Qiao Rongqin2, Liu Shaojin3
- 1Guangdong Jiangmen Chinese Medical College, Jiangmen 529000, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China)
摘要:
文题释义:
氧化应激:是指体内氧化与抗氧化作用失衡的一种状态,倾向于氧化,导致中性粒细胞炎性浸润,蛋白酶分泌增加,产生大量氧化中间产物。氧化应激是由自由基在体内产生的一种负面作用,并被认为是导致衰老和疾病的一个重要因素。
自噬:是一种动态的分解代谢过程,与细胞损伤、修复、增殖等密切相关,在细胞应激和环境适应中起重要作用,也是维持细胞内环境稳定性的一种保护机制。它使用溶酶体降解,恢复细胞内损伤、衰老的细胞器和生物分子,并实现蛋白质和能量更新代谢。
背景:氧化应激被认为是骨质疏松发生的最重要的始动因素之一,氧化应激除直接激活经典的线粒体和内质网凋亡途径外,还激活细胞自噬信号通路,而骨质疏松发病中成骨细胞抗氧化功能的调控机制并未被清晰阐述。
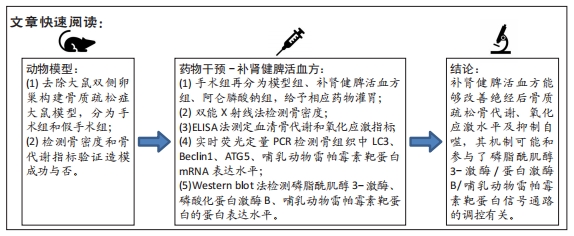
目的:探讨补肾健脾活血方改善氧化应激与自噬对骨质疏松大鼠磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、蛋白激酶B、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的影响。
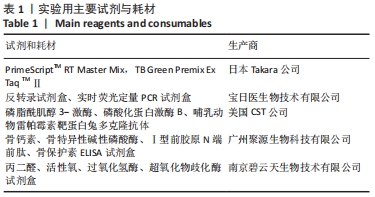
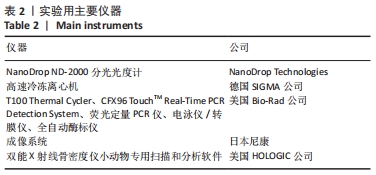
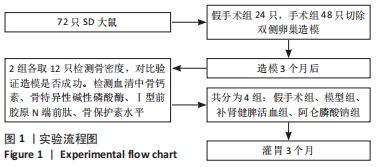
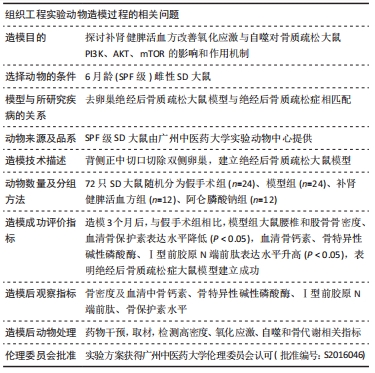
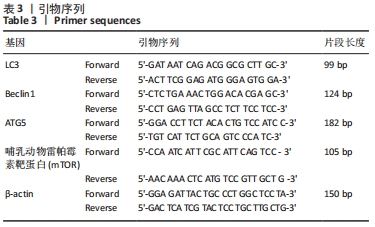
方法:72只6月龄雌性SD大鼠随机分为假手术组24只及手术组48只,去除卵巢造模;术后3个月两组各取12只检测骨密度及血清中骨钙素、骨特异性碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型前胶原N端前肽、骨保护素水平。剩余手术组的36只大鼠分为模型组、补肾健脾活血方组及阿仑膦酸钠组,每组12只,药物组给予相应药物灌胃,假手术组和模型组灌胃等体积生理盐水。12周后处死各组大鼠,双能X射线法检测大鼠腰椎和股骨骨密度,ELISA法测定血清骨代谢指标及氧化应激指标,实时荧光定量PCR检测股骨组织中LC3、Beclin1、ATG5、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的mRNA表达情况,Western blot法检测磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、磷酸化蛋白激酶B、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的蛋白表达情况。
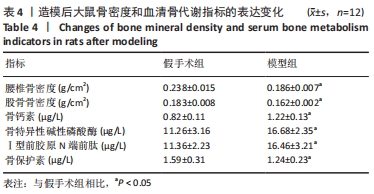
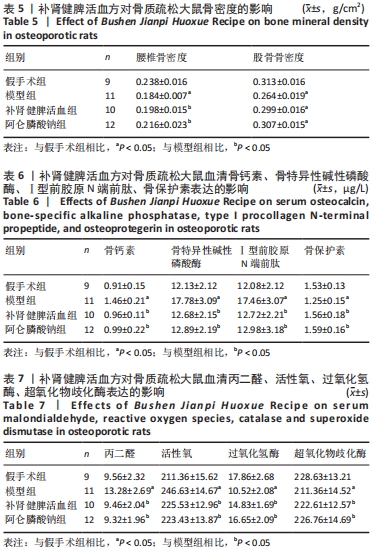
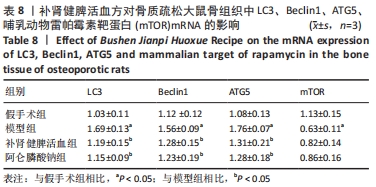
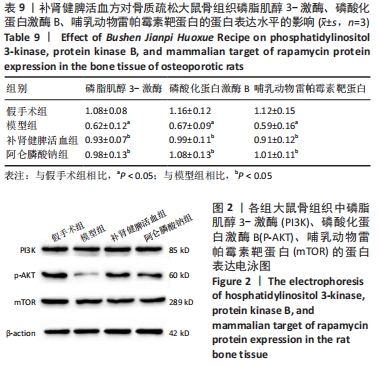
结果与结论:①造模3个月及药物干预3个月后,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠骨密度及骨保护素表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),骨钙素、骨特异性碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型前胶原N端前肽表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05);②药物干预3个月后,与假手术组比较,模型组丙二醛、活性氧表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05);LC3、Beclin1、ATG5的mRNA表达水平显著升高(P < 0.05);过氧化氢酶、超氧化物歧化酶及哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白mRNA、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、磷酸化蛋白激酶B、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05);③药物干预3个月后,与模型组比较,补肾健脾活血方组、阿仑膦酸钠组的上述指标均显著改善(P < 0.05);④提示补肾健脾活血方能够改善绝经后骨质疏松骨代谢、氧化应激水平并抑制自噬,其机制可能和参与了磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路的调控有关。
缩略语:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶:phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K;蛋白激酶B:protein kinase B,AKT;哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白:mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7629-2191 (米健国)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: