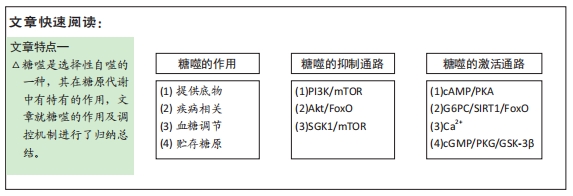
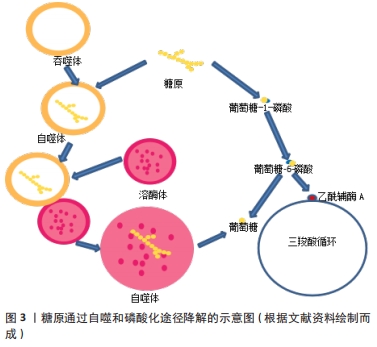
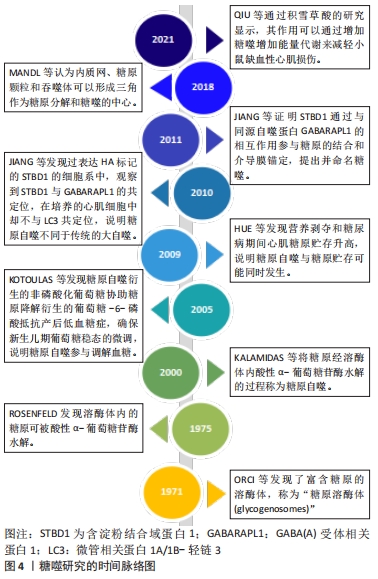
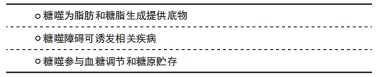
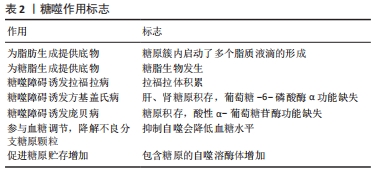
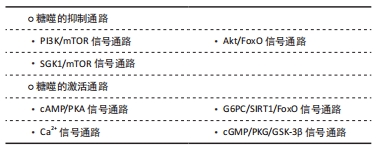
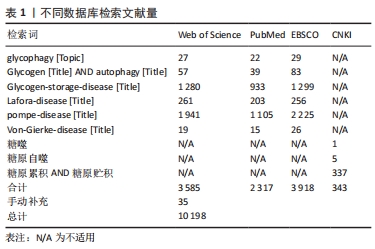
[1] ZHAO H, TANG MZ, LIU MQ, et al. Glycophagy: An emerging target in pathology. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;484:298-303.
[2] CONDELLO M, PELLEGRINI E, CARAGLIA M, et al. Targeting Autophagy to Overcome Human Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):725.
[3] JIANG SX, WELLS CD, ROACH PJ. Starch-binding domain-containing protein 1 (Stbd1) and glycogen metabolism: Identification of the Atg8 family interacting motif (AIM) in Stbd1 required for interaction with GABARAPL1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;413(3):420-425.
[4] KOLB-LENZ D, FUCHS R, LOHBERGER B, et al. Characterization of the endolysosomal system in human chordoma cell lines: is there a role of lysosomes in chemoresistance of this rare bone tumor? Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;150:83-92.
[5] SINHA P, VERMA B, GANESH S. Trehalose Ameliorates Seizure Susceptibility in Lafora Disease Mouse Models by Suppressing Neuroinflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58:1088-1101.
[6] PURI R, GANESH S. Laforin in autophagy: A possible link between carbohydrate and protein in Lafora disease? . Autophagy. 2010;6(8): 1229-1231.
[7] CHOU JY, JUN HS, MANSFIELD BC. Glycogen storage disease type I and G6Pase-β deficiency: etiology and therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6(12):676-688.
[8] PASCARELLA A, TERRACCIANO C, FARINA O, et al. Vacuolated PAS-positive lymphocytes as an hallmark of Pompe disease and other myopathies related to impaired autophagy. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(8): 5829-5837.
[9] KISHNANI PS, CORZO D, NICOLINO M, et al. Recombinant human acid α-glucosidase: major clinical benefits in infantile-onset Pompe disease. Neurology. 2007;68(20):99-109.
[10] GREENBERG CC, JURCZAK MJ, DANOS AM, et al. Glycogen branches out: new perspectives on the role of glycogen metabolism in the integration of metabolic pathways. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006;291(1):E1-E8.
[11] IWAMASA T, TSURU T, HAMADDA T, et al. Physicochemical and Ultrastructural Studies on Glycogenosomes in Newborn Rat Hepatocytes. Pathol Res Pract. 1980;167(2):363-373.
[12] RYU JH, DRAIN J, KIM JH, et al. Comparative structural analyses of purified glycogen particles from rat liver, human skeletal muscle and commercial preparations. Int J Biol Macromol. 2009;45(5):478-482.
[13] PRATS C, GRAHAM TE, SHEARER J. The dynamic life of the glycogen granule. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(19):7089-7098.
[14] BESFORD QA, SULLIVAN MA, ZHENG L, et a. The structure of cardiac glycogen in healthy mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5):887-891.
[15] REICHELT ME, MELLOR KM, CURL CL, et al. Myocardial glycophagy-a specific glycogen handling response to metabolic stress is accentuated in the female heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;65:67-75.
[16] ORCI L, STAUFFACHER W. Glycogenosomes in renal tubular cells of diabetic animals. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971;36(3-4):499-503.
[17] ROSENFELD EL. Alpha-glucosidases (gamma-amylases) in human and animal organisms. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1975;23(1):71-84.
[18] CAVANAGH JB, JONES HB. Glycogenosomes in the aging rat brain: their occurrence in the visual pathways. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;99(5):496-502.
[19] REYES-LUGO M, SÁNCHEZ T, FINOL HJ, et al. Neurotoxic activity and ultrastructural changes in muscles caused by the brown widow spider Latrodectus geometricus venom. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2009;51(2):95-101.
[20] KALAMIDAS SA, KOTOULAS OB. Glycogen autophagy in newborn rat hepatocytes. Histol Histopathol. 2000;15(4):1011-1018.
[21] KOTOULAS OB, KALAMIDAS SA, KONDOMERKOS DJ. Glycogen Autophagy. Microsc Res Tech. 2004;64(1):10-20.
[22] KOTOULAS OB, KALAMIDAS SA, KONDOMERKOS DJ. Glycogen autophagy in glucose homeostasis. Pathol Res Pract. 2006;202:631-638.
[23] MANDL J, BANHEGYI G. The ER - Glycogen Particle - Phagophore Triangle: A Hub Connecting Glycogenolysis and Glycophagy? Pathol Oncol Res. 2018;24(4):821-826.
[24] KUMA A, HATANO M, MATSUI M, et al. The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature. 2004;432(7020):1032-1036.
[25] KOMATSU M, WAGURI S, UENO T, et al. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2005;169(3):425-434.
[26] YANG L, LI P, FU SN. Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance. Cell Meta. 2010;11(6):467-478.
[27] KONDOMERKOS DJ, KALAMIDAS SA, KOTOULAS OB, et al. Glycogen autophagy in the liver and heart of newborn rats. The effects of glucagon, adrenalin or rapamycin. Histol Histopathol. 2005;20(3):689-696.
[28] HUE L, TAEGTMEYER H. The Randle cycle revisited: a new head for an old hat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;297(3):E578-E591.
[29] MASOUD WGT, CLANACHAN AS, LOPASCHUK GD. The Failing Heart: Is It an Inefficient Engine or an Engine Out of Fuel? . Cardiac Remodeling. 2013;5:65-84.
[30] ZHANG XN, YAN HJ, YUAN Y, et al. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy. 2013;9(9):1321-1333.
[31] JIANG SX, HELLER B, TAGLIABRACCI VS, et al. Starch binding domain-containing protein 1/genethonin 1 is a novel participant in glycogen metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(45):34960-34971.
[32] KARSLI-UZUNBAS G, GUO JY, PRICE S, et al. Autophagy is Required for Glucose Homeostasis and Lung Tumor Maintenance. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(8):914-927.
[33] DELBRIDGE LM, MELLOR KM, TAYLOR DJ, et al. Myocardial autophagic energy stress responses-macroautophagy, mitophagy, and glycophagy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;308(10):H1194-H1204.
[34] MAYEUF-LOUCHART A, LANCEL S, Sebti Y, et al. Glycogen Dynamics Drives Lipid Droplet Biogenesis during Brown Adipocyte Differentiation. Cell Rep. 2019;29(6):1410-1418.e6.
[35] MAYEUF-LOUCHART A. Uncovering the Role of Glycogen in Brown Adipose Tissue. Pharm Res. 2021;38:9-14.
[36] PALHEGYI AM, SERANOVA E, DIMOVA S,et al. Biomedical Implications of Autophagy in Macromolecule Storage Disorders. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:179.
[37] KAUR J, DEBNATH J. Autophagy at the crossroads of catabolism and anabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16(8):461-472.
[38] ZHANG WZ, HAN Z, XUE Y, et al. iCAL: a new pipeline to investigate autophagy selectivity and cancer. Autophagy. 2021;17(7):1799-1801.
[39] PARIHAR R, RAI A, GANESH S, et al. Lafora disease: from genotype to phenotype. J Genet. 2018;97(3):611-624.
[40] CONWAY O, AKPINAR HA, ROGOV VV, et al. Selective Autophagy Receptors in Neuronal Health and Disease. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(8): 2483-2509.
[41] SINGH PK, SINGH S, GANESH S. The Laforin-Malin Complex Negatively Regulates Glycogen Synthesis by Modulating Cellular Glucose Uptake via Glucose Transporters. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32(3):652-663.
[42] FARAH BL, LANDAU DJ, SINHA RA, et al. Induction of autophagy improves hepatic lipid metabolism in glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. J Hepatol. 2016;64:(2):370-379.
[43] FARAH BL, LANDAU DJ, WU YJ, et al. Renal Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress is Coupled to Impaired Autophagy in a Mouse Model of GSD Ia. Mol Genet Metab. 2017;122(3):95-98.
[44] GJORGJIEVA M, CALDERARO J, MONTEILLET L, et al. Dietary exacerbation of metabolic stress leads to accelerated hepatic carcinogenesis in glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Hepatol. 2018; 69(5):1074-1087.
[45] ZHANG LS, LEE C, ARNAOUTOVA I, et al. Gene therapy using a novel G6PC-S298C variant enhances the longterm efficacy for treating glycogen storage disease type Ia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020; 527(3):824-830.
[46] SHEA L, RABEN N. Autophagy in skeletal muscle: implications for Pompe disease. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009;47(Suppl 1):S42-S47.
[47] ASHE KM, TAYLOR KM, CHU QM, et al. Inhibition of glycogen biosynthesis via mTORC1 suppression as an adjunct therapy for Pompe disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2010;100(4):310-315.
[48] PHUPONG V, SHUANGSHOTI S, SUTTHIRUANGWONG P, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of Pompe disease by electron microscopy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2005;271(3):259-261.
[49] RODRÍGUEZ-ARRIBAS M, BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, Gómez-Sánchez R, et al. Pompe Disease and Autophagy: Partners in Crime, or Cause and Consequence? Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(21):2275-2285.
[50] HEDEN TD, CHOW LS, HUGHEY CC, et al. Regulation and role of glycophagy in skeletal muscle energy metabolism. Autophagy. 2021;1-12. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1969633.
[51] QIU F, YUAN Y, LUO W, et al. Asiatic acid alleviates ischemic myocardial injury in mice by modulating mitophagy- and glycophagy-based energy metabolism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021; doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00763-9.
[52] CHANDRAMOULI C, VARMA U, STEVENS EM, et al. Myocardial glycogen dynamics: New perspectives on disease mechanisms. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015;42(4):415-425.
[53] MENAHAN LA, SOBOCINSKI KA. Comparison of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in mice and rats during fasting. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1983;74(4):859-864.
[54] BERNASOCHI GB, BOON WC, DELBRIDGE LMD, et al. The myocardium and sex steroid hormone influences. Curr Opin Physiol. 2018;6:1-9.
[55] REICHELT M, MELLOR K, STAPLETON D, et al. Glycogen Responses During Metabolic Stress are Accentuated in Female Hearts: A Role for Myocardial Glycophagy. Heart Lung Circulation. 2013;22:S63-S63.
[56] REICHELT ME, MELLOR KM, BELL JR, et al. Sex, sex steroids, and diabetic cardiomyopathy: making the case for experimenta focus. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;305(6):H779-H792.
[57] FESCHENKO MS, STEVENSON E, NAIRN AC, et al. A Novel cAMP-Stimulated Pathway in Protein Phosphatase 2A Activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;302(1):111-118.
[58] KALAMIDAS SA, KONDOMERKOS DJ, KOTOULAS OB,et al. Electron Microscopic and Biochemical Study of the Effects of Rapamycin on Glycogen Autophagy in the Newborn Rat Liver. Microsc Res Tech. 2004; 63:215-219.
[59] MELLOR KM, VARMA U, STEPLETON DI, et al. Cardiomyocyte glycophagy is regulated by insulin and exposure to high extracellular glucose. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306(8):H1240-H1245.
[60] PAULA-GOMES S, GONCALVES DA, BAVIERA AM, et al. Insulin suppresses atrophy‐and autophagy‐related genes in heart tissue and cardiomyocytes through AKT/FOXO signaling. Horm Metab Res. 2013; 45(12):849-855.
[61] MO JW, ZHANG DF, YANG RZ. MicroRNA-195 regulates proliferation, migration, angiogenesis and autophagy of endothelial progenitor cells by targeting GABARAPL1. Biosci Rep. 2016;36(5):e00396.
[62] DELBRIDGE LMD, MELLOR KM, TAYLOR DJ, et al. Myocardial stress and autophagy: mechanisms and potential therapies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017;14(7):412-425.
[63] SENGUPTA A, MOLKENTIN JD, YUTZEY KE. FoxO transcription factors promote autophagy in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(41): 28319-28331.
[64] SINGH PK, SINGH S, GANESH S. Activation of serum/glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1 (SGK1) underlies increased glycogen levels, mTOR activation, and autophagy defects in Lafora disease. Mol Biol Cell. 2013;24(24):3776-3786.
[65] LIM JA, LI LS, SHIRIHAI OS,et al. Modulation of mTOR signaling as a strategy for the treatment of Pompe disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2017; 9(3):353-370.
[66] CHO JH, KIM GY, PAN CJ, et al. Downregulation of SIRT1 signaling underlies hepatic autophagy impairment in glycogen storage disease type Ia. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(5):e1006819.
[67] GAUTAM S, ZHANG L, ARNAOUTOVA I, et al. The signaling pathways implicated in impairment of hepatic autophagy in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum Mol Genet. 2020;29(5):834-844.
[68] KALAMIDAS SA, KOTOULAS OB, HANN AC. Studies on Glycogen Autophagy: Effects of Phorbol Myristate Acetate, Ionophore A23187, or Phentolamine. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;57(6):507-511.
[69] NISHINO I, FU J, TANJI K, et al. Primary LAMP-2 deficiency causes X-linked vacuolar cardiomyopathy and myopathy (Danon disease). Nature. 2000; 406(6798):906-910.
[70] 张娜.糖噬在晚发型Pompe病(LOPD)病程转归和致病机制中的作用[D].济南:山东大学,2019.
[71] LIU Y, YANG Y, WANG BB, et al. Infantile Pompe disease: A case report and review of the Chinese literature. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(1):235-238.
[72] RABEN N, WONG A, RALSTON E, et al. Autophagy and mitochondria in Pompe disease: Nothing is so new as what has long been forgotten. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2012;160C (1):13-21.
[73] KONDOMERKOS DJ, KALAMIDAS SA, KOTOULAS OB. An electron microscopic and biochemical study of the effects of glucagon on glycogen autophagy in the liver and heart of newborn rats. Microsc Res Tech. 2004;63(2):87-93.
[74] LIU Y, WANG Y, WU C, et al. Dimerization of Laforin Is Required for Its Optimal Phosphatase Activity, Regulation of GSK3 Phosphorylation, and Wnt Signaling. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(46):34768-34774.
[75] GIORGI FS, BIAGIONI F, LENZI P, et al. The role of autophagy in epileptogenesis and in epilepsy-induced neuronal alterations. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122(6):849-862.
[76] ZHAI PY, SADOSHIMA J. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta controls autophagy during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Autophagy. 2012;8(1):138-139.
[77] KONG DF, HUA XW, QIN T, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta protects liver against ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating 5 ‘ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-mediated autophagy. Hepatol Res. 2019;49(4):462-472.
[78] GALLUZZI L, PIETROCOLA F, LEVINE B, et al. Metabolic Control of Autophagy. Cell. 2014;159:1263-1276.
[79] SMITH BK, MARCINKO K, DESJARDINS EM, et al. Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of AMPK. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;311:E730-E740.
[80] SHAW RJ, LAMIA KA, VASQUEZ D, et al. The Kinase LKB1 Mediates Glucose Homeostasis in Liver and Therapeutic Effects of Metformin. Science. 2005;310(5754):1642-1646.
[81] XIE ZL, HE CY, ZOU MH. AMP-activated protein kinase modulates cardiac autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Autophagy. 2011;7(10):1254-1255.
[82] LOOS JA, NICOLAO MC, CUMINO AC. Metformin promotes autophagy in Echinococcus granulosus larval stage. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2018;224:61-70.
[83] ELGENDY M, CIRÒ M, HOSSEINI A, et al. Combination of Hypoglycemia and Metformin Impairs Tumor Metabolic Plasticity and Growth by Modulating the PP2A-GSK3b-MCL-1 Axis. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(5):798-815.e5.
[84] REN F, ZHANG L, ZHANG X, et al. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes autophagy to protect mice from acute liver failure mediated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2151.
[85] GAO JM, LONG L, XU F, et al. Icariside II, a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, attenuates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta-mediated activation of autophagy. Br J Pharmacol. 2020;177(6):1434-1452.
[86] DIVARI S, De LUCIA F, BERIO E, et al. Dexamethasone and prednisolone treatment in beef cattle: influence on glycogen deposition and gene expression in the liver. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2020;72:106444.
[87] NAPOLI E, PANOUTSOPOULOS AA, KYSAR P, et al. Wdfy3 regulates glycophagy, mitophagy, and synaptic plasticity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021;271678X211027384. doi: 10.1177/0271678X211027384.
|