[1] HAHN CL, LIEWEHR FR. Relationships between Caries Bacteria, Host Responses, and Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Pulpitis. J Endod. 2007; 33(3):213-219.
[2] JONTELL M, OKIJI T, DAHLGREN U, et al. Immune defense mechanisms of the dental pulp. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1998;9(2):179-200.
[3] HOU CW, LAURO ML, GRIMES CL. Redefining the Defensive Line: Critical Components of the Innate Immune System. ACS Infect Dis. 2016;2(11):746-748.
[4] LIU J, CAO X. Cellular and molecular regulation of innate inflammatory responses. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016;13(6):711-721.
[5] HIRAO K, YUMOTO H, TAKAHASHI K, et al.Roles of TLR2, TLR4, NOD2, and NOD1 in pulp fibroblasts. J Dent Res. 2009;88(8):762-767.
[6] TOKUDA M, SAKUTA T, FUSHUKU A, et al.Regulation of interleukin-6 expression in human dental pulp cell cultures stimulated with Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide. J Endod. 2001;27(4):273-277.
[7] NAGAOKA S, TOKUDA M, SAKUTA T, et al. Interleukin-8 gene expression by human dental pulp fibroblast in cultures stimulated with Prevotella intermedialipopolysaccharide. J Endod. 1996;22(1):9-12.
[8] BARKHORDAR RA, GHANI QP, RUSSELL TR, et al. Interleukin-1beta activity and collagen synthesis in human dental pulp fibroblasts. J Endod. 2002;28:157-159.
[9] SCHRODER K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140:821-832.
[10] SONG Z, LIN Z, HE F, et al. NLRP3 Is Expressed in Human Dental Pulp Cells and Tissues. J Endod. 2012;38:1592-1597.
[11] JIANG W, LV H, WANG H, et al. Activation of the NLRP3/caspase-1 inflammasome in human dental pulp tissue and human dental pulp fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;361(2):541-455.
[12] BAUERNFEIND FG, HORVATH G, STUTZ A, et al. Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol. 2009;183:787-791.
[13] 蒋文凯,童忠春,王迪雅,等.NLRP3、Caspase-1炎症体通路在人牙髓成纤维细胞中表达和相关调控因素的初步检测[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013,23(1):1-5.
[14] CASO F, COSTA L, NUCERA V, et al. From autoinflammation to autoimmunity: old and recent findings. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(9): 2305-2321.
[15] FUSCO R, SIRACUSA R, GENOVESE T, et al. Focus on the Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4223.
[16] THEOHARIDES TC. Danger Signals and Inflammation. Clin Ther. 2016; 38(5):996-999.
[17] ELLIOTT EI, SUTTERWALA FS. Initiation and perpetuation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and assembly. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1): 35-52.
[18] NOONIN C, THONGBOONKERD V. Exosome-inflammasome crosstalk and their roles in inflammatory responses. Theranostics. 2021;11(9): 4436-4451.
[19] SHEN R, YIN P, YAO H, et al. Punicalin Ameliorates Cell Pyroptosis Induced by LPS/ATP Through Suppression of ROS/NLRP3 Pathway. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:711-718.
[20] MEZZASOMA L, ANTOGNELLI C, TALESA VN. Atrial natriuretic peptide down-regulates LPS/ATP-mediated IL-1β release by inhibiting NF-kB, NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1 activation in THP-1 cells. Immunol Res. 2016;64(1):303-312.
[21] HAMILTON IR. Ecological basis for dental caries. In: Kuramitsu HK, Ellen RP, editors. Oral bacterial ecology: the molecular basis. Wymondham, UK: Horizon Scientific Press, 2000:219-274.
[22] NARDO DD, BALKA KR, GLORIA YC, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) plays a dual role in myddosome formation and Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(39):15195-15207.
[23] ZHANG J, MACARTNEY T, PEGGIE M, et al. Interleukin-1 and TRAF6-dependent activation of TAK1 in the absence of TAB2 and TAB3. Biochem J. 2017;474(13):2235-2248.
[24] FENG H, ZHANG YB, GUI JF, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) and anti-pathogen innate immune responses. PLoS Pathog. 2021; 17(1):e1009220.
[25] SCHMITZ F, HEIT A, GUGGEMOOS S, et al. Interferonregulatory-factor 1 controls Toll-like receptor 9-mediated IFN-beta production in myeloid dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:315-327.
[26] FUNAMI K, MATSUMOTO M, OSHIUMI H, et al. Functional interfaces between TICAM-2/TRAM and TICAM-1/TRIF in TLR4 signaling. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017;45(4):929-935.
[27] ZHAO XY, HUO RX, YAN XL, et al. IRF3 Negatively Regulates Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated NF-κB Signaling by Targeting TRIF for Degradation in Teleost Fish. Front Immunol. 2018;9:867.
[28] BERTHELOOT D, LATZ E, FRANKLIN BS. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021; 18(5):1106-1121.
[29] Cui J, Chen Y, Wang HY, et al. Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-3285.
|
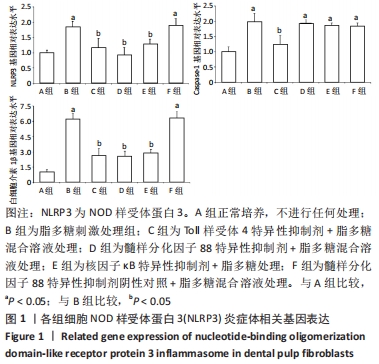
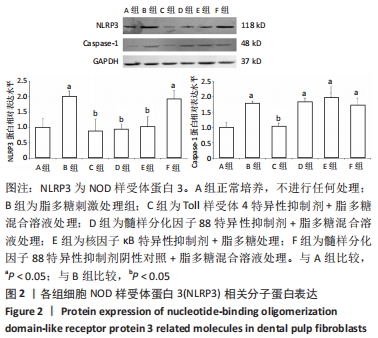
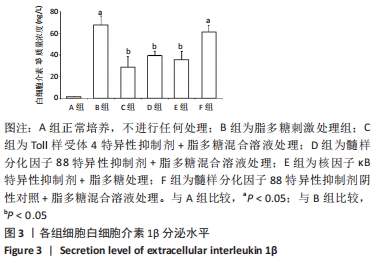

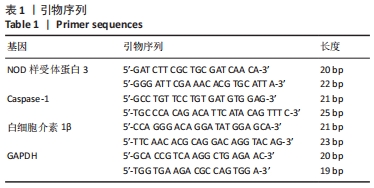
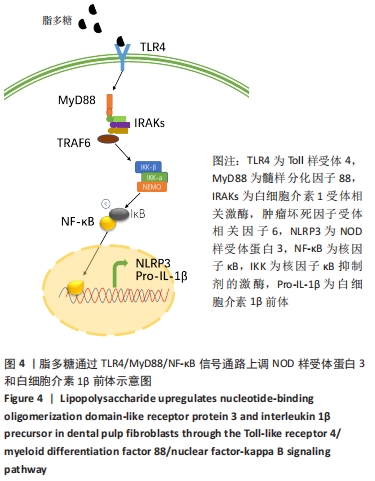 脂多糖是革兰阴性菌细胞壁主要成分,其作用是诱导NOD样受体蛋白3和白细胞介素β前体的表达[19]。ATP通常由死亡细胞释放,其作用是激活NOD样受体蛋白3炎症体[20]。据文献报道,当龋坏发展到牙髓-牙本质界时,革兰阴性菌成为菌群中的优势菌[21],因此实验选择使用脂多糖+ATP激活牙髓成纤维细胞中NOD样受体蛋白3炎症体,以模拟牙髓炎症环境。
脂多糖是革兰阴性菌细胞壁主要成分,其作用是诱导NOD样受体蛋白3和白细胞介素β前体的表达[19]。ATP通常由死亡细胞释放,其作用是激活NOD样受体蛋白3炎症体[20]。据文献报道,当龋坏发展到牙髓-牙本质界时,革兰阴性菌成为菌群中的优势菌[21],因此实验选择使用脂多糖+ATP激活牙髓成纤维细胞中NOD样受体蛋白3炎症体,以模拟牙髓炎症环境。