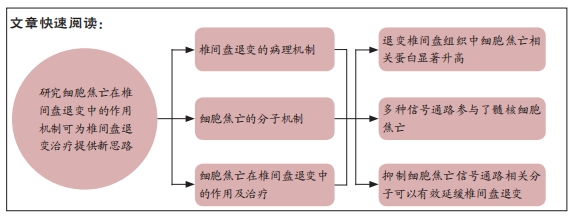
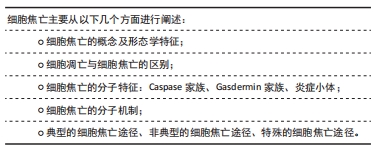
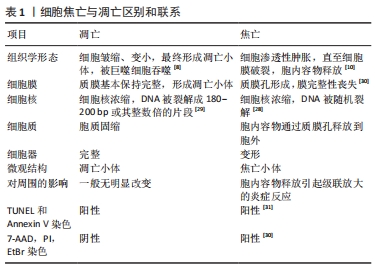
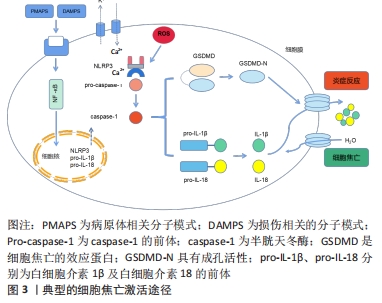
[1] GBD 2017 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] HOY D, MARCH L, BROOKS P, et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):968-974.
[3] KATZ JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:21-24.
[4] OICHI T, TANIGUCHI Y, OSHIMA Y, et al. Pathomechanism of intervertebral disc degeneration. JOR spine. 2020;3(1):e1076.
[5] CHENG X, ZHANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-21 via exosomes to inhibit nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and reduce intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(1):261-276.
[6] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death:recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541.
[7] JIN L, DING M, OKLOPCIC A, et al. Nanoparticle fullerol alleviates radiculopathy via NLRP3 inflammasome and neuropeptides. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(6):2049-259.
[8] 胡宝阳,杨学军. MicroRNA影响椎间盘退变过程的研究进展及可发展空间[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(21):3372-3378.
[9] GRUBER HE, HOELSCHER GL, INGRAM JA, et al. Autophagy in the degenerating human intervertebral disc: in vivo molecular and morphological evidence, and induction of autophagy in cultured annulus cells exposed to proinflammatory cytokines-implications for disc degeneration. Spine. 2015;40(11):773-782.
[10] MCKENZIE BA, DIXIT VM, POWER C. Fiery cell death: pyroptosis in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43(1):55-73.
[11] DE MIGUEL C, PELEGR NP. Emerging role of the inflammasome and pyroptosis in hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1064.
[12] RUAN J, WANG S, WANG J. Mechanism and regulation of pyroptosis-mediated in cancer cell death. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020109052.
[13] MAN SM, KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):61-75.
[14] JOHNSON ZI, SCHOEPFLIN ZR, CHOI H, et al. Disc in flames: roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 2015;30:104-116; discussion 16-17.
[15] CHAO-YANG G, PENG C, HAI-HONG Z. Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(6):793-801.
[16] RISBUD MV, SCHOEPFLIN ZR, MWALE F, et al. Defining the phenotype of young healthy nucleus pulposus cells: recommendations of the Spine Research Interest Group at the 2014 annual ORS meeting. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(3):283-293.
[17] WU Y, CISEWSKI S, SACHS B L, et al. Effect of cartilage endplate on cell based disc regeneration: a finite element analysis. Mol Cell Biomech. 2013;10(2):159-182.
[18] TONG W, LU Z, QIN L, et al. Cell therapy for the degenerating intervertebral disc. Transl Res. 2017;181:49-58.
[19] LI P, HOU G, ZHANG R, et al. High-magnitude compression accelerates the premature senescence of nucleus pulposus cells via the p38 MAPK-ROS pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):209.
[20] WANG SZ, RUI YF, TAN Q, et al. Enhancing intervertebral disc repair and regeneration through biology: platelet-rich plasma as an alternative strategy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):220.
[21] FENG Y, EGAN B, WANG J. Genetic factors in intervertebral disc degeneration. Genes Dis. 2016;3(3):178-185.
[22] ZYCHLINSKY A, PREVOST MC, SANSONETTI PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992;358(6382):167-169.
[23] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114.
[24] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526(7575):660-665.
[25] KAYAGAKI N, STOWE IB, LEE BL, et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature. 2015;526(7575):666-671.
[26] WANG Y, GAO W, SHI X, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547(7661):99-103.
[27] LI MY, ZHU XL, ZHAO BX, et al. Adrenomedullin alleviates the pyroptosis of Leydig cells by promoting autophagy via the ROS-AMPK-mTOR axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10(7):489.
[28] JORGENSEN I, MIAO EA. Pyroptotic cell death defends against intracellular pathogens. Immunol Rev. 2015;265(1):130-142.
[29] ZHANG Y, CHEN X, GUEYDAN C, et al. Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res. 2018;28(1):9-21.
[30] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis:mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128.
[31] VANDEN BERGHE T, HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P. An outline of necrosome triggers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(11-12):2137-2152.
[32] ZHOU B, ZHANG JY, LIU XS, et al. Tom20 senses iron-activated ROS signaling to promote melanoma cell pyroptosis. Cell Res. 2018;28(12):1171-1185.
[33] HOU J, ZHAO R, XIA W, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(10):1264-1275.
[34] ROGERS C, ERKES DA, NARDONE A, et al. Gasdermin pores permeabilize mitochondria to augment caspase-3 activation during apoptosis and inflammasome activation. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1689.
[35] KUANG S, ZHENG J, YANG H, et al. Structure insight of GSDMD reveals the basis of GSDMD autoinhibition in cell pyroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(40): 10642-10647.
[36] LIU Z, WANG C, YANG J, et al. Crystal Structures of the Full-Length Murine and Human Gasdermin D Reveal Mechanisms of Autoinhibition, Lipid Binding, and Oligomerization. Immunity. 2019;51(1):43-49.e4.
[37] DING J, WANG K, LIU W, et al. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 2016;535(7610):111-116.
[38] XIA S, HOLLINGSWORTH LRT, WU H. Mechanism and Regulation of Gasdermin-Mediated Cell Death. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020;12(3):31451512.
[39] ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, LIEBERMAN J. Lighting a fire: can we harness pyroptosis to ignite antitumor immunity? Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(1):2-7.
[40] 胡新力,周凯亮,吴晨宇,等.脊髓损伤中细胞焦亡的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(7):657-662.
[41] PY BF, KIM MS, VAKIFAHMETOGLU-NORBERG H, et al. Deubiquitination of NLRP3 by BRCC3 critically regulates inflammasome activity. Mol Cell. 2013;49(2):331-338.
[42] HE B, NIE Q, WANG F, et al. Role of pyroptosis in atherosclerosis and its therapeutic implications. J Cell Physiol. 2021. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30366.
[43] JIN Y, FU J. Novel Insights Into the NLRP 3 Inflammasome in Atherosclerosis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(12):e012219.
[44] KAYAGAKI N, WARMING S, LAMKANFI M, et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature. 2011;479(7371):117-121.
[45] RÜHL S, BROZ P. Caspase-11 activates a canonical NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting K(+) efflux. Eur J Immunol. 2015;45(10):2927-2936.
[46] KAMBARA H, LIU F, ZHANG X, et al. Gasdermin d exerts anti-inflammatory effects by promoting neutrophil death. Cell Rep. 2018;22(11):2924-2936.
[47] KAYAGAKI N, KORNFELD OS. NINJ1 mediates plasma membrane rupture during lytic cell death. Nature. 2021;591(7848):131-136.
[48] CHEN ZH, JIN SH, WANG MY, et al. Enhanced NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL- 1β levels in degenerate human intervertebral disc and their association with the grades of disc degeneration. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2015;298(4):720-726.
[49] BAI Z, LIU W, HE D, et al. Protective effects of autophagy and NFE2L2 on reactive oxygen species-induced pyroptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):7534-7548.
[50] TANG P, ZHU R, JI WP, et al. The NLRP3/Caspase-1/interleukin-1β axis is active in human lumbar cartilaginous endplate degeneration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474(8):1818-1826.
[51] BRAND FJ 3rd, FOROUZANDEH M, KAUR H, et al. Acidification changes affect the inflammasome in human nucleus pulposus cells. J Inflamm (Lond). 2016;13(1):29.
[52] ZHANG A, WANG K, DING L, et al. Bay11-7082 attenuates neuropathic pain via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B and nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation in dorsal root ganglions in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J Pain Res. 2017;10:375-382.
[53] ZHANG J, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(20):11742-11754.
[54] FU F, BAO R, YAO S, et al. Aberrant spinal mechanical loading stress triggers intervertebral disc degeneration by inducing pyroptosis and nerve ingrowth. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):772.
[55] SONG Y, WANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Advanced glycation end products regulate anabolic and catabolic activities via NLRP3-inflammasome activation in human nucleus pulposus cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(7):1373-1387.
[56] XU Q, XING H, WU J, et al. miRNA-141 induced pyroptosis in intervertebral disk degeneration by targeting ROS generation and activating TXNIP/NLRP3 signaling in nucleus pulpous cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:871.
[57] TANG G, HAN X, LIN Z, et al. Propionibacterium acnes Accelerates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Inducing Pyroptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells via the ROS-NLRP3 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:4657014.
[58] ZHAO Y, QIU C, WANG W, et al. Cortistatin protects against intervertebral disc degeneration through targeting mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Theranostics. 2020;10(15):7015-7033.
[59] ZHAO K, AN R, XIANG Q, et al. Acid-sensing ion channels regulate nucleus pulposus cell inflammation and pyroptosis via the NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1):e12941.
[60] ZHOU Y, CHEN Z, YANG X, et al. Morin attenuates pyroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of the TXNIP/NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;559:106-112.
[61] TANG P, GU JM, XIE ZA, et al. Honokiol alleviates the degeneration of intervertebral disc via suppressing the activation of TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;120:368-379.
[62] HONG J, LI S, MARKOVA DZ, et al. Bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibition alleviates matrix degradation by enhancing autophagy and suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activity in NP cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(7-8):5736-5749.
[63] SUN Y, LENG P, SONG M, et al. Piezo1 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome in nucleus pulposus cell-mediated by Ca(2+)/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;85:106681.
[64] CHEN F, JIANG G, LIU H, et al. Melatonin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting the IL-1β/NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome positive feedback loop. Bone Res. 2020;8:10.
[65] HUANG Y, PENG Y, SUN J, et al. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase controls NLRP3 Inflammasome Activity Through MAPK and NF-κB signaling in nucleus pulposus cells, as suppressed by melatonin. Inflammation. 2020;43(3):796-809.
[66] 吴子健,胡昭端,周晓红,等.通督活血汤含药血清可抑制椎间盘纤维环细胞的焦亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2148-2154.
|