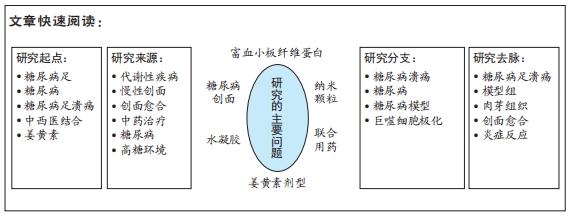
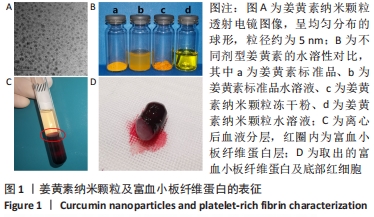
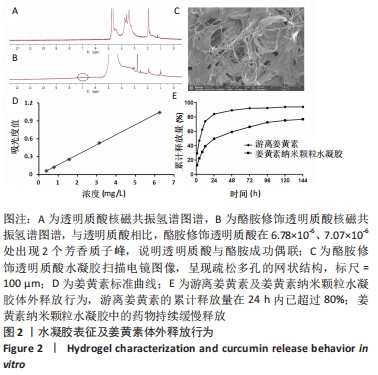
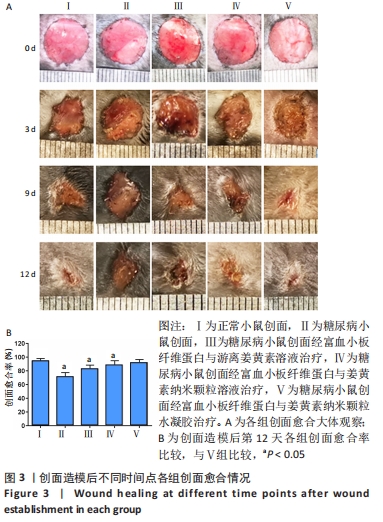
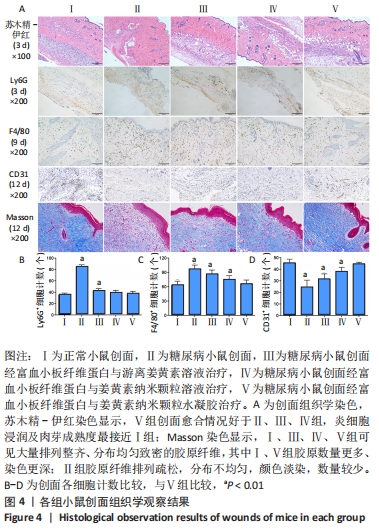
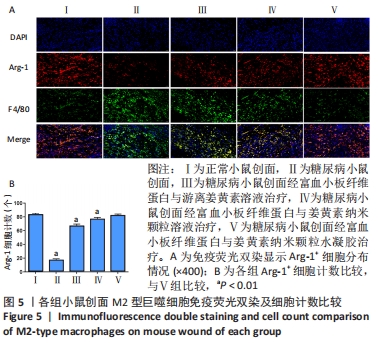
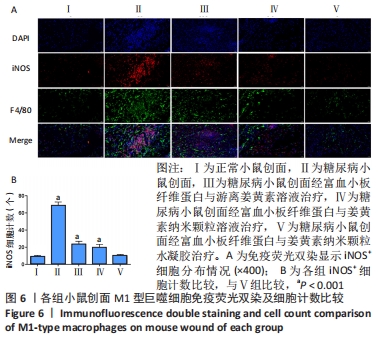
[1] ZHANG P, LU J, JING Y, et al. Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2017; 49(2):106-116.
[2] RAMIREZ-ACUÑA JM, CARDENAS-CADENA SA, MARQUEZ-SALAS PA,
et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Current Advances in Antimicrobial Therapies and Emerging Treatments. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019;8(4):193.
[3] HARDING JL, PAVKOV ME, GREGG EW, et al. Trends of Nontraumatic Lower-Extremity Amputation in End-Stage Renal Disease and Diabetes: United States, 2000-2015. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(8):1430-1435.
[4] 冉兴无,杨兵全,许樟荣.我国糖尿病足病的诊治现状与未来的研究方向[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2014,6(7):437-439.
[5] SKREPNEK GH, MILLS JL SR, LAVERY LA, et al. Health Care Service and Outcomes Among an Estimated 6.7 Million Ambulatory Care Diabetic Foot Cases in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(7):936-942.
[6] 姜玉峰.中国体表慢性难愈合创面流行病学研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2011.
[7] 李炳旻,王芳芳,李倩坤,等.糖尿病溃疡的发生机制与治疗进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2019,40(10):992-994.
[8] 姜臻宇.糖尿病足患者流行病学调查及其截肢的相关危险因素分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2020.
[9] CHIARAVALLOTI AJ, ZUBKOV B, ZUBKOV A. Treatment of a Chronic Cutaneous Surgical Wound With Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44(3):449-452.
[10] KARIMI K, ROCKWELL H. The Benefits of Platelet-Rich Fibrin. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2019;27(3):331-340.
[11] SOUSA F, MACHADO V, BOTELHO J, et al. Effect of A-PRF Application on Palatal Wound Healing after Free Gingival Graft Harvesting: A Prospective Randomized Study. Eur J Dent. 2020;14(1):63-69.
[12] LI Y, ZHAO S, DER LV, et al. Efficacy of curcumin for wound repair in diabetic rats/mice: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(3):187-197.
[13] DENG X, LI F, LI Y, et al. Effect of curcumin on wound healing in a murine model of diabetic foot. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(5):1879-1884.
[14] GHUFRAN H, MEHMOOD A, AZAM M, et al. Curcumin preconditioned human adipose derived stem cells co-transplanted with platelet rich plasma improve wound healing in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2020;257: 118091.
[15] NOWAK NC, MENICHELLA DM, MILLER R, et al. Cutaneous innervation in impaired diabetic wound healing. Transl Res. 2021;236:87-108.
[16] ELEFTHERIADOU I, SAMAKIDOU G, TENTOLOURIS A, et al. Nonpharmacological Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: An Update. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2021;20(3):188-197.
[17] 谷涌泉.中国糖尿病足诊治指南[J].中国临床医生杂志,2020,48(1): 19-27.
[18] YANG S, HU L, HAN R, et al. Neuropeptides, Inflammation, Biofilms, and diabetic Foot Ulcers. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2021;10.1055/a-1493-0458.
[19] DING Y, CUI L, ZHAO Q, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin Accelerates Skin Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;79(3):15-19.
[20] BILGEN F, URAL A, BEKERECIOGLU M. Platelet-rich fibrin: An effective chronic wound healing accelerator. J Tissue Viability. 2021;30(4):616-620.
[21] 章登辉.人源富血小板纤维蛋白促进大鼠糖尿病创面愈合的实验研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2019.
[22] KUMAR RV, SHUBHASHINI N. Platelet rich fibrin: a new paradigm in periodontal regeneration. Cell Tissue Bank. 2013;14(3):453-463.
[23] 刘国涛,王军.中药姜黄在创面治疗中研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(9):118-122.
[24] PANCHATCHARAM M, MIRIYALA S, GAYATHRI VS, et al. Curcumin improves wound healing by modulating collagen and decreasing reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006;290(1-2):87-96.
[25] 屠卓隆,林才.姜黄素对糖尿病创面的促愈合作用及其机制研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2021,37(4):391-394.
[26] YEN YH, PU CM, LIU CW, et al. Curcumin accelerates cutaneous wound healing via multiple biological actions: The involvement of TNF-α, MMP-9, α-SMA, and collagen. Int Wound J. 2018;15(4):605-617.
[27] GENG K, MA X, JIANG Z, et al. Innate Immunity in Diabetic Wound Healing: Focus on the Mastermind Hidden in Chronic Inflammatory. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:653940.
[28] GALINIAK S, BIESIADECKI M, CZUBAT B, et al. Antiglycation activity of curcumin. Advances in Hygiene and Experimental Medicine. 2019;73: 182-188.
[29] CABEZA L, ORTIZ R, PRADOS J, et al. Improved antitumor activity and reduced toxicity of doxorubicin encapsulated in poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles in lung and breast cancer treatment: An in vitro and in vivo study. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;102:24-34.
[30] 王太兵,李颖,贾卓翰,等.白蛋白/透明质酸纳米颗粒制备及递送顺铂效果[J].功能高分子学报.doi: 10.14133/j.cnki.1008-9357. 20210318001
[31] 陶胜岩,王梅,翟光喜.基于透明质酸的刺激响应纳米给药系统的研究进展[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2021,40(5):330-335.
[32] WANG H, GU Y, HUANG L, et al. Effectiveness of fire needle combining with moist healing dressing to promote the growth of granulation tissue in chronic wounds: A case report. Int J Nurs Sci. 2020;7(3):386-390.
[33] NI Z, SUN J, QI S. Application of Easy Wet Healing Therapy for Chronic Noninfectious Wounds in Limbs. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2020; 1534734620924260.
[34] 苏金玲.湿性敷料在慢性伤口中的应用研究进展[J].微创医学,2019, 14(3):364-366.
[35] QIAN Z, WANG H, BAI Y, et al. Improving Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing through an Injectable and Self-Healing Hydrogel with Platelet-Rich Plasma Release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(50):55659-55674.
[36] 陈琳,宁宁,陈慧,等.皮肤创伤湿性愈合治疗的临床效果观察[J].华西医学,2015,30(10):1810-1813.
[37] 杨群英.糖尿病足的临床特点及P物质在糖尿病足溃疡愈合中的作用[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.
[38] 杨沛瑯.中性粒细胞NETs致糖尿病创面难愈及机制研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2017.
[39] WANG Q, ZHU G, CAO X, et al. Blocking AGE-RAGE Signaling Improved Functional Disorders of Macrophages in Diabetic Wound. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:1428537.
[49] 刘宸.富血小板血浆对糖尿病大鼠创面巨噬细胞浸润变化的影响[D].广州:南京医科大学,2014.
[41] WEAR-MAGGITTI K, LEE J, CONEJERO A, et al. Use of topical sRAGE in diabetic wounds increases neovascularization and granulation tissue formation. Ann Plast Surg. 2004;52(5):519-522.
[42] HAN Y, SUN T, TAO R, et al. Clinical application prospect of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells on clearance of advanced glycation end products through autophagy on diabetic wound. Eur J Med Res. 2017;22(1):11.
[43] LI Q, XIA S, YIN Y, et al. miR-5591-5p regulates the effect of ADSCs in repairing diabetic wound via targeting AGEs/AGER/JNK signaling axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):566.
[44] OLEKSON MP, FAULKNOR RA, HSIA HC, et al. Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Improves Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Activity in Model Diabetic Environments. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016;5(12):527-538.
|