中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (27): 4335-4339.doi: 10.12307/2022.834
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
姜黄素纳米粒对人视网膜色素上皮细胞增殖的影响
郑海生1,蓝育青2,钟兴武1,丁 辉1
- 1中山大学中山眼科中心海南眼科医院(海南省眼科医院),海南省眼科学重点实验室,海南省海口市 570311;2中山大学附属孙逸仙纪念医院,广东省广州市 510120
Effect of curcumin nanoparticles on proliferation of human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Zheng Haisheng1, Lan Yuqing2, Zhong Xingwu1, Ding Hui1
- 1Hainan Eye Hospital, Zhongshan Eye Center, Sun Yat-sen University (Hainan Provincial Eye Hospital), Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology of Hainan Province, Haikou 570311, Hainan Province, China; 2Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital Affiliated to Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
纳米药物:药剂学中的纳米粒或称纳米药物,其尺寸界定于1-100 nm之间。纳米载体是指溶解或分散有药物的各种纳米粒。纳米药物是指直接将原料药加工成纳米粒。纳米药物涉及的给药途径包括口服、注射和眼部给药等。与传统药物相比,药物传输系统中的纳米粒及相关技术主要用于促进药物溶解,更容易通过血-视网膜屏障、血-脑屏障定向作用于视网膜及中枢神经,具有缓释性、靶向性,可提高药物疗效、减少不良反应等。
姜黄素:是从姜科、天南星科一些植物根茎中提取的一种二酮类化合物,为橙黄色结晶粉末,味稍苦,不溶于水,具有抗新生血管、抗炎、抗病毒、抗肿瘤、抗动脉粥样硬化等广泛的药理活性,且药源广泛、价格低廉、无明显毒副作用。
背景:姜黄素具有抑制人视网膜色素上皮细胞增殖及抗新生血管的作用,在防治眼底新生血管性病变中可以发挥重要作用,但其水溶性较差、体内半衰期短,需要长期、多次注射用药,因此研制姜黄素的新剂型具有重要临床意义。
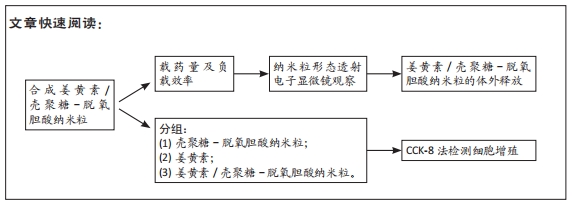
目的:探讨脱氧胆酸基接枝的壳聚糖衍生物负载姜黄素纳米粒的合成方法,以及其对人视网膜色素上皮细胞增殖的影响。
方法:首先制备壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒,随后制备姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒,检测姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒的载药量、负载效率及体外释药性能。将人视网膜色素上皮细胞分别与姜黄素(5,10,20,40 mg/L)、壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒(5,10,20,40 mg/L)、姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒(5,10,20,40 mg/L)共培养,采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖。
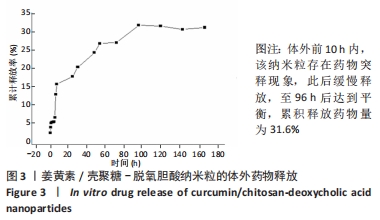
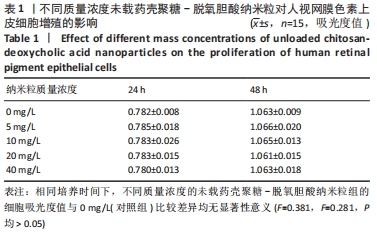
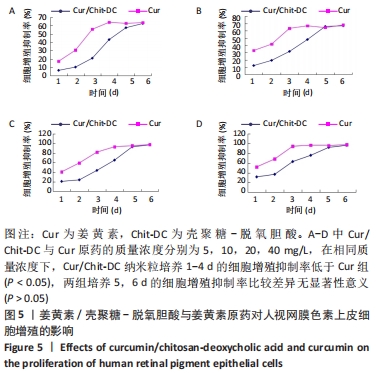
结果与结论:①姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒的载药量、负载效率分别为27.5%,55%,体外前10 h内,该纳米粒存在药物突释现象,此后缓慢释放,至96 h后达到平衡,累积释放药物量为31.6%;②培养24,48 h,不同质量浓度的壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒对人视网膜色素上皮细胞的增殖无明显影响;③不同质量浓度的姜黄素与姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒均可抑制人视网膜色素上皮细胞的增殖,且具有时间与浓度依赖性;在相同质量浓度下,姜黄素/壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒培养1-4 d的细胞增殖抑制率低于姜黄素组(P < 0.05),两组培养5,6 d的细胞增殖抑制率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④结果表明,载姜黄素壳聚糖-脱氧胆酸纳米粒对人视网膜色素上皮细胞具有抑制作用,并且该纳米粒没有降低姜黄素原药成分的生物学活性。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9867-9423 (郑海生)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: