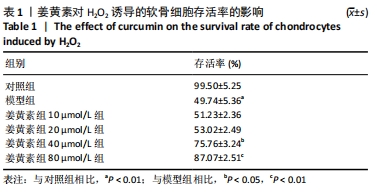
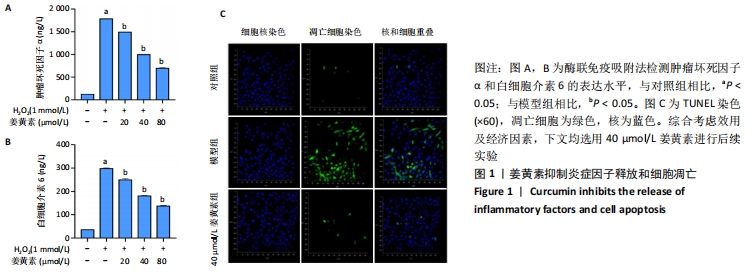
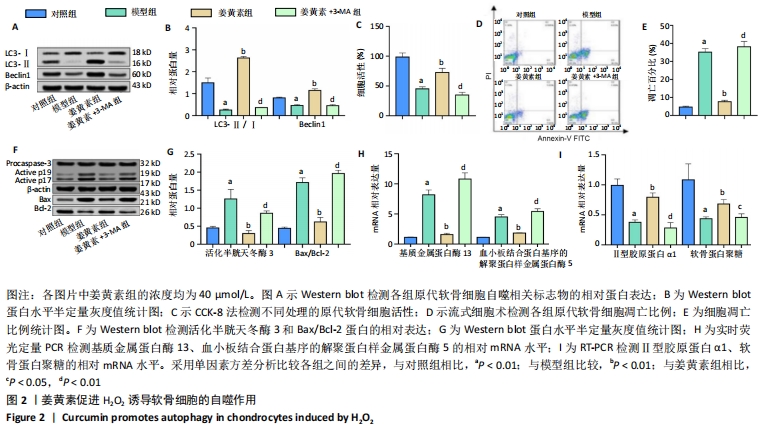
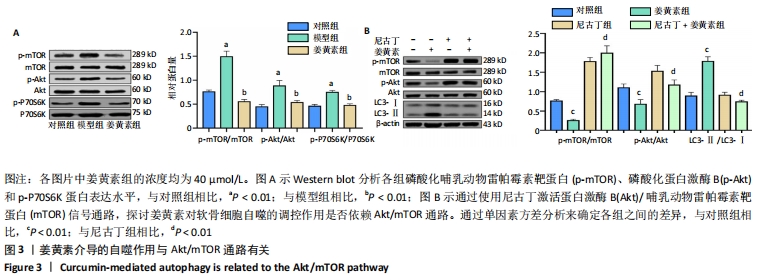
[1] KRAUS VB, KARSDAL MA. Osteoarthritis: current molecular biomarkers and the way forward. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020. doi: 10.1007/s00223-020-00701-7.
[2] PEARSON SH. Proactive wellness care for patients with osteoarthritis. Nurs Clin North Am. 2020;55:133-147.
[3] GUERRERO EM, BULLOCK GS, HELMKAMP JK, et al. The clinical impact of arthroscopic vs. open osteocapsular debridement for primary osteoarthritis of the elbow: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29:689-698.
[4] BILLESBERGER LM, FISHER KM, QADRI YJ, et al. Procedural treatments for knee osteoarthritis: a review of current injectable therapies. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:3873098.
[5] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30:160-167.
[6] MCALINDON TE, BANNURU RR, SULLIVAN MC, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22:363-388.
[7] EL KHOURY D, MATAR R, TOUMA T. Curcumin and endometrial carcinoma: an old spice as a novel agent. Int J Womens Health. 2019; 11:249-256.
[8] HAY E, LUCARIELLO A, CONTIERI M, et al. Therapeutic effects of turmeric in several diseases: An overview. Chem Biol Interact. 2019; 310:108729.
[9] HONG L, SUREDA A, DEVKOTA HP, et al. Curcumin, the golden spice in treating cardiovascular diseases. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;38:107343.
[10] SATHISH S, NICOLETTE H, HEIDI A. Therapeutic Potential and Recent Advances of Curcumin in the Treatment of Aging-Associated Diseases. Molecules. 2018;23(4):835.
[11] CLUTTERBUCK AL, ALLAWAY D, HARRIS P, et al. Curcumin reduces prostaglandin E2, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and proteoglycan release in the secretome of interleukin 1beta-treated articular cartilage. F1000Res. 2013;2:147.
[12] VILLAREJO-ZORI B, BOYA P. Autophagy and vision. Med Sci (Paris). 2017; 33:297-304.
[13] ZHANG B, HOU R, ZOU Z, et al. Mechanically induced autophagy is associated with ATP metabolism and cellular viability in osteocytes in vitro. Redox Biol. 2018;14:492-498.
[14] SACITHARAN PK, BOU-GHARIOS G, EDWARDS JR. SIRT1 directly activates autophagy in human chondrocytes. Cell Death Discov. 2020; 6:41.
[15] CASTROGIOVANNI P, RAVALLI S, MUSUMECI G. Apoptosis and Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. J Invest Surg. 2020; 33(9):874-875.
[16] BARRANCO C. Osteoarthritis: activate autophagy to prevent cartilage degeneration? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11:127.
[17] HUANG X, NI B, XI Y, et al. Protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR-2) antagonist AZ3451 as a novel therapeutic agent for osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11:12532-12545.
[18] HILIGSMANN M, COOPER C, ARDEN N, et al. Health economics in the field of osteoarthritis: an expert’s consensus paper from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2013;43:303-313.
[19] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862(4):576-591.
[20] CARAMES B, TANIGUCHI N, OTSUKI S, et al. Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:791-801.
[21] VINATIER C, DOMINGUEZ E, GUICHEUX J, et al. Role of the inflammation- autophagy-senescence integrative network in osteoarthritis. Front Physiol. 2018;9:706.
[22] AL-BARI M. A current view of molecular dissection in autophagy machinery. J Physiol Biochem. 2020;76(3):357-372.
[23] LI YS, ZHANG FJ, ZENG C, et al. Autophagy in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83:143-148.
[24] KIM J, KUNDU M, VIOLLET B, et al. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:132-141.
[25] CARAMES B, HASEGAWA A, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Autophagy activation by rapamycin reduces severity of experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:575-581.
|