中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (14): 2144-2149.doi: 10.12307/2022.474
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
转化生长因子β1及Ras同源基因家族成员A在软骨细胞分化过程中对细胞形态和细胞骨架的影响
陈宇婷1,贺飞明1,向 伟1,2,王 超1,2,曹薇薇1,王维山2,刘 伟1
- 1石河子大学医学院/新疆地方与民族高发病教育部重点实验室,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000;2石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨科中心,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000
Effects of transforming growth factor beta1 and Ras homolog gene family member A on cell morphology and cytoskeleton during chondrocyte differentiation
Chen Yuting1, He Feiming1, Xiang Wei1, 2, Wang Chao1, 2, Cao Weiwei1, Wang Weishan2, Liu Wei1
- 1Shihezi University School of Medicine/Laboratory of Xinjiang Endemic and Ethnic Diseases, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, Shihezi University School of Medicine, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:

文题释义:
转化生长因子β1:是来自转化生长因子β超家族中具有多种生物学功能的生长因子,可调节细胞生长、增殖和分化,参与骨组织基质中胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖的生成,保持软骨细胞处在未分化的状态,抑制其终末肥大,能够保护和修复关节软骨、抑制骨关节炎的发生。
骨关节炎:是一种在中老年人群中常见的退化性关节疾病,主要表现为关节软骨的退化、软骨下骨硬化及骨质增生。
背景:骨关节炎的重要病理变化是关节软骨的退变,转化生长因子β1和Ras同源基因家族成员A分别在维持关节软骨稳态和骨关节炎的发生发展中起重要作用。
目的:探讨转化生长因子β1、Ras同源基因家族成员A在软骨细胞分化过程中对细胞形态、骨架及相关因子表达的影响,以及转化生长因子β1与Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9之间的相互调控关系。
方法:外源性添加转化生长因子β1不同质量浓度、不同时间刺激ATDC5细胞,检测Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的蛋白表达情况;转化生长因子β1、LY-364947(一种有效的ATP竞争性转化生长因子β受体Ⅰ抑制剂)、溶血磷脂酸(Ras同源基因家族成员A激动剂)不同组合处理ATDC5细胞72 h,检测Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9、转化生长因子β的蛋白表达情况,并观察细胞形态、细胞骨架的变化情况。
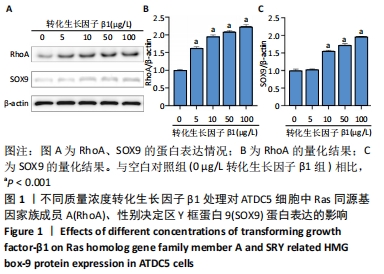
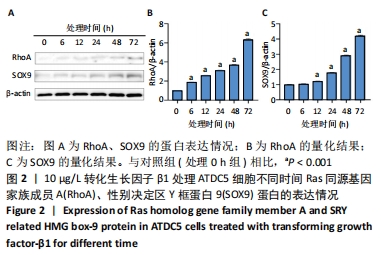
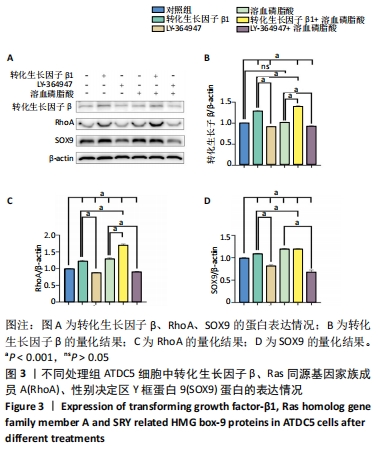
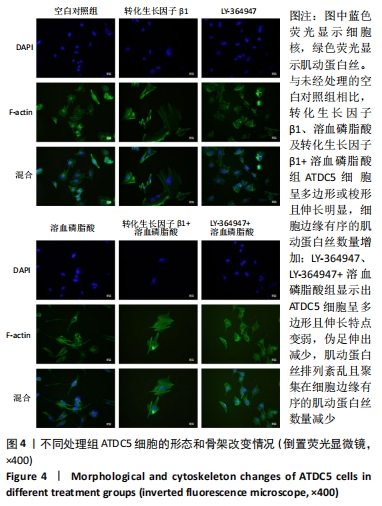
结果与结论:①随着转化生长因子β1作用质量浓度和时间的增加,Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9蛋白表达水平显著升高(P < 0.001);②相比空白对照组,溶血磷脂酸能够显著提高Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9蛋白表达水平(P < 0.001),但溶血磷脂酸对转化生长因子β的蛋白表达水平没有影响(P > 0.05),转化生长因子β1+溶血磷脂酸处理细胞使Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9和转化生长因子β的蛋白表达水平都显著升高(P < 0.001),LY-364947使Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.001),并且显著减弱了溶血磷脂酸对Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的激活作用(P < 0.001);③相比未经处理的空白对照组,转化生长因子β1、溶血磷脂酸、转化生长因子β1+溶血磷脂酸处理ATDC5细胞后,细胞形态伸长、胞内肌动蛋白丝排列更加有序,聚集在细胞边缘的肌动蛋白丝增多,LY-364947使细胞形态变为多边形,肌动蛋白丝排列紊乱,细胞边缘的肌动蛋白丝减少;LY-364947+溶血磷脂酸对细胞形态和骨架的改变情况与LY-364947处理组有类似的结果;④提示在ATDC5细胞中,转化生长因子β1对Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的蛋白表达水平有浓度剂量和时间叠加作用,转化生长因子β1可能是Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的上游因子,转化生长因子β1通过调控Ras同源基因家族成员A、性别决定区Y框蛋白9的表达调节细胞骨架的功能,进而参与调节骨关节炎的发生发展过程。
缩略语:性别决定区Y框蛋白9:SRY related HMG box-9,SOX-9;Ras同源基因家族成员A:Ras homolog gene family member A,RhoA
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9331-0654 (陈宇婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: