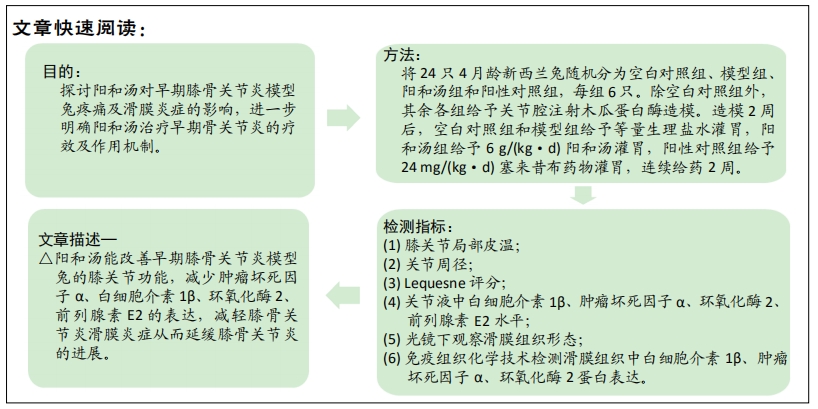
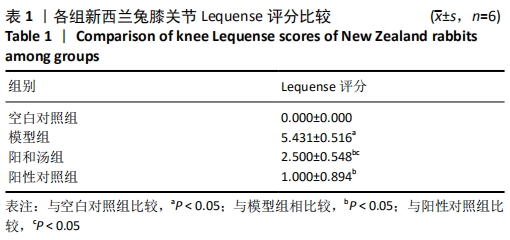
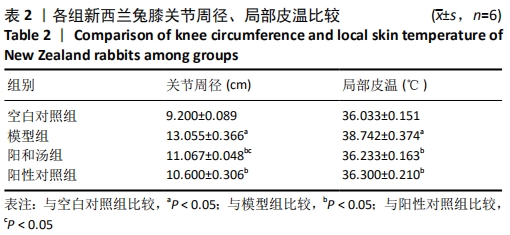
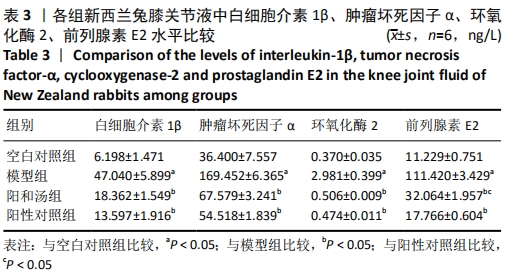
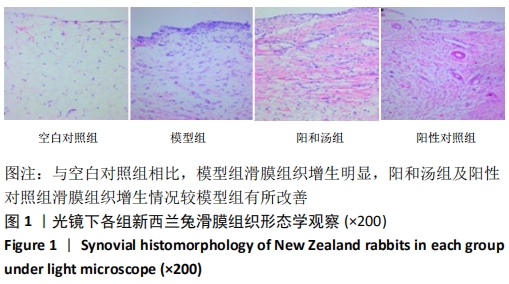
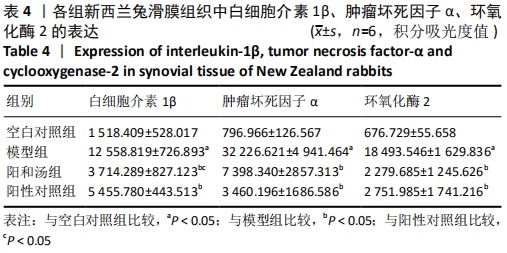
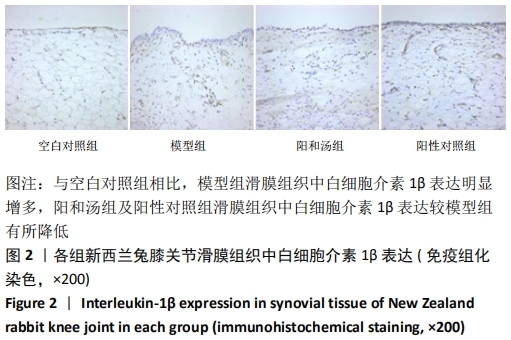
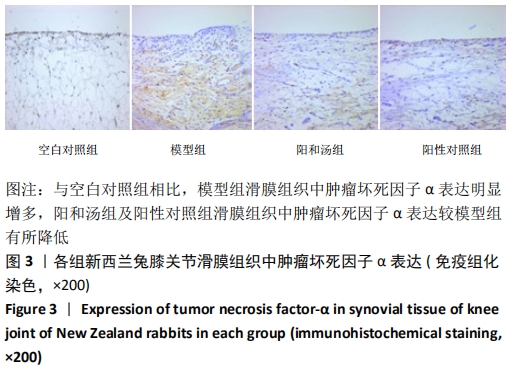
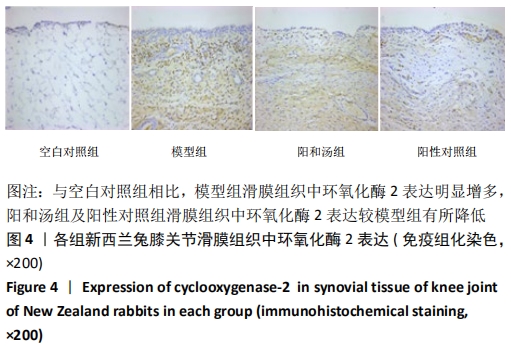
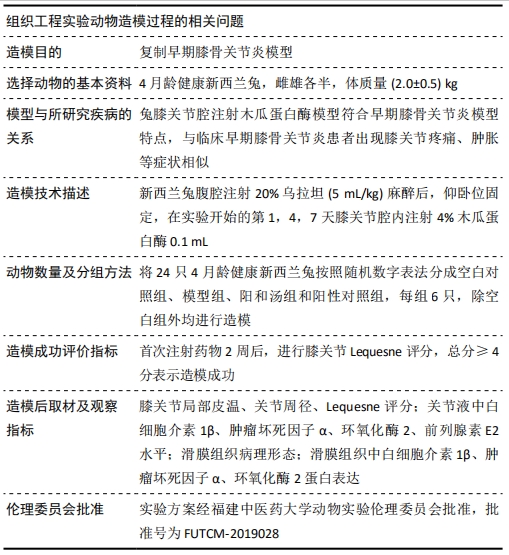
[1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[2] HILL CL, HUNTER DJ, NIU J, et al. Synovitis detected on magnetic resonance imaging and its relation to pain and cartilage loss in knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(12):1599-1603.
[3] STANNUS OP, JONES G, BLIZZARD L, et al. Associations between serum levels of inflammatory markers and change in knee pain over 5 years in older adults: a prospective cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):535-540.
[4] SOWERS M, KARVONEN-GUTIERREZ CA, JACOBSON JA, et al. Associations of anatomical measures from MRI with radiographically defined knee osteoarthritis score, pain, and physical functioning. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(3):241-251.
[5] CHEN B, ZHAN H, MARSZALEK J, et al. Traditional Chinese Medications for Knee Osteoarthritis Pain: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(4):677-703.
[6] 刘姗姗,王建国.阳和汤配合玻璃酸钠关节腔内注射治疗膝骨性关节炎40例[J].中国民间疗法,2015,23(9):69-70.
[7] 温莹莹,秦丹,宋美乐.阳和汤治疗关节痹痛临床疗效观察[J].中国实用医药,2016,11(29):201-202.
[8] 姜水现.阳和汤治疗痛痹80例[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2013, 11(15):19.
[9] 汤俊,吴文虎,倪卫祖.阳和汤治疗轻中度疼痛膝关节炎临床疗效探讨[J].中国现代药物应用,2014,8(11):149-150.
[10] 丑钢,王柯,张劲.阳和汤配合玻璃酸钠注射治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2015,17(6):94-95.
[11] 陈朝蔚,陈永强.阳和汤治疗兔膝骨性关节炎的作用机制[J].中医正骨,2008,20(4):11-12.
[12] 王文波,董建文,杨振国,等.加味阳和汤对早期膝骨关节炎兔关节软骨的影响[J].中医正骨,2015,27(1):1-4.
[13] 许波.阳和汤对兔膝骨关节炎模型IL-1、TNF-α含量影响的实验研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2016.
[14] 黄泽灵,何俊君,施珊妮,等.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨阳和汤对兔膝骨关节炎的影响[J].福建中医药,2020,51(3):60-63.
[15] 张康乐,郭珈宜,刘源,等.低浓度木瓜蛋白酶诱导兔早期膝骨关节炎滑膜炎症的时间曲线[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(36): 5787-5792.
[16] 何俊君,黄泽灵,洪振强,等.早期骨关节炎动物模型的建立与评价[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(4):358-360.
[17] KOPP S, MEJERSJÖ C, CLEMENSSON E. Induction of osteoarthrosis in the guinea pig knee by papain. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1983;55(3):259-266.
[18] 杨峰,史素道.用木瓜蛋白酶建立兔颞颌关节骨关节炎模型[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2002,12(5):330-333.
[19] LEQUESNE MG, SAMSON M. Indices of severity in osteoarthritis for weight bearing joints. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991;27:16-18.
[20] 黄继汗,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9):1069-1072.
[21] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.
[22] 井雨.北京地区膝骨关节炎的中医证候特征和用药规律研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2017.
[23] 梁杜,陈志冲,黄世良.膝骨性关节炎中医证型与炎症因子的关联性探讨[J].中医药导报,2017,23(12):69-71.
[24] 刘志豪,卢敏,肖学锋,等.长沙市膝关节骨性关节炎中医证型分布调查研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,18(8):39-42.
[25] 孙可.JKOM骨关节炎功能评估量表在中药熏蒸方治疗阳虚寒凝型膝痹病疗效评价中的应用[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(6):1482-1484.
[26] 柴爽.冬病夏治治疗膝骨关节炎阳虚寒凝证的临床疗效观察[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2016.
[27] 吴献毅,李盛华,叶丙霖,等.浅析扶阳气思想在膝骨关节炎治疗中的应用[J].中国中医急症,2017,26(12):2130-2132.
[28] 王桂彬.温阳益髓法治疗早期膝骨关节炎的临床疗效及对骨代谢指标的影响[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2020.
[29] 史鹏博,赵如意,赵利敬,等.膝骨关节炎疼痛机制研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2016,5(3):63-66.
[30] 刘小立.骨关节炎神经病理性疼痛诊疗概述[J].中国新药杂志, 2015,24(18):2073-2076.
[31] 张华伟,李皓桓,彭文飞,等.骨髓病变、关节积液和滑膜炎与膝骨关节炎疼痛的相关性[J].武大学学报(医学版),2014,35(3):418-421.
[32] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499.
[33] 王景红,夏坤,张志千,等.骨关节炎相关细胞因子及生物标志物的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(10):225-230.
[34] 袁发浒,胡松,黄丽霞,等.基于基因芯片的TNF-α诱导骨关节炎细胞模型生物信息学分析[J].中国比较医学杂志,2019,29(7):53-60.
[35] 何俊君,吴子健,洪振强.骨性关节炎致病因素的研究进展[J].中国中医药现代远程教育,2017,15 (10):149-152.
[36] MCCOY JM, WICKS JR, AUDOLY LP. The role of prostaglandin E2 receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(5):651-658. |