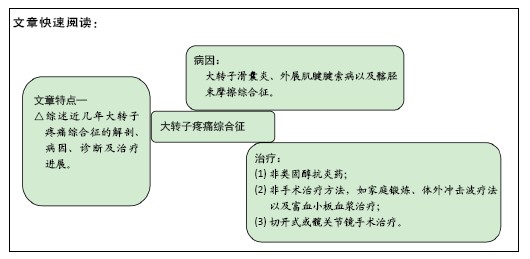
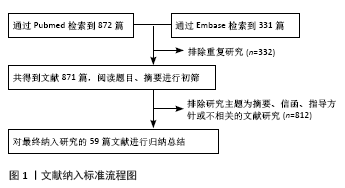
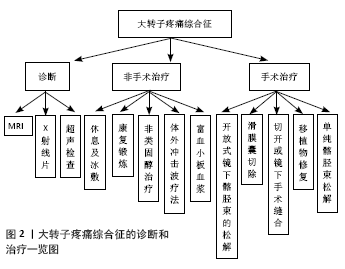
[1] REDMOND JM, CHEN AW, DOMB BG. Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(4):231-240.
[2] FEARON AM, SCARVELL JM, NEEMAN T, et al. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome: defining the clinical syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2013; 47(10):649-653.
[3] TORRES A, FERNÁNDEZ-FAIREN M, SUEIRO-FERNÁNDEZ J. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome and gluteus medius and minimus tendinosis: nonsurgical treatment. Pain Manag. 2018;8(1):45-55.
[4] MALLOW M, NAZARIAN LN. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome diagnosis and treatment. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2014;25(2): 279-289.
[5] REID D. The management of greater trochanteric pain syndrome: A systematic literature review. J Orthop. 2016;13(1):15-28.
[6] FEARON AM, COOK JL, SCARVELL JM, et al. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome negatively affects work, physical activity and quality of life: a case control study. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(2):383-386.
[7] BESOMI M, MACLACHLAN L, MELLOR R, et al. Tensor Fascia Latae Muscle Structure and Activation in Individuals With Lower Limb Musculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2020;50(5):965-985.
[8] ALLISON K, SALOMONI SE, BENNELL KL, et al. Hip abductor muscle activity during walking in individuals with gluteal tendinopathy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(2):686-695.
[9] DOMB BG, NASSER RM, BOTSER IB. Partial-thickness tears of the gluteus medius: rationale and technique for trans-tendinous endoscopic repair. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(12):1697-1705.
[10] FLACK NA, NICHOLSON HD, WOODLEY SJ. The anatomy of the hip abductor muscles. Clin Anat. 2014;27(2):241-53.
[11] PIERCE TP, ISSA K, KUROWICKI J, et al. Abductor Tendon Tears of the Hip. JBJS Rev. 2018;6(3):e6.
[12] Long SS, Surrey DE, Nazarian LN. Sonography of greater trochanteric pain syndrome and the rarity of primary bursitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(5):1083-1086.
[13] KENANIDIS E, KYRIAKOPOULOS G, KAILA R, et al. Lesions of the abductors in the hip. EFORT Open Rev. 2020;5(8):464-476.
[14] DUNDEVA-BALEVA P, ABDEL-MEGID A, BORHAM A, et al. Trochanteric bursitis: Is there ultrasonographic evidence to suggest inflammation? Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63:275(abstr).
[15] TORRES A, FERNÁNDEZ-FAIREN M, SUEIRO-FERNÁNDEZ J. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome and gluteus medius and minimus tendinosis: nonsurgical treatment. Pain Manag. 2018;8(1):45-55.
[16] REICH MS, SHANNON C, TSAI E, et al. Hip arthroscopy for extra-articular hip disease. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2013;6(3):250-257.
[17] STEINERT L, ZANETTI M, HODLER J, et al. Are radiographic trochanteric surface irregularities associated with abductor tendon abnormalities?. Radiology. 2010;257(3):754-763.
[18] VIRADIA NK, BERGER AA, DAHNERS LE. Relationship between width of greater trochanters and width of iliac wings in tronchanteric bursitis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2011;40(9):E159-E162.
[19] WESTACOTT DJ, MINNS JI, FOGUET P. The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography in gluteal tendon tears--a systematic review. Hip Int. 2011;21(6):637-645.
[20] BUREAU NJ. Sonographic evaluation of snapping hip syndrome. J Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(6):895-900.
[21] CONNELL DA, BASS C, SYKES CA, et al. Sonographic evaluation of gluteus medius and minimus tendinopathy. Eur Radiol. 2003;13(6):1339-1347.
[22] FEARON AM, SCARVELL JM, COOK JL, et al. Does ultrasound correlate with surgical or histologic findings in greater trochanteric pain syndrome? A pilot study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1838-1844.
[23] BLANKENBAKER DG, ULLRICK SR, DAVIS KW, et al. Correlation of MRI findings with clinical findings of trochanteric pain syndrome. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(10):903-909.
[24] CVITANIC O, HENZIE G, SKEZAS N, et al. MRI diagnosis of tears of the hip abductor tendons (gluteus medius and gluteus minimus). AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(1):137-143.
[25] SUTTER R, KALBERER F, BINKERT CA, et al. Abductor tendon tears are associated with hypertrophy of the tensor fasciae latae muscle. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42(5):627-633.
[26] TORRES A, FERNÁNDEZ-FAIREN M, SUEIRO-FERNÁNDEZ J. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome and gluteus medius and minimus tendinosis: nonsurgical treatment. Pain Manag. 2018;8(1):45-55.
[27] LUSTENBERGER DP, NG VY, BEST TM, et al. Efficacy of treatment of trochanteric bursitis: a systematic review. Clin J Sport Med. 2011;21(5): 447-453.
[28] KORAKAKIS V, WHITELEY R. The Effectiveness of ESWT in Lower Limb Tendinopathy: Letter to the Editor. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(10): NP43-NP44.
[29] ROMPE JD, SEGAL NA, CACCHIO A, et al. Home training, local corticosteroid injection, or radial shock wave therapy for greater trochanter pain syndrome. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(10):1981-1990.
[30] LEE JJ, HARRISON JR, BOACHIE-ADJEI K, et al. Platelet-rich plasma injections with needle tenotomy for gluteus medius tendinopathy: A registry study with prospective followup. Orthop J Sports Med. 2016;4: 2325967116671692.
[31] FITZPATRICK J, BULSARA MK, O’DONNELL J, et al. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections in Gluteal Tendinopathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind Controlled Trial Comparing a Single Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection With a Single Corticosteroid Injection. Am J Sports Med. 2018; 46(4):933-939.
[32] ALI M, ODERUTH E, ATCHIA I, et al. The use of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of greater trochanteric pain syndrome: a systematic literature review. J Hip Preserv Surg. 2018;5(3):209-219.
[33] KORAKAKIS V, WHITELEY R, TZAVARA A, et al. The effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in common lower limb conditions: a systematic review including quantification of patient-rated pain reduction. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(6):387-407.
[34] MAUTNER K, COLBERG RE, MALANGA G, et al. Outcomes after ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for chronic tendinopathy: a multicenter, retrospective review. PM R. 2013;5(3): 169-175.
[35] FILARDO G, DI MATTEO B, KON E, et al. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: results and indications. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(7):1984-1999.
[36] WALKER-SANTIAGO R, WOJNOWSKI NM, LALL AC, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Surgery for the Management of Recalcitrant Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy. 2020; 36(3):875-888.
[37] BAKER CL JR, MASSIE RV, HURT WG, et al. Arthroscopic bursectomy for recalcitrant trochanteric bursitis. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(8):827-832.
[38] GOVAERT LH, VAN DIJK CN, ZEEGERS AV, et al. Endoscopic bursectomy and iliotibial tract release as a treatment for refractory greater trochanteric pain syndrome: a new endoscopic approach with early results. Arthrosc Tech. 2012;1(2):e161-e164.
[39] BROOKER AF JR. The surgical approach to refractory trochanteric bursitis.Johns Hopkins Med J. 1979;145(3):98-100.
[40] GOVAERT LH, VAN DER VIS HM, MARTI RK, et al. Trochanteric reduction osteotomy as a treatment for refractory trochanteric bursitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(2):199-203.
[41] FOX JL. The role of arthroscopic bursectomy in the treatment of trochanteric bursitis. Arthroscopy. 2002;18(7):E34.
[42] BAKER CL JR, MASSIE RV, HURT WG, et al. Arthroscopic bursectomy for recalcitrant trochanteric bursitis. Arthroscopy. 2007;23(8):827-832.
[43] HARTIGAN DE, PERETS I, HO SW, et al.Endoscopic repair of partial-thickness undersurface tears of the abductor tendon: Clinical outcomes with minimum 2 year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2018;34:1193-1199.
[44] WALSH MJ, WALTON JR, WALSH NA. Surgical repair of the gluteal tendons: a report of 72 cases. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1514-1519.
[45] RAO BM, KAMAL TT, VAFAYE J, et al. Surgical repair of hip abductors. A new technique using Graft Jacket allograft acellular human dermal matrix. Int Orthop. 2012;36(10):2049-2053.
[46] DAVIES JF, STIEHL JB, DAVIES JA, et al. Surgical treatment of hip abductor tendon tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(15):1420-1425.
[47] MCCORMICK F, ALPAUGH K, NWACHUKWU BU, et al. Endoscopic repair of full-thickness abductor tendon tears: surgical technique and outcome at minimum of 1-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29(12):1941-1947.
[48] DOMB BG, BOTSER I, GIORDANO BD. Outcomes of endoscopic gluteus medius repair with minimum 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(5):988-997.
[49] COULOMB R, ESSIG J, MARES O, et al. Clinical results of endoscopic treatment without repair for partial thickness gluteal tears. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(3):391-395.
[50] THAUNAT M, CHATELLARD R, NOËL E, et al. Endoscopic repair of partial-thickness undersurface tears of the gluteus medius tendon. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):853-857.
[51] HARTIGAN DE, MANSOR Y, PERETS I, et al. Knotless “Suture Staple” Technique for Endoscopic Partial Thickness Abductor Tendon Repair. Arthrosc Tech. 2018;7(10):e975-e980.
[52] EBERT JR, BUCHER TA, MULLAN CJ, et al. Clinical and functional outcomes after augmented hip abductor tendon repair. Hip Int. 2018; 28(1):74-83.
[53] BUCHER TA, DARCY P, EBERT JR, et al. Gluteal tendon repair augmented with a synthetic ligament: surgical technique and a case series. Hip Int. 2014;24(2):187-193.
[54] FINK B, BRAUN L.Treatment of Extensive Gluteus Muscle Tears With Transosseous Fixation and a Nonresorbable Collagen Patch. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):555-559.
[55] FEHM MN, HUDDLESTON JI, BURKE DW, et al. Repair of a deficient abductor mechanism with Achilles tendon allograft after total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(13):2305-2311.
[56] BETZ M, ZINGG PO, PEIRRMANN CW, et al. Advancement of the vastus lateralis muscle for irreparable hip abductor tears: clinical and morphological results. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012;78(3):337-343.
[57] WHITESIDE LA. Surgical technique: Transfer of the anterior portion of the gluteus maximus muscle for abductor deficiency of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(2):503-510.
[58] ILIZALITURRI VM JR, MARTINEZ-ESCALANTE FA, CHAIDEZ PA, et al. Endoscopic iliotibial band release for external snapping hip syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(5):505-510.
[59] PROVENCHER MT, HOFMEISTER EP, MULDOON MP. The surgical treatment of external coxa saltans (the snapping hip) by Z-plasty of the iliotibial band. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(2):470-476. |