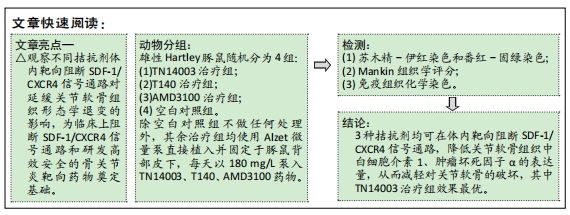
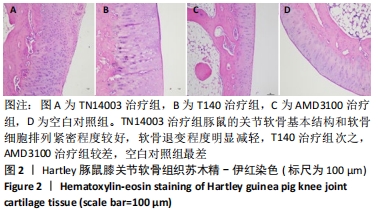
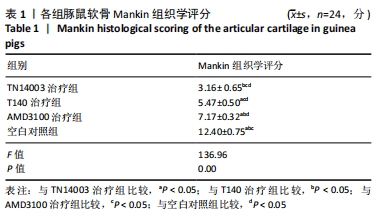
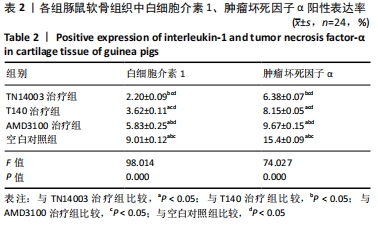
[1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[2] JAMSHIDI A, PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J. Machine-learning-based patient-specific prediction models for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(1):49-60.
[3] 马珂,李晓林,李彦林,等.T140体外阻断SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路阻止人关节软骨Ⅱ型胶原蛋白降解的研究[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(12):1879-1882.
[4] 蒙旭晗.三种拮抗剂体内靶向阻断SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路调控关节软骨退变的研究[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2018.
[5] 李彦林,王国梁,曹斌,等.体外阻断基质细胞衍生因子1/CXC趋化因子受体4信号通路后人关节软骨组织Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(46):8607-8610.
[6] 赵沣凯.T140靶向阻断SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路调节关节软骨退变的实验研究[J].昆明:昆明医科大学,2014.
[7] 李建,李彦林,王鑫,等. AMD3100体内干预SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对关节软骨组织退变的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(1):37-41.
[8] JIA D, LI Y, HAN R, et al. miR‑146a‑5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4 antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF‑1‑induced cartilage degradation. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(5):4388-4400.
[9] SAKYIAMAH MM, KOBAYAKAWA T, FUJINO M, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of low molecular weight CXCR4 ligands. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019;27(6):1130-1138.
[10] WANG J, TANNOUS BA, POZNANSKY MC, et al. CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 (plerixafor): From an impurity to a therapeutic agent. Pharmacol Res. 2020;159: 105010.
[11] LI SH, DONG WC, FAN L, et al. Suppression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression by CXCR4 inhibitor WZ811. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(9):3812-3821.
[12] PAGANESSI LA, WALKER AL, TAN LL, et al. Effective mobilization of hematopoietic progenitor cells in G-CSF mobilization defective CD26-/- mice through AMD3100-induced disruption of the CXCL12-CXCR4 axis. Exp Hematol. 2011;39(3):384-390.
[13] RIOS A, HSU SH, BLANCO A, et al. Durable response of glioblastoma to adjuvant therapy consisting of temozolomide and a weekly dose of AMD3100 (plerixafor), a CXCR4 inhibitor, together with lapatinib, metformin and niacinamide. Oncoscience. 2016;3(5-6):156-163.
[14] CHEN Y, LIN S, SUN Y, et al. Attenuation of subchondral bone abnormal changes in osteoarthritis by inhibition of SDF-1 signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017; 25(6):986-994.
[15] QIN HJ, XU T, WU HT, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis coordinates crosstalk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2019;125:140-150.
[16] WEI F, MOORE DC, WEI L, et al. Attenuation of osteoarthritis via blockade of the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(4):R177.
[17] LI P, DENG J, WEI X, et al. Blockade of hypoxia-induced CXCR4 with AMD3100 inhibits production of OA-associated catabolic mediators IL-1β and MMP-13. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1475-1482.
[18] GALIL SM, EL-SHAFEY AM, HAGRASS HA, et al. Baseline serum level of matrix metalloproteinase-3 as a biomarker of progressive joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(4):377-384.
[19] MISHRA RK, SHUM AK, PLATANIAS LC, et al. Discovery and characterization of novel small-molecule CXCR4 receptor agonists and antagonists. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30155.
[20] BERNING P, SCHAEFER C, CLEMENS D, et al. The CXCR4 antagonist plerixafor (AMD3100) promotes proliferation of Ewing sarcoma cell lines in vitro and activates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Cell Commun Signal. 2018;16(1):21.
[21] MONA CE, BESSERER-OFFROY É, CABANA J, et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of CXCR4 ligands. Org Biomol Chem. 2016;14(43):10298-10311.
[22] WANG K, LI Y, HAN R, et al. T140 blocks the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway and prevents cartilage degeneration in an osteoarthritis disease model. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0176048.
[23] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI ŁA, SZUKIEWICZ D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:561459.
[24] ZENG L, RONG XF, LI RH, et al. Icariin inhibits MMP‑1, MMP‑3 and MMP‑13 expression through MAPK pathways in IL‑1β‑stimulated SW1353 chondrosarcoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(5):2853-2858.
[25] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734.
[26] WANG MN, LIU L, ZHAO LP, et al. Research of inflammatory factors and signaling pathways in knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2020;33(4):388-392.
|