[1] NOORI A, ASHRAFI SJ, VAEZ-GHAEMI R, et al. A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:4937-4961.
[2] 官晨雨,侯世达,周洋,等.磁性四氧化三铁纳米颗粒作用于前成骨细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(38):5684-5690.
[3] LAURENT S, FORGE D, PORT M, et al. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem Rev. 2008;108(6): 2064-2110.
[4] ASSA F, JAFARIZADEH-MALMIRI H, AJAMEIN H, et al. Chitosan magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery systems. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017;37(4):492-509.
[5] YU P, ZHENG L, WANG P, et al. Development of a novel polysaccharide-based iron oxide nanoparticle to prevent iron accumulation-related osteoporosis by scavenging reactive oxygen species. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt B):1634-1645.
[6] LIU Y, AI K, LU L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem Rev. 2014;114(9):5057-5115.
[7] HUANG Z, HE Y, CHANG X, et al. A Magnetic Iron Oxide/Polydopamine Coating Can Improve Osteogenesis of 3D-Printed Porous Titanium Scaffolds with a Static Magnetic Field by Upregulating the TGFβ-Smads Pathway. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(14):e2000318.
[8] DUAN L, ZUO J, ZHANG F, et al. Magnetic Targeting of HU-MSCs in the Treatment of Glucocorticoid-Associated Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Through Akt/Bcl2/Bad/Caspase-3 Pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:3605-3620.
[9] MONTASER AS, REHAN M, EL-NAGGAR ME. pH-Thermosensitive hydrogel based on polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/N-isopropyl acrylamide composite for treating re-infected wounds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;124:1016-1024.
[10] AFSANA, JAIN V, HAIDER N, JAIN K. 3D Printing in Personalized Drug Delivery. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(42):5062-5071.
[11] LAZARATOS M, KARATHANOU K, MAINAS E, et al. Coating of magnetic nanoparticles affects their interactions with model cell membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020;1864(11):129671.
[12] SCHULZE F, GRAMOUN A, CROWE LA, et al. Accumulation of amino-polyvinyl alcohol-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in bone marrow: implications for local stromal cells. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(14):2139-2151.
[13] KONG L, CAMPBELL F, KROS A. DePEGylation strategies to increase cancer nanomedicine efficacy. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019;4(2):378-387.
[14] BLACHE U, METZGER S, VALLMAJO-MARTIN Q, et al. Dual Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Allows for Microvascularized Bone Tissue-Like Environments in PEG Hydrogels. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(4):489-498.
[15] FILIPPI M, DASEN B, GUERRERO J, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels and static magnetic field stimulate the osteoblastic and vasculogenic profile of adipose-derived cells. Biomaterials. 2019;223: 119468.
[16] FRAZER RQ, BYRON RT, OSBORNE PB, et al. PMMA: an essential material in medicine and dentistry. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005;15(6):629-639.
[17] LI Z, KAWAMURA K, KAWASHITA M, et al. In vitro assessment of poly(methylmethacrylate)-based bone cement containing magnetite nanoparticles for hyperthermia treatment of bone tumor. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(10):2537-2545.
[18] YU K, LIANG B, ZHENG Y, et al. PMMA-Fe3O4 for internal mechanical support and magnetic thermal ablation of bone tumors. Theranostics. 2019;9(14):4192-4207.
[19] REDDY AM, KWAK BK, SHIM HJ, et al. Functional characterization of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with a novel PVP-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2009;4(3):118-126.
[20] DOMINGUES RM, GOMES ME, REIS RL. The potential of cellulose nanocrystals in tissue engineering strategies. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(7):2327-2346.
[21] KIM M, JEE SC, SUNG JS, et al. Supermagnetic Sugarcane Bagasse Hydrochar for Enhanced Osteoconduction in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(9): 1793.
[22] RANGANATHAN S, BALAGANGADHARAN K, SELVAMURUGAN N. Chitosan and gelatin-based electrospun fibers for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;133:354-364.
[23] SHI SF, JIA JF, GUO XK, et al. Biocompatibility of chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles with osteoblast cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5593-5602.
[24] NEHRA P, CHAUHAN RP, GARG N, et al. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of chitosan coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Br J Biomed Sci. 2018;75(1):13-18.
[25] RABEL AM, NAMASIVAYAM SKR, PRASANNA M, et al. A green chemistry to produce iron oxide - Chitosan nanocomposite (CS-IONC) for the upgraded bio-restorative and pharmacotherapeutic activities - Supra molecular nanoformulation against drug-resistant pathogens and malignant growth. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;138:1109-1129.
[26] BHARATHI D, RANJITHKUMAR R, VASANTHARAJ S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/iron oxide nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;132:880-887.
[27] 杨滨羽,罗霞,刘佳伶,等.葡聚糖包裹超顺磁性氧化铁纳米材料用于关节软骨磁共振T_2-Map成像研究[J].生物医学工程研究, 2020,39(1):36-40.
[28] ZHU N, JI H, YU P, et al. Surface Modification of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018;8(10):810.
[29] HAO L, LI L, WANG P, et al. Synergistic osteogenesis promoted by magnetically actuated nano-mechanical stimuli. Nanoscale. 2019; 11(48):23423-23437.
[30] SHELAT R, BHATT LK, PAUNIPAGAR B, et al. Regeneration of hyaline cartilage in osteochondral lesion model using L-lysine magnetic nanoparticles labeled mesenchymal stem cells and their in vivo imaging. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(11):1604-1617.
[31] WANG Y, WANG Y, WANG L, et al. Preparation and evaluation of magnetic nanoparticles for cell labeling. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(5):3749-3756.
[32] SILVA LH, DA SILVA JR, FERREIRA GA, et al. Labeling mesenchymal cells with DMSA-coated gold and iron oxide nanoparticles: assessment of biocompatibility and potential applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016;14(1):59.
[33] SHI M, ZHOU Y, SHAO J, et al. Stimulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis of hBMSCs by delivering Si ions and functional drug from mesoporous silica nanospheres. Acta Biomater. 2015;21:178-189.
[34] JIA Y, ZHANG P, SUN Y, et al. Regeneration of large bone defects using mesoporous silica coated magnetic nanoparticles during distraction osteogenesis. Nanomedicine. 2019;21:102040.
[35] LEE DH, KANG M, LEE HJ, et al. Enhanced Cellular Uptake of Silica-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles Compared with PEG-Coated Ones in Stem Cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(8):5512-5519.
[36] MITRAGOTRI S, LAHANN J. Physical approaches to biomaterial design. Nat Mater. 2009;8(1):15-23.
[37] WANG HH, WANG YX, LEUNG KC, et al. Durable mesenchymal stem cell labelling by using polyhedral superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chemistry. 2009;15(45):12417-12425.
[38] YAO D, LIU NN, MO BW. Assessment of proliferation, migration and differentiation potentials of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells labeling with silica-coated and amine-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Cytotechnology. 2020;72(4):513-525.
[39] DAY RM. Bioactive glass stimulates the secretion of angiogenic growth factors and angiogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(5-6):768-777.
[40] SINGH S, SINGH G, BALA N, et al. Characterization and preparation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded bioglass-chitosan nanocomposite coating on Mg alloy and in vitro bioactivity assessment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:519-528.
[41] KESSE X, ADAM A, BEGIN-COLIN S, et al. Elaboration of Superparamagnetic and Bioactive Multicore-Shell Nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3@SiO2-CaO): A Promising Material for Bone Cancer Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(42):47820-47830.
[42] ŚWIĘTEK M, BROŽ A, TARASIUK J, et al. Carbon nanotube/iron oxide hybrid particles and their PCL-based 3D composites for potential bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109913.
[43] VALVERDE TM, CASTRO EG, CARDOSO MH, et al. A novel 3D bone-mimetic scaffold composed of collagen/MTA/MWCNT modulates cell migration and osteogenesis. Life Sci. 2016;162:115-124.
[44] SABER-SAMANDARI S, MOHAMMADI-AGHDAM M, SABER-SAMANDARI S. A novel magnetic bifunctional nanocomposite scaffold for photothermal therapy and tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;138:810-818.
[45] XIA Y, GUO Y, YANG Z, et al. Iron oxide nanoparticle-calcium phosphate cement enhanced the osteogenic activities of stem cells through WNT/β-catenin signaling. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109955.
[46] TRAN N, WEBSTER TJ. Increased osteoblast functions in the presence of hydroxyapatite-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(3):1298-1306.
[47] KAMITAKAHARA M, OHTOSHI N, KAWASHITA M, et al. Spherical porous hydroxyapatite granules containing composites of magnetic and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for the hyperthermia treatment of bone tumor. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(5):93.
[48] YI C, LIU D, FONG CC, et al. Gold nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through p38 MAPK pathway. ACS Nano. 2010;4(11):6439-6448.
[49] YUAN M, WANG Y, QIN YX. SPIO-Au core-shell nanoparticles for promoting osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells: Concentration-dependence study. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017; 105(12):3350-3359.
[50] LI Z, DU T, RUAN C, et al. Bioinspired mineralized collagen scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(5):1491-1511.
[51] ZHUANG J, LIN S, DONG L, et al. Magnetically actuated mechanical stimuli on Fe3O4/mineralized collagen coatings to enhance osteogenic differentiation of the MC3T3-E1 cells. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:49-60.
|
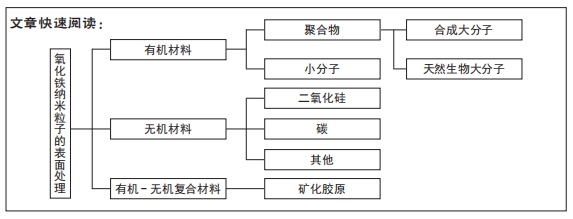

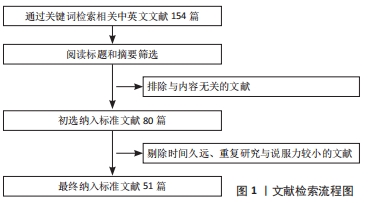
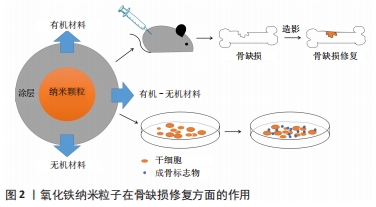 不同的材料进行汇总,见表1。
不同的材料进行汇总,见表1。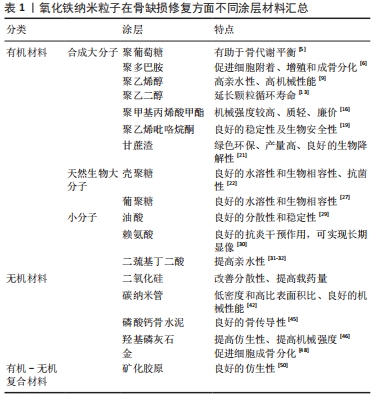 综上,无论是何种材料进行表面修饰,骨缺损修复时,纳米粒子基本都达到了以下几种要求:①具备良好的生物相容性和较低的毒性;②需要降低纳米粒子间的团聚,提高分散性;③可促进细胞的黏附,促进细胞成骨向分化与增殖;④尽量提高载药量并达到良好的缓释效果;⑤可以对细胞进行标记跟踪,从而能够利用影像学对治疗效果进行评估。通过表面处理的方式能够改善氧化铁纳米粒子的分散性、生物相容性、理化性能等。磁性纳米粒子为骨缺损修复提供了一个新思路,尽管氧化铁纳米粒子的表面处理已经取得了一定的突破,但如何控制纳米粒子的尺寸、增加其稳定性仍需进一步探索;此外在外加磁场的环境下,纳米粒子与细胞间的生物学机制还需更多的实验来研究和验证,为更好地应用于临床奠定坚实的理论基础。
综上,无论是何种材料进行表面修饰,骨缺损修复时,纳米粒子基本都达到了以下几种要求:①具备良好的生物相容性和较低的毒性;②需要降低纳米粒子间的团聚,提高分散性;③可促进细胞的黏附,促进细胞成骨向分化与增殖;④尽量提高载药量并达到良好的缓释效果;⑤可以对细胞进行标记跟踪,从而能够利用影像学对治疗效果进行评估。通过表面处理的方式能够改善氧化铁纳米粒子的分散性、生物相容性、理化性能等。磁性纳米粒子为骨缺损修复提供了一个新思路,尽管氧化铁纳米粒子的表面处理已经取得了一定的突破,但如何控制纳米粒子的尺寸、增加其稳定性仍需进一步探索;此外在外加磁场的环境下,纳米粒子与细胞间的生物学机制还需更多的实验来研究和验证,为更好地应用于临床奠定坚实的理论基础。