2.1 m6A甲基化修饰概述 在表观遗传学研究中,已鉴定出超过150种发生在mRNA上的化学修饰,其中m6A是真核生物mRNA中最常见、含量最丰富的一种动态可逆的甲基化修饰,广泛参与RNA的生物合成和功能调节[7-8]。m6A修饰通常发生于包含RRACH的保守RNA基序中(R?表示?G、A;H?表示?A、C或U),并富集于长外显子、近终止密码子和3'非翻译区(3' UTRs),提示m6A修饰时的序列分布具有特殊性及稳定性[9]。具体来讲,m6A修饰的发生通常有如下过程:首先由归为写入器(writers)的甲基转移酶样3(methyltransferase
like 3,METTL3)、甲基转移酶样14(methyltransferase Like 14,METTL14)和Wilms 肿瘤相关蛋白(Wilms tumor associated
protein,WTAP)等使RNA修饰位点上的腺苷酸第6位N发生甲基化;接下来由擦除器(erasers)如脂肪量及肥胖相关蛋白(fat mass and obesity associated protein,FTO)和α-酮戊二酸依赖性双加氧酶同源蛋白5(α-ketoglutarate-dependent
dioxygenase alkB homolog 5,ALKBH5)等去除已经发生m6A
修饰的甲基;最后再由读取器(Readers)如YTHDC1、YTHDF1、
YTHDF2等识别m6A修饰的碱基位点,从而参与mRNA的下游翻译、剪切、表达与降解等生物学功能[6,10-11]。
2.1.1 写入器(Writers)——甲基转移酶类 为了更好地理解m6A甲基转移酶复合物的生物学结构,研究发现甲基转移酶结构域中METTL3和METTL14彼此紧密相连[12],形成腺嘌呤的催化中心,但是仅由METTL3提供催化活性,这可能由于丝氨酸等磷酸化位点均位于METTL3上,它们是蛋白质相互作用和定位所必须的[13],这预示在m6A甲基化修饰作用中METTL3可能起着主导作用,而METTL14则为METTL3
在活性位点附近提供支持结构促进催化完成[12]。WTAP作为另外一种甲基转移复合酶,主要在m6A修饰中起定位作用,敲除WTAP后,METTL3与RNA的结合能力明显下降,这提示WTAP具有募集甲基转移酶复合物与mRNA特定靶点结合的作用[14]。而且无论是敲低还是过度表达METTL3
后,WTAP表达均会上调,表明METTL3水平对WTAP蛋白酶的稳定性至关重要[15]。由此看来,“METTL3-METTL14-WTAP”复合物在m6A甲基化修饰过程中相互定位、稳定和发挥作用,在研究设计中应主次分明而兼顾内外[12,16]。
2.1.2 擦除器(Erasers)——去甲基转移酶类 在去甲基转移酶类中, ALKB基因早在20世纪70年代就被发现,并显示其具有免受因甲基化修饰而损伤DNA的作用,随着后续研究的深入,具有序列同源性的ALKBH1-8和FTO也受到关注。m6A作为一种在mRNA上的甲基化修饰,首先ALKBH8含有RNA识别序列结构域及ALKB结构域,可靶向5-甲氧基羰基甲基尿苷的tRNA羟化酶,从而发挥剪切和稳定mRNA的作用[17]。此外,ALKBH5作为另外一种哺乳动物羟化酶,能与FTO一起影响mRNA的下游翻译进程。也就是说,ALKBH8、ALKBH5和FTO是哺乳动物mRNA甲基化修饰时去甲基转移酶中的主要角色,在生殖、免疫炎症、肿瘤等方面受到深入探索和研究[18-19]。
2.1.3 读取器(Readers)——YTH结构域蛋白酶及其他酶类 在人类的基因组学中,已发现的YTH结构域蛋白主要有5种:YTHDF1-3、YTHDC1-2。根据他们的序列和结构分析大体分为3类:YTHDC1(DC1)、YTHDC2(DC2家族)和YTHDF1-3(DF家族),它们通过招募不同的复合体聚集于m6A识别位点上,以完成基因调控转录后的多个过程,其中DC1介导了甲基化修饰中mRNA的出核过程,这主要与mRNA剪切因子和出核衔接蛋白SRSF3的相互作用有关[20],DC2蛋白家族作为m6A的另外一种读取器,主要包含3种结构域:YTH结构域、锚蛋白结构域和解螺旋酶结构域[21],参与动物的生殖繁育功能[22],
DF家族是存在于细胞质中的蛋白,其过表达可抑制人类免疫缺陷病毒(HIV)的反转录表达,具有较大发展前景[23],
其他m6A读取器如真核起始因子3(eIF3)、真核起始因子4(eIF4)等也陆续被发现,参与mRNA翻译过程[24]。
2.2 m6A在骨髓间充质干细胞分化过程中的作用
2.2.1 m6A在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化中的研究 作为一种高度保守的蛋白,METTL3是甲基转移酶的核心亚基,也是骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化的主要催化酶,在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中起正性调控作用。通过检测经成骨诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞中的甲基转移酶(METTL3、
METTL14)及去甲基转移酶(FTO、ALKBH5)表达,研究人员发现METTL3上调较多,并且在敲低METTL3表达后,骨形成相关基因如Runx2和Osterix均降低,骨相关碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化结节形成也相应降低[25-26]。YAN等[27]最新研究已证明pre-miR-320(miRNA为单链小编码RNA的一种,pre-miRNA
为miRNA未剪切前体)是骨髓间充质干细胞中METTL3的靶标,抑制METTL3可使骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-320表达水平显著上升,从而影响下游靶基因Runx2的表达。类似地一项研究也证实来自骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体包裹的miR-22-3p
可通过抑制FTO表达来促进成骨分化,其靶向成骨相关基因Runx2、OCN及OPN [28]。这些从细胞分子水平的研究证实了在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化中METTL3起一定的主导作用,并与成骨相关基因的表达息息相关。
2.2.2 m6A在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化中的研究 去甲基转移酶FTO的早期研究多集中于与脂肪形成相关,但其实在骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化中,存在一个骨动态平衡概念,若细胞向成脂分化加强,则可引起骨质疏松等疾病的发生,因此在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化过程中m6A亦得到研究人员的关注。LI等[29]研究显示抑制miR-149-3p的表达会促进靶向FTO mRNA的3’UTR结合从而增加了脂肪量和肥胖相关基因的表达,这是通过靶向下游成脂相关基因CEBPA、
CEBPB、CEBPD、FABP4及PPARG的表达完成的,促进了骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化。研究表明,与促骨质疏松相关的生长分化因子11会靶向FTO的表达[25],调控下游靶基因过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma,Pparg γ)的mRNA并使其去甲基化,从而导致Pparg γ mRNA表达增加,促进骨髓间充质干细胞分化为脂肪细胞。上述研究提示在骨相关疾病发生过程中,FTO过表达能促进骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化,成骨分化的相对不足使得骨平衡环境被打破,加速骨相关疾病的发生发展。具有争议的是,尽管FTO在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化中起正向调控作用,但对于正常的骨骼生长和矿化,FTO却是不可或缺的,有研究显示FTO能靶向Hspa1a基因的表达,间接保护骨髓间充质干细胞免受消极遗传修饰的影响,维持正常骨骼的生长和矿化[30-31]。因此,如何恰当利用FTO的功能修饰骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化尚需进一步探索。
在读取器中,YTH结构蛋白酶也与骨髓间充质干细胞成脂向分化相关。YAO等[32]敲低骨髓间充质干细胞中METTL3
表达后发现JAK1的m6A mRNA水平降低,导致依赖性
YTHDF2的JAK1 mRNA稳定性增强,提示METTL3与YTHDF2在骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化中具有相互作用。事实上,m6A的修饰通常需要多种酶的参与,它们之间起协同或抑制作用对骨髓间充质干细胞的分化进程产生影响,从而参与骨代谢平衡。YU等[10]研究显示去甲基转移酶ALKBH5能动态逆转 METTL3的功能。也就是说,m6A甲基化修饰酶之间亦存在相互积极或消极影响,从而改变酶性能及其调控作用。
总之,以上研究阐述了m6A的甲基化酶、去甲基化酶和识别蛋白的功能,进一步研究了与m6A修饰相关的骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学功能。不难发现,这些研究设计多采用过表达或敲除骨髓间充质干细胞中m6A相应修饰酶的方法,检测骨髓间充质干细胞分化相关的下游基因分子的表达差异,从而探究骨髓间充质干细胞表型和功能特征,这为科学家们研究m6A甲基化修饰提供了重要参考。
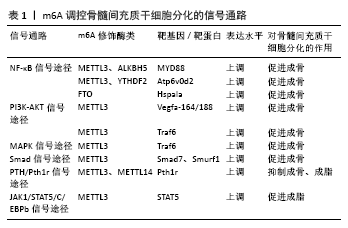
2.3 m6A调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的信号通路机制
2.3.1 NF-κB信号通路 NF-κB信号通路是骨相关疾病的经典信号通路,它通过调控成骨细胞、破骨细胞等骨相关细胞的增殖、分化和凋亡等生物学过程,调控骨的发育和重塑,影响骨相关疾病的发生[33]。YU等[10]研究发现甲基转移酶METTL3协同ALKBH5甲基化修饰mRNA上的MYD88基因位点,当MYD88表达上调后,NF-κB信号通路中κBα蛋白降解, P65、S536蛋白磷酸化位点被激活,由此调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化进程。同样,LI等[34]敲低METTL3及YTHDF2的表达后,mRNA上Atp6v0d2基因被激活,NF-κB信号通路的相关分子磷酸化水平亦差异性表达。另外,去甲基转移酶也参与了NF-κB信号通路途径。ZHANG等[31]研究数据表明FTO通过靶向Hspa1a基因同样会激活NF-κB信号传导通路中的关键因子P65的表达,从而保护成骨细胞正常增殖、分化。上述研究提示,探索骨髓间充质干细胞分化的分子调节机制,可以发现m6A各项酶类可以协同或抑制共同参与mRNA靶基因位点的修饰,而这些靶基因是NF-κB信号的关键上游调控因子,当NF-κB信号通路激活后,调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的关键开关被打开,从而影响其生物学特性表现。
2.3.2 PI3K-AKT信号通路 PI3K-AKT信号通路能通过促进成骨细胞增殖、分化和骨形成而参与骨相关疾病的进程[35]。TIAN等[26]研究结果显示敲低METTL3后AKT磷酸化水平显著降低,再通过热图及KEGG信号通路富集等分析,发现在信号通路差异性表达的前10位中,PI3K-AKT信号通路最接近与成骨分化相关。研究同时提出Vegfa-164/188可能为METTL3的mRNA靶基因。同样在其他研究中也证实METTL3会影响PI3K-AKT信号通路中关键分子AKT的磷酸化水平差异性表达,对成骨分化产生作用[34,36],这些发现均为阐明骨髓间充质干细胞分化进程中RNA表观遗传调控奠定了基础。
2.3.3 MAPK信号通路 MAPK信号通路由MAPK激酶激酶(MAP kinase kinase kinase,MKKK)、MAPK激酶(MAP kinase kinase,MKK)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated
protein kinase,MAPK)3种激酶能依次激活完成,在骨微环境中共同调节着骨髓间充质干细胞生理及病理过程[37]。为了检测METTL3在骨微环境代谢中的意义,研究发现,在炎症环境下成骨细胞中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、肿瘤坏死因子α炎症细胞因子表达上调,MAPK信号通路中关键因子ER、p38被激活,从而对细胞产生保护性作用[34,38]。在敲低METTL3的研究中,ZHANG等[38]发现其能调控Traf6在破骨细胞中的分布,并进一步影响其下游MAPK信号通路及激活,调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化。
2.3.4 其他信号通路 研究发现敲除METTL3会降低骨髓间充质干细胞谱系分化调控机制中甲状旁腺激素受体1(Pth1r)的翻译效率,并破坏体内甲状旁腺激素诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨、成脂反应,从机制上确定PTH/Pth1r信号轴是m6A调控骨髓间充质干细胞的重要下游途径[25]。从骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中的信号通路出发,亦有其他研究人员发现Smad信号转导的负调控因子Smad7和Smurf1的mRNA表达和稳定性与METTL3的表达相关联[38]。从成脂分化方向出发,YAO等[32]发现在猪骨髓间充质干细胞中JAK1可通过调节其磷酸化作用结合CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β(C/EBPβ)的启动子,从而激活信号转导子和转录激活子5(STAT5),最终调节猪骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂进程。以上信号通路的研究为骨髓间充质干细胞中m6A的潜在分子机制提供了新颖的见解,为干细胞再生医学领域提供了有效的治疗策略。m6A调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的信号通路,见表1。
2.4 m6A修饰调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的相关分析方法简述 在分析RNA修饰的生物学功能时,往往需要特定的分析工具才能实现。在目前的分析方法中,主要有用于RNA修饰定量和定位的分析方法,其在于能特异性检测、量化修饰核苷并对RNA修饰的分布位点进行高灵敏度分析。
就目前研究来总结RNA表观遗传修饰调控真核生物基因表达的方法,首先可进行m6A整体含量信息分析。一般经酶或化学处理样本使其释放RNA组分后,可使用液相色谱、液相色谱-质谱联用、薄层色谱、荧光标记和免疫检测等方法检测RNA整体含量[39]。将操作简单、重复性好的液相色谱法联合定性能力较好的质谱法联用,是目前RNA修饰的主要研究方法,也是近几年主要研究骨髓间充质干细胞中m6A含量的方法,其不仅能检测样本中核苷的量还能测定修饰位点,简化了操作程序。WU等[25]首先将骨髓间充质干细胞中mRNA水解成单核苷,然后酶混合后使核苷去磷酸化,再使用多反应监测模式的液相色谱-质谱联用/质谱法检测修饰核苷的量,以m6A与标准品的比值为基准进行数据统计。YAO等[32]首先使用RNase酶解获得猪骨髓间充质干细胞中RNA短片段,然后使用液相色谱-质谱联用/质谱法分析,发现敲低METTL3表达后m6A修饰总含量降低。也就是说,通过与基因序列数据比对后确定RNA片段上修饰的序列位点是METTL3,METTL3影响了骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂进程。
为进一步提高测试的特异性,高通量测序技术也是目前分析m6A修饰调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的重要方法,其中m6A免疫沉淀测序方法(m6A-specific methyled RNA immunoprecipitation coupled with next-generation sequencing,MeRIP-seq/m6A-seq)是主要定位方法,被众多研究学者采纳[40]。WU等[25]
将骨髓间充质干细胞中mRNA富集纯化后,进行免疫沉淀和高通量分析测序,发现Pth1r多富集于m6A翻译的终止密码子附近,MeRIP-qPCR也验证了Pth1r m6A峰值具有特异性,提示Pth1r是重要的表达调控基因。TIAN等[26]通过高通量测序方法检测敲低METTL3的骨髓间充质干细胞中的表达基因,发现556个基因上调,641个基因下调,最后经GO分析和KEGG分析发现PI3K-AKT信号通路是METTL3影响骨髓间充质干细胞分化的重要下游通路。通过了解每种分析方法的特性,研究人员可以选择合适的分析方法进行m6A甲基化修饰的定量及定位分析。