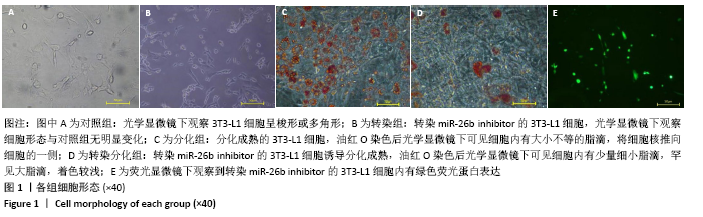
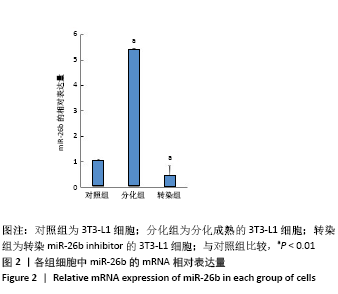
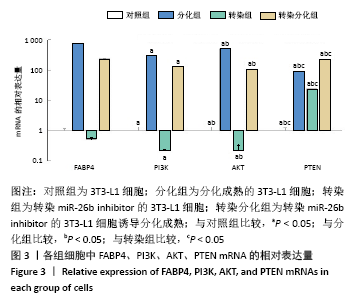
[1] Palmer AK, Kirkland JL. Aging and adipose tissue: potential interventions for diabetes and regenerative medicine. Exp Gerontol. 2016;86:97-105.
[2] Ahima RS. Connecting obesity, aging and diabetes. Nat Med. 2009; 15(9):996-997.
[3] Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303(3):235-241.
[4] Maurizi G, Della Guardia L, Maurizi A, et al. Adipocytes properties and crosstalk with immune system in obesity-related inflammation. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):88-97.
[5] Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. 2017;542(7640):177-185.
[6] Prentice KJ, Saksi J, Hotamisligil GS. Adipokine FABP4 integrates energy stores and counterregulatory metabolic responses. J Lipid Res. 2019;60(4):734-740.
[7] Shi C, Huang F, Gu X, et al. Adipogenic miRNA and meta-signature miRNAs involved in human adipocyte differentiation and obesity. Oncotarget. 2016;7(26):40830-40845.
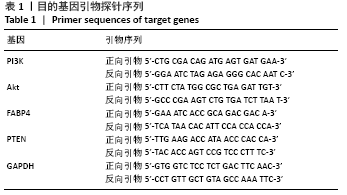
[8] Li G, Ning C, Ma Y, et al. miR-26b Promotes 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation Through Targeting PTEN. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36(8): 672-681.
[9] Friedman JM. Obesity in the new millennium. Nature. 2000;404 (6778):632-634.
[10] Lutz A. Internalising dietary norms and transforming food practices: social inequalities in the management of childhood obesity. Health Sociol Rev. 2020;29(1):16-30.
[11] Skelton JA, Palakshappa D, Moore JB, et al. Community engagement and pediatric obesity: Incorporating social determinants of health into treatment. J Clin Transl Sci. 2019;4(4):279-285.
[12] Zhong H, Ma M, Liang T, et al. Role of MicroRNAs in Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder and Immune Response. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:2835761.
[13] Goody D, Pfeifer A. MicroRNAs in brown and beige fat. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019;1864(1):29-36.
[14] Furuhashi M, Saitoh S, Shimamoto K, et al. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2015;8(Suppl 3):23-33.
[15] Sun J, Zhang D, Xu J, et al. Circulating FABP4, nesfatin-1, and osteocalcin concentrations in women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19(1):199.
[16] Hotamisligil GS, Bernlohr DA. Metabolic functions of FABPs--mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015; 11(10):592-605.
[17] Yang VW, Christy RJ, Cook JS, et al. Mechanism of regulation of the 422(aP2) gene by cAMP during preadipocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86(10):3629-3633.
[18] Rodríguez-Calvo R, Girona J, Alegret JM, et al. Role of the fatty acid-binding protein 4 in heart failure and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol. 2017;233(3):R173-R184.
[19] Trojnar M, Patro-Małysza J, Kimber-Trojnar Ż, et al. Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4⁻A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells. 2019;8(3):227.
[20] Kralisch S, Fasshauer M. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein: a novel adipokine involved in the pathogenesis of metabolic and vascular disease? Diabetologia. 2013;56(1):10-21.
[21] Elie AGIM, Bloksgaard M, Sun WY, et al. Local enrichment of fatty acid-binding protein 4 in the pericardial cavity of cardiovascular disease patients. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0206802.
[22] Demirsoy İH, Ertural DY, Balci Ş, et al. Profiles of Circulating MiRNAs Following Metformin Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J Med Biochem. 2018;37(4):499-506.
[23] Stępień EŁ, Durak-Kozica M, Kamińska A, et al. Circulating ectosomes: Determination of angiogenic microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Theranostics. 2018;8(14):3874-3890.
[24] Xu G, Ji C, Song G, et al. Obesity-associated microRNA-26b regulates the proliferation of human preadipocytes via arrest of the G1/S transition. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(3):3648-3654.
[25] Yu ZW, Eriksson JW. The upregulating effect of insulin and vanadate on cell surface insulin receptors in rat adipocytes is modulated by glucose and energy availability. Horm Metab Res. 2000;32(8):310-315.
[26] 迟毓婧,李晶,管又飞,等.PI3K-Akt信号传导通路对糖代谢的调控作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2010,26(10):879-885.
[27] Zhang L, Huang C, Guo Y, et al. MicroRNA-26b Modulates the NF-κB Pathway in Alveolar Macrophages by Regulating PTEN. J Immunol. 2015;195(11):5404-5414.
[28] Xu G, Ji C, Song G, et al. MiR-26b modulates insulin sensitivity in adipocytes by interrupting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39(10):1523-1530.
[29] Makowski L, Brittingham KC, Reynolds JM, et al. The fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, coordinates macrophage cholesterol trafficking and inflammatory activity. Macrophage expression of aP2 impacts peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and IkappaB kinase activities. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(13):12888-12895.
[30] Dong X, Yang L. Inhibition of fatty acid binding protein 4 attenuates gestational diabetes mellitus. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020;161:102179. |