[1] YU T, GAO M, YANG P, et al. Insulin promotes macrophage phenotype transition through PI3K/Akt and PPAR-gamma signaling during diabetic wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 2018;234(4):4217-4231.
[2] MCBRIDE JD, JENKINS AJ, LIU X, et al. Elevated circulation levels of an antiangiogenic SERPIN in patients with diabetic microvascular complications impair wound healing through suppression of Wnt signaling. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(6):1725-1734.
[3] MORENO-MARIN N, MERINO JM, ALVAREZ-BARRIENTOS A, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes liver polyploidization and inhibits PI3K, ERK, and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. iScience. 2018;4:44-63.
[4] FAN YS, LI Q, HAMDAN N, et al. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside regulates proliferation, differentiation, and OPG/RANKL/M-CSF expression in MC3T3-E1 cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Molecules. 2018;23(9):2306-2309.
[5] SONG BQ, CHI Y, LI X, et al. Inhibition of notch signaling promotes the adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through autophagy activation and PTEN-PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):1991-2002.
[6] YOKOTA J, CHOSA N, SAWADA S, et al. PDGF-induced PI3K-mediated signaling enhances the TGF-beta-induced osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a TGF-beta-activated MEK-dependent manner. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(3):534-542.
[7] YEH YH, HSIAO HF, YEH YC, et al. Inflammatory interferon activates HIF-1α-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):70.
[8] XIAOYAN H, ZHIYING H, XINWEI J, et al. Folic Acid Represses Hypoxia-Induced Inflammation in THP-1 Cells through Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α Pathway. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0151553.
[9] CHOI YH, JIN GY, LI LC, et al. Inhibition of Protein Kinase C Delta Attenuates Allergic Airway Inflammation through Suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 Alpha/VEGF Pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e81773.
[10] DINDA M, DASGUPTA U, SINGH N, et al. PI3K-mediated proliferation of fibroblasts by Calendula officinalis tincture: implication in wound healing. Phytother Res. 2015; 29(4):607-616.
[11] 农庆文,李顺堂,刘达恩,等.弱激光促进糖尿病大鼠皮肤创伤愈合及对PI3K/Akt-HIF-1α信号系统的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(10):2459-2462.
[12] JINSONG L, LEI C, JIAN X, et al. Effects of Periploca forrestii Schltr on wound healing by Src meditated Mek/Erk and PI3K/Akt signals. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019; 237:116-127.
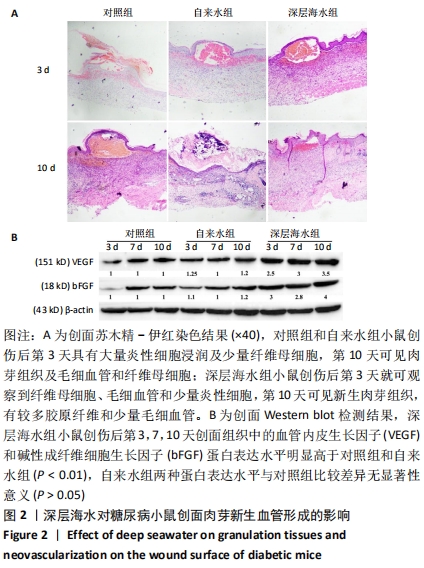
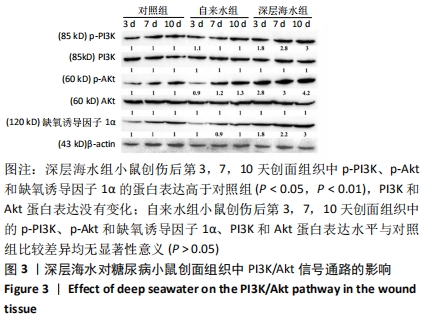
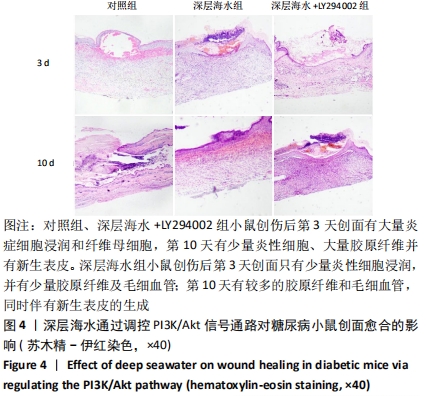
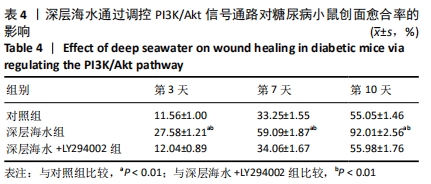
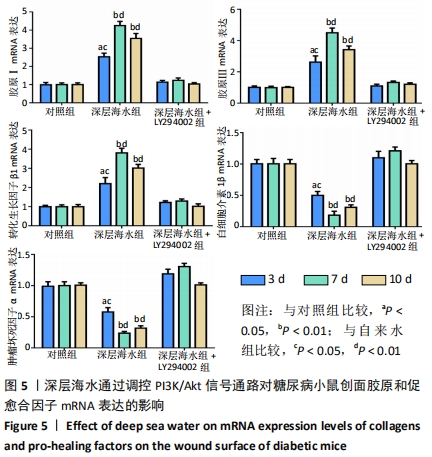
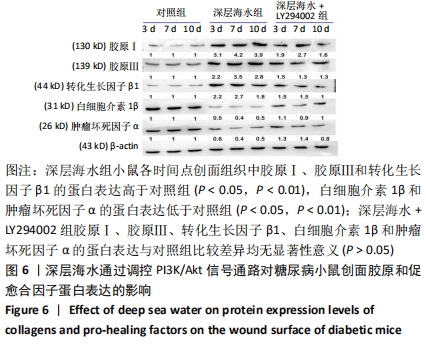
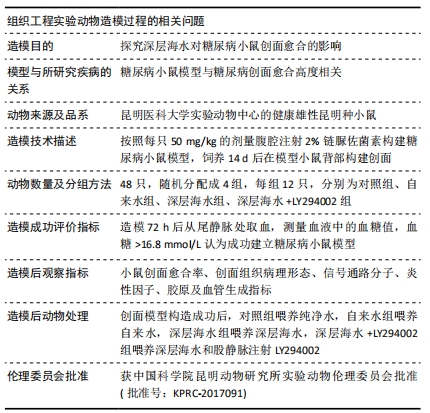
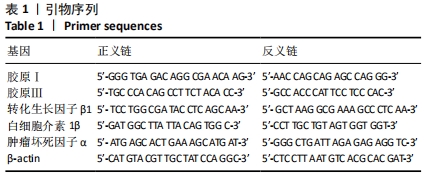
[13] 李为明,崔进,徐鹏远,等.深层海水对小鼠创面愈合的促进作用[J].重庆医学,2014,43(4):462-464.
[14] 李为明,崔进,徐鹏远,等.“深层海水”对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发,2013,25(7):903-906.
[15] 李为明,崔进,徐鹏远,等.“深层海水”对小鼠耐受力的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发,2013(6):103-106.
[16] PEI Y, DEMIN Y, JIANCHENG Q, et al. High D-glucose alters PI3K and Akt signaling and leads to endothelial cell migration, proliferation and angiogenesis dysfunction. National Med J Chin. 2006;86(48):3425-3430.
[17] ASSOCIATION AD. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(Suppl 1):S51-S54.
[18] WHITING DR, GUARIGUATA L, WEIL C, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 94(3):311-321.
[19] BARROS JF, WACLAWIAK I, PECLI C, et al. Role of Chemokine Receptor CCR4 and Regulatory T Cells in Wound Healing of Diabetic Mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2018; 139(5):1161-1170.
[20] BONIAKOWSKI AE, KIMBALL AS, JACOBS BN, et al. Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Normal and Diabetic Wound Healing. J Immunol. 2017;199(1):17.
[21] BALTZIS D, ELEFTHERIADOU I, VEVES A. Pathogenesis and Treatment of Impaired Wound Healing in Diabetes Mellitus: New Insights. Adv Ther. 2014;31(8):817-836.
[22] HA BG, JUNG SS, JANG YK, et al. Mineral-Enriched Deep-Seawater Modulates Lactate Metabolism via PGC-1α-Mediated Metabolic Reprogramming. Mar Drugs. 2019;17(11):611.
[23] BYUNG H, EUN S, JUNG-EUN P, et al. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Balanced Deep-Seawater and Its Mode of Action in High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Mice. Mar Drugs. 2013;11(11):4193-4212.
[24] HA BG, PARK JE, SHIN EJ, et al. Modulation of Glucose Metabolism by Balanced Deep-Seawater Ameliorates Hyperglycemia and Pancreatic Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102095.
[25] SHIRAISHI H, FUJINO M, SHIRAKAWA N, et al. Effect of minerals on intestinal IgA production using deep seawater drinks. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(10):1700-1705.
[26] LEE CL. The advantages of deep ocean water for the development of functional fermentation food. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015;99(6):2523-2531.
[27] BAK JP, KIM YM, SON J, et al. Application of concentrated deep seawater inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012;12:108.
[28] YANG CC, YAO CA, LIN YR, et al. Deep-Seawater Containing Selenium Provides Intestinal Protection against Duodenal Ulcers through the Upregulation of Bcl-2 and Thioredoxin Reductase 1. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e96006.
[29] YUE Q, PAN X, LIU Y, et al. Protective effects of deep seawater against subacute alcoholic liver injury. J of hygiene Res. 2018;47(5):798-803.
[30] CHUN SY, LEE KS, NAM KS. Refined deep-seawater suppresses inflammatory responses via the MAPK/AP-1 and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2282.
[31] CHUN SY, KIM SNAM KS. The inhibitory effects of deep-seawater on doxorubicininduced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(2): 1163-1171.
[32] KIMATA H, TAI H, NAKAGAWA K, et al. Improvement of skin symptoms and mineral imbalance by drinking deep seawater in patients with atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome (AEDS). Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2002;45(2):83-84.
[33] YOU L, GU W, CHEN L, et al. MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10):7249-7261.
[34] MA P, GU B, XIONG W, et al. Glimepiride promotes osteogenic differentiation in rat osteoblasts via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in a high glucose microenvironment. PLoS One. 2014; 9(11):e112243.
[35] ZIRU L, LEI Y, JIN Z, et al. Nobiletin protects PC12 cells from ERSinduced apoptosis in OGD/R injury via activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):1470-1476.
[36] XIA P, XU XY. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells: from basic research to clinical application. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(5):1602-1609.
[37] KIM JH, BAE HC, KIM J, et al. HIF-1alpha-mediated BMP6 down-regulation leads to hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes in vitro. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27(11):1287-1293.
[38] DU J, LIU L, LAY F, et al. Combination of HIF-1α gene transfection and HIF-1-activated bone marrow-derived angiogenic cell infusion improves burn wound healing in aged mice. Gene Ther. 2013;20(11):1070-1076.
[39] YANG HL, TSAI YC, KORIVI M, et al. Lucidone promotes the cutaneous wound healing process via activation of the PI3K/AKT, Wnt/beta-catenin and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017;1864(1):151-168.
[40] ZHANG W, BAI X, ZHAO B, et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):333-342. |