中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 2034-2039.doi: 10.12307/2022.329
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
低氧预处理改善去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化潜能
黄晓雄1,2,陈维凯1,2,刘 滔1,杨惠林1,2,何 帆1,2
- 1苏州大学附属第一医院骨科,江苏省苏州市 215006;2苏州大学骨科研究所,江苏省苏州市 215007
Hypoxic precondition rescues osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from ovariectomized rats
Huang Xiaoxiong1, 2, Chen Weikai1, 2, Liu Tao1, Yang Huilin1, 2, He Fan1, 2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopaedics at Soochow University, Suzhou 215007, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨髓间充质干细胞:是一种具有高水平增殖能力的多能基质细胞,可分化为多种细胞,如成骨细胞、软骨细胞和脂肪细胞。来源于骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨细胞在骨基质中起着重要的作用,因而在组织工程研究和再生医学应用领域引起广泛关注,但骨质疏松患者的骨髓间充质干细胞与健康细胞相比有着较低的生长速率和成骨潜能。
低氧预处理:在进行体内干细胞移植或体外成骨分化前先进行一段时间的低氧环境培养可以提高干细胞的治疗潜力、成骨分化能力,如果在低氧条件下进行预处理,骨髓间充质干细胞在致命缺氧攻击后将存活更长时间并且保持更好的成骨分化能力。此外,低氧诱导因子1α通路的激活加速了体内骨再生,提示低氧是骨愈合的重要辅助因素。
背景:低氧是调节血管生成-成骨分化过程的主要驱动力之一,细胞在分化前进行低氧预处理能够保持干细胞干性和增强干细胞的成骨分化能力,但低氧预处理能否改善去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力尚不清楚。
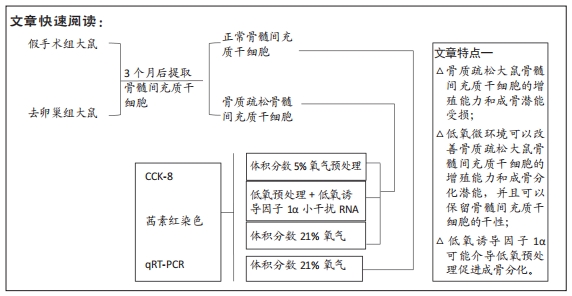
目的:探讨低氧预处理对去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力的影响以及低氧诱导因子1α在其中的作用。
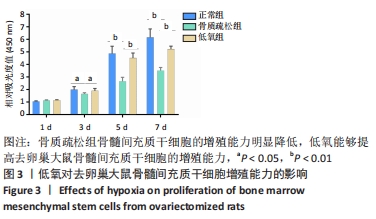
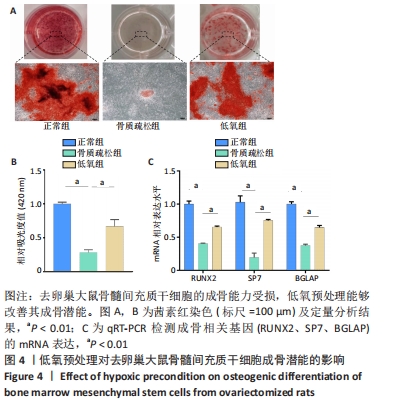
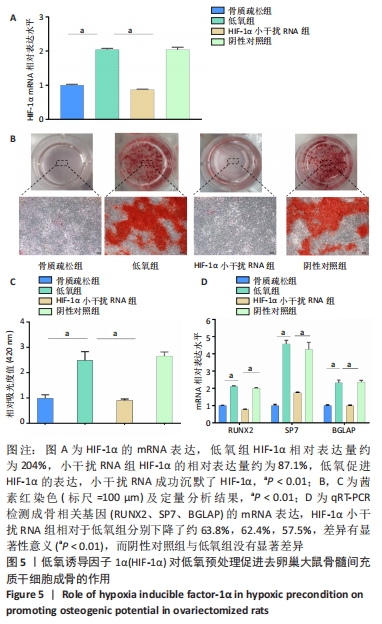
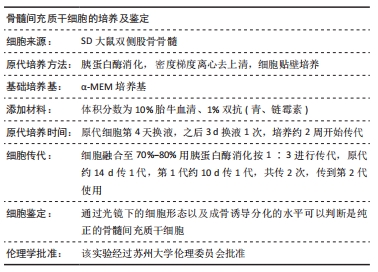
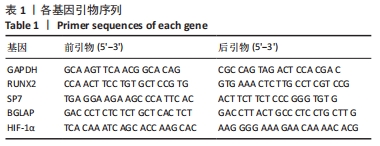
方法:首先建立去卵巢SD大鼠模型,提取假手术大鼠和去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞。将细胞分为3组,①正常组:假手术组大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在常氧环境培养(体积分数21%氧气);②骨质疏松组:去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在常氧环境培养(体积分数21%氧气);③低氧组:去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞在低氧环境培养(体积分数5%氧气)。采用CCK-8法检测第1,3,5,7天的吸光度值来反映各组细胞的增殖能力;在低氧环境培养72 h后,转移至正常培养箱进行成骨诱导分化14 d,采用茜素红染色和qRT-PCR检测成骨相关基因表达水平。最后将骨质疏松组骨髓间充质干细胞转染小干扰RNA沉默低氧诱导因子1α表达,在低氧环境培养72 h,转移至正常培养箱进行成骨诱导分化14 d,观察沉默低氧诱导因子1α后成骨能力变化。
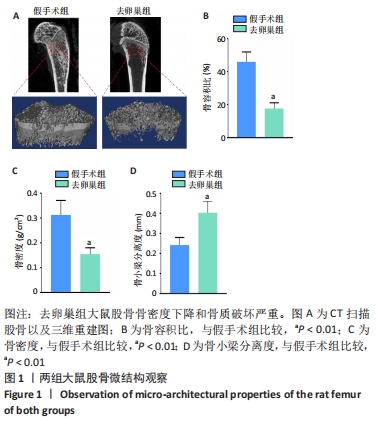
结果与结论:①去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖能力下降,同时成骨分化能力受损;②低氧环境可以促进去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖,提高钙结节的沉积以及成骨相关基因的表达;③沉默低氧诱导因子1α后,低氧预处理改善成骨能力的效应被消除;④结果表明,低氧预处理可以改善去卵巢大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及成骨分化能力,低氧诱导因子1α在低氧预处理促进成骨分化过程中起到重要作用。
缩略语:骨髓间充质干细胞:bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells,BMMSCs;低氧诱导因子1α:hypoxia -inducible factor 1α,HIF-1α
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4062-0530(黄晓雄)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: