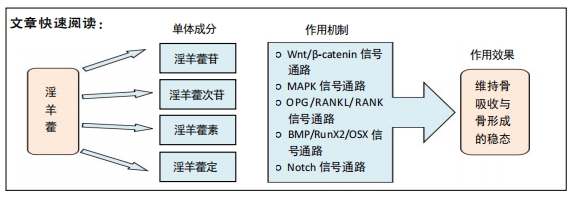
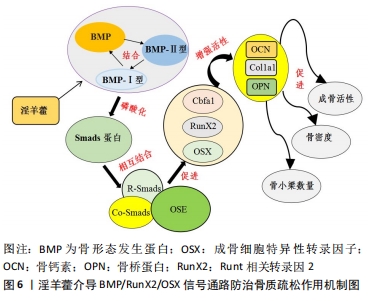
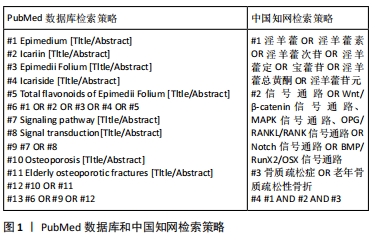
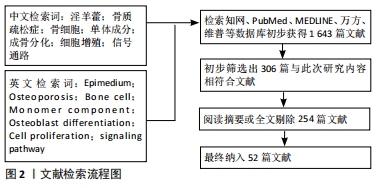
[1] KANIS JA, MCCLOSKEY EV, HARVEY NC, et al. Intervention thresholds and the diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(10):1747-1753.
[2] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis- related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(7): 1929-1937.
[3] BURNS RB, ROSEN H, BERRY S, et al. How would You manage this patient with osteoporosis? Grand rounds discussion from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. Ann Intern Med. 2018;168(11):801-808.
[4] VIDAL M, THIBODAUX RJ, NEIRA LFV, et al. Osteoporosis: A clinical and pharmacological update. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(2):385-395.
[5] EASTELL R, SZULC P. Use of bone turnover markers in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(11):908-923.
[6] 李建国,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.中药淫羊藿治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(3):389-393.
[7] AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sciences. 2016;147:46-58.
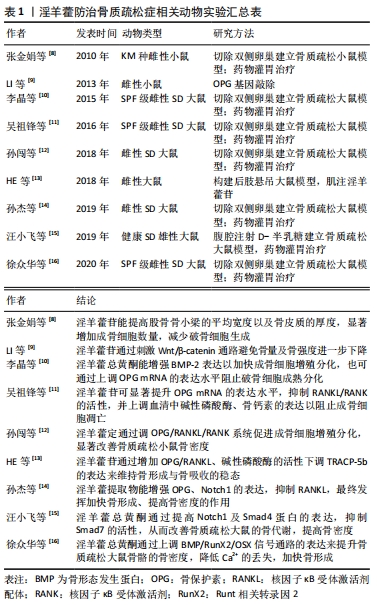
[8] 张金娟,文娱,张贵林,等.淫羊藿苷对骨质疏松模型小鼠骨组织形态计量学指标的影响[J].贵州医药,2010,34(5):22-23.
[9] LI XF, XU H, ZHAO YJ, et al. Icariin augments bone formation and reverses the phenotypes of osteoprotegerin-deficient mice through the activation of Wnt/β- Catenin-BMP signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:652317.
[10] 李晶,宋敏,罗晓,等.淫羊藿总黄酮对去势大鼠骨组织BMP-2和OPGmRNA表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(7):2529-2531.
[11] 吴祖锋,袁垒,吴风晴,等.淫羊藿苷对骨质疏松症模型大OPG/RANKL/RANK轴系统影响的实验研究[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):4-7.
[12] 孙闯,杨大威,姜明久,等.淫羊藿定对骨质疏松大鼠的治疗作用及机制研究[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2018,52(3):234-237.
[13] HE JP, FENG X, WANG JF, et al. Icariin prevents bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and stabilizing bone biological apatite in a hindlimb suspension rodent model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(11):1760-1767.
[14] 孙杰,宋鑫,王健.淫羊藿提取物对骨质疏松骨折大鼠愈合过程Notch信号通路的影响[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(4):611-614.
[15] 汪小飞,李晶晶.淫羊藿总黄酮对老年骨质疏松大鼠Notch和Smads通路蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(2):1-5.
[16] 徐众华,莫雨晴,周驰.基于BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路研究淫羊藿总黄酮改善绝经后骨质疏松模型大鼠的作用机制[J].中国药房, 2020,31(19): 2333-2338.
[17] 刘铁汉,王本祥,王毅,等.淫羊藿苷及其肠菌代谢产物对THP-1细胞分泌细胞因子的影响[J].药学学报,2000(4):245-248.
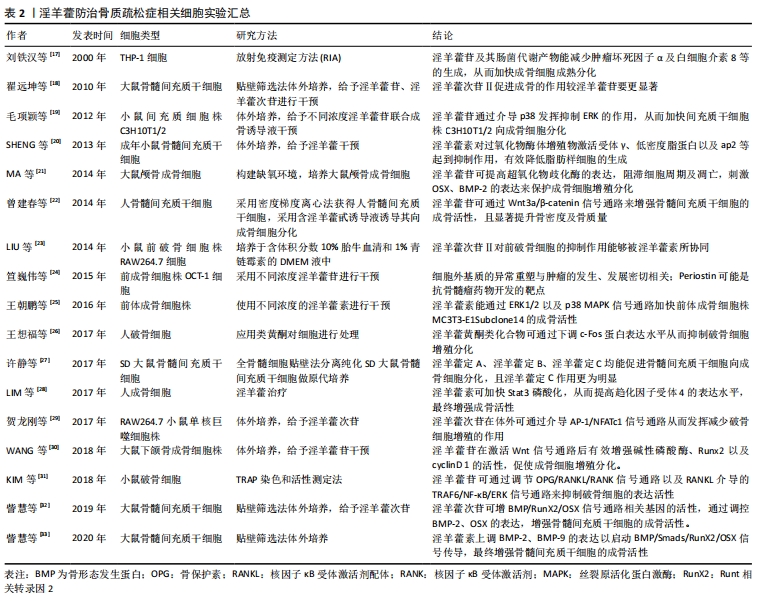
[18] 翟远坤,葛宝丰,陈克明,等.淫羊藿苷与其代谢产物淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨性分化影响的比较研究[J].中药材, 2010, 33(12):1896-1900.
[19] 毛项颖,卞琴,沈自尹.淫羊藿苷介导MAPK信号通路促进间充质干细胞株C3H10T1/2成骨分化的体外研究[J].中西医结合学报, 2012, 10(11):1272-1278.
[20] SHENG H, RUI XF, SHENG CJ, et al. A novel semisynthetic molecule icaritinstimulates osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenesis of mesenchymalstem cells. Int J Med Sci. 2013;10(6):782-789.
[21] MA HP, MA XN, GE BF, et al. Icariin attenuates hypoxia- induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro. Cell Proliferation. 2014;47(6):527-539.
[22] 曾建春,曾意荣,樊粤光,等.淫羊藿甙诱导MSCs向成骨细胞分化过程中对Wnt信号通路的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2014,31(4): 607-611.
[23] LIU YQ, YANG QX, CHENG MC, et al. Synergistic inhibitory effect of icariside Ⅱ with icaritin from herba Epimedii on pre-osteoclastic raw264.7 cell Growth. Phytomedicine. 2014;21(12):1633-1637.
[24] 笪巍伟,赵永见,王拥军,等.淫羊藿苷对前成骨细胞株OCT1细胞BMP-2 mRNA、Runx-2 mRNA表达的影响[J].上海中医药杂志, 2015, 49(5):90-94.
[25] 王朝鹏.淫羊蕾素对MC3T3-E1 Subclone14ER/MAPK信号通路的影响[D].广州:暨南大学,2016.
[26] 王想福,孙凤歧,叶丙霖,等.类黄酮对人体外周血破骨细胞分化p38MAPK/c-Fos信号通路调控的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017, 23(11):1488-1491,1529.
[27] 许静,张晶晶,郭非非,等.淫羊藿黄酮类主要成分促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞增殖分化作用及机制的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017,23(14):113-120.
[28] LIM R, LI L, CHEW N, et al. The prenylflavonoid Icaritin enhances osteoblast proliferation and function by signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 (STAT-3) regulation of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) expression. Bone. 2017;105:122-133.
[29] 贺龙刚,高奥,邱煌沛,等.淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ及其代谢产物淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ通过AP-1/NFATc1信号通路调控破骨细胞生成[J].中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(3):1299-1302.
[30] WANG Y, WANG R, ZHANG F. Icariin promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from the rat mandible by the Wnt /β-catenin signalling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18 (3):3445-3450.
[31] 王宇,董婉茹,杨晓旭,等.淫羊藿活性单体抗骨质疏松药理研究进展[J].中药药理与临床,2016,32(3):197-201.
[32] 訾慧,范颖,蒋宁,等.淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ及淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):690-695.
[33] 訾慧,郑洪新,蒋宁,等.淫羊藿素通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2020,38(7): 212-215+270.
[34] WANG Z, WANG D, YANG D, et al. The effect of icariin on bone metabolism and its potential clinical application. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(3):535-544.
[35] HUANG Z, CHENG C, WANG J, et al. Icariin regulates the osteoblast differentiation and cell proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells through microRNA-153 by targeting Runt-related transcription factor 2. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5159-5166.
[36] LIU M, XU H, MA Y, et al. Osteoblasts Proliferation and Differentiation Stimulating Activities of the Main Components of Epimedii folium. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017;13(49):90-94.
[37] LIU W, MAO L, JI F, et al. Icariside II activates EGFR-Akt-Nrf2 signaling and protects osteoblasts from dexamethasone. Oncotarget. 2017;8(2): 2594-2603.
[38] TAN EM, LI L, INDRAN IR, et al. TRAF6 Mediates Suppression of Osteoclastogenesis and Prevention of Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss by a Novel Prenylflavonoid. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(4):846-860.
[39] LIM RZL, LI L, YONG EL, et al. STAT-3 regulation of CXCR4 is necessary for the prenylflavonoid icaritin to enhance mesenchymal stem cell proliferation,migration and osteogenic differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018;1862(7):1680-1692.
[40] KIM B, LEE KY, PARK B. Icariin abrogates osteoclast formationthrough the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6 /NF-κB / ERK signaling pathway in Raw264. 7 cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:181-190.
[41] HUANG M, WANG Y, PENG R. Icariin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through EphB4/ Ephrin-B2 axis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:2982480.
[42] XU S, ZHANG Y, LIU B, et al. Activation of mTORC1 in B Lymphocytes Promotes Osteoclast Formation via Regulation of β-Catenin and RANKL/OPG. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(7):1320-1333.
[43] 刘颖,柴丽娟,黄菊阳,等.朝藿定A对原代骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的作用[J].中国兽医学报,2021,41(5):980-984+991.
[44] TORRE E. Molecular signaling mechanisms behind polyphenol- induced bone anabolism. Phytochem Rev. 2017;16(6):1183-1226.
[45] SONG N, WANG ZM, HE LJ, et al. Estradiol enhanced osteogenesis of rat bone marrow stromal cells is associated with the JNK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):8589-8594.
[46] WANG W, BAI J, ZHANG W, et al. Protective Effects of Punicalagin on Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Inflammation via the NF-κB and MAPK Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:696.
[47] 龚一昕,刘尚全,袁媛,等.淫羊藿次苷II通过p38 MAPK调控成骨细胞护骨素表达的体外研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2016,51(12):1790-1793,1794.
[48] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and Mechanotransduction Synergize to Drive Osteogenic Differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931.
[49] 梁广胜,陈伟才,殷嫦嫦,等.淫羊藿总黄酮对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程BMP-2/RunX2/OSX通路的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2016,36(5):614-618.
[50] YANG M, LIU H, WANG Y, et al. Hypoxia reduces the osteogenic differentiation of peripheral blood mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating Notch-1 expression. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;60(6):583-596.
[51] ZANOTTI S, CANALIS E. Notch Signaling and the Skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2016; 37(3):223-253.
[52] 邓宇,陈廖斌.淫羊藿苷通过激活Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中医学报,2017,32(12):2393-2398.
|