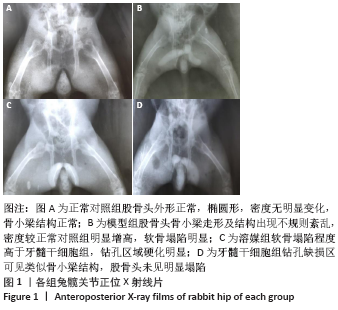
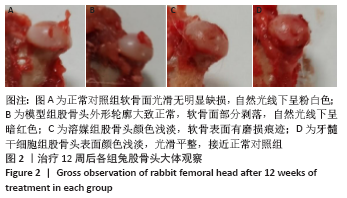
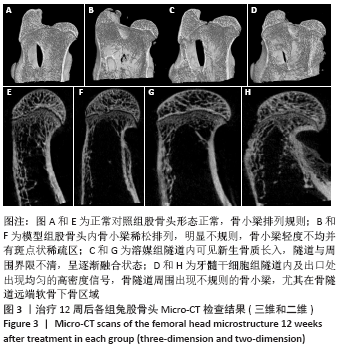
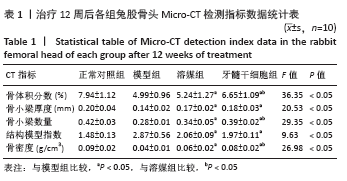
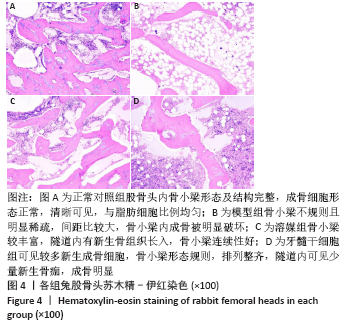
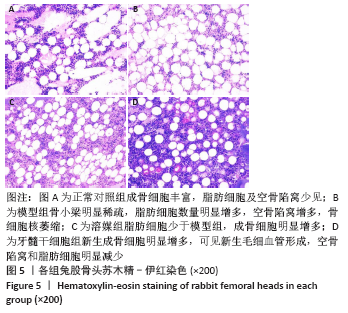
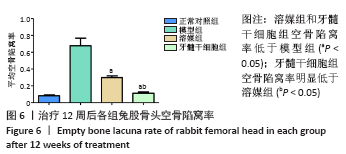
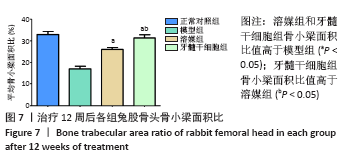
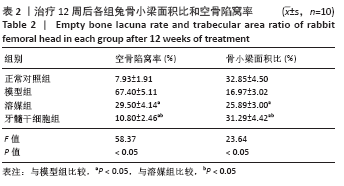
[1] LI B, YANG M, YU L. Vascular bundle transplantation combined with porous bone substituted scaffold for the treatment of early-stage avascular necrosis of femoral head. Med Hypotheses. 2019;132:109374.
[2] FU Q, TANG NN, ZHANG Q, et al. Preclinical Study of Cell Therapy for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head with Allogenic Peripheral Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(4):1006-1015.
[3] YUAN HF, ZHANG J, GUO CA, et al. Clinical outcomes of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after autologous bone marrow stem cell implantation: a meta-analysis of seven case-control studies. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016;71(2):110-113.
[4] FANG SH, LI YF, JIANG JR, et al. Relationship of α2-Macroglobulin with Steroid-Induced Femoral Head Necrosis: A Chinese Population-Based Association Study in Southeast China. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):481-486.
[5] GÓMEZ-MONT LANDERRECHE JG, GIL-ORBEZO F, MORALES-DOMINGUEZ H, et al. Nontraumatic causes of bilateral avascular necrosis of the femoral head: link between hepatitis C and pegylated interferon. Acta Ortop Mex. 2015;29(3): 172-175.
[6] CHAO PC, CUI MY, LI XA, et al. Correlation between miR-1207-5p expression with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head and VEGF expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7):2710-2718.
[7] WANG Z, SUN QM, ZHANG FQ, et al. Core decompression combined with autologous bone marrow stem cells versus core decompression alone for patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2019;69:23-31.
[8] ANDRONIC O, SHOMAN H, WEISS O, et al. What are the outcomes of core decompression in patients with avascular necrosis? Protocol for a systematic review. F1000Res. 2020;9:71.
[9] WANG SL, HU YB, CHEN H, et al. Efficacy of bone marrow stem cells combined with core decompression in the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(25):e20509.
[10] HERNIGOU P, DUBORY A, HOMMA Y, et al. Cell therapy versus simultaneous contralateral decompression in symptomatic corticosteroid osteonecrosis: a thirty year follow-up prospective randomized study of one hundred and twenty five adult patients. Int Orthop. 2018;42(7):1639-1649.
[11] ZHANG XL, SHI KQ, JIA PT, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma on angiogenesis and osteogenesis-associated factors in rabbits with avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(7):2143-2152.
[12] 骆瑜,李若涵,彭友俭.牙髓干细胞来源外泌体修复兔颞下颌关节软骨损伤后软骨组织修复的实验研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2020,36(4):202-205.
[13] ARAÚJO AB, FURLAN JM, SALTON GD, et al. Isolation of human mesenchymal stem cells from amnion, chorion, placental decidua and umbilical cord: comparison of four enzymatic protocols. Biotechnol Lett. 2018;40(6):989-998.
[14] PHAM H, TONAI R, WU M, et al. CD73, CD90, CD105 and Cadherin-11 RT-PCR Screening for Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Cryopreserved Human Cord Tissue. Int J Stem Cells. 2018;11(1):26-38.
[15] KOBOLAK J, DINNYES A, MEMIC A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Identification, phenotypic characterization, biological properties and potential for regenerative medicine through biomaterial micro-engineering of their niche. Methods. 2016; 99:62-68.
[16] XIAO D, YE M, LI X, et al. Biomechanics analysis for the treatment of ischemic necrosis of the femoral head by using an interior supporting system. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):4551-4556.
[17] HUA KC, YANG XG, FENG JT, et al. The efficacy and safety of core decompression for the treatment of femoral head necrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):306.
[18] THEOPOLD J, ARMONIES S, PIEROH P, et al. Nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head : Arthroscopic and navigation-supported core decompression. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2020;32(2):107-115.
[19] XU S, ZHANG L, JIN H, et al. Autologous Stem Cells Combined Core Decompression for Treatment of Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:6136205.
[20] PENG K, WANG Y, ZHU J, et al. Repair of non-traumatic femoral head necrosis by marrow core decompression with bone grafting and porous tantalum rod implantation. Pak J Med Sci. 2020;36(6):1392-1396.
[21] KOSUKEGAWA I, OKAZAKI S, Yamamoto M, et al. The proton pump inhibitor, lansoprazole, prevents the development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: an experimental and prospective clinical trial. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(4):713-721.
[22] FAN L, ZHANG C, YU Z, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and osteogenesis in rabbit femoral head osteonecrosis. Bone. 2015;81:544-553.
[23] HERNIGOU P, FLOUZAT-LACHANIETTE CH, DELAMBRE J, et al. Osteonecrosis repair with bone marrow cell therapies: state of the clinical art. Bone. 2015;70:102-109.
[24] JUNIOR AL, PINHEIRO CCG, TANIKAWA DYS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth and the Orbicularis Oris Muscle: How Do They Behave When Exposed to a Proinflammatory Stimulus? Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:3670412.
[25] AYOUB S, BERBÉRI A, FAYYAD-KAZAN M. An update on human periapical cyst-mesenchymal stem cells and their potential applications in regenerative medicine. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(3):2381-2389.
[26] HENG BC, ZHU S, XU J, et al. Effects of decellularized matrices derived from periodontal ligament stem cells and SHED on the adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro. Tissue Cell. 2016;48(2):133-143.
[27] CHEN Y, ZHANG F, FU Q, et al. In vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in injectable thermo-sensitive chitosan/β-glycerophosphate/hydroxyapatite hydrogel. J Biomater Appl. 2016;31(3):317-327.
[28] PINHEIRO CCG, LEYENDECKER JUNIOR A, TANIKAWA DYS, et al. Is There a Noninvasive Source of MSCs Isolated with GMP Methods with Better Osteogenic Potential? Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7951696.
[29] CHAMIEH F, COLLIGNON AM, COYAC BR, et al. Accelerated craniofacial bone regeneration through dense collagen gel scaffolds seeded with dental pulp stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38814.
[30] KERMANI S, MEGAT ABDUL WAHAB R, ZARINA ZAINOL ABIDIN I, et al. Differentiation capacity of mouse dental pulp stem cells into osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Cell J. 2014;16(1):31-42.
[31] WOLOSZYK A, HOLSTEN DIRCKSEN S, BOSTANCI N, et al. Influence of the mechanical environment on the engineering of mineralised tissues using human dental pulp stem cells and silk fibroin scaffolds. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e111010.
[32] 毛丽霞,刘加强,赵晶蕾,等.人牙髓干细胞体外成骨向分化的实验研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2014,15(4):193-198.
[33] WANG C, WANG Y, MENG HY, et al. Application of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):3127-3135.
[34] HERNIGOU P, BEAUJEAN F. Abnormalities in the bone marrow of the iliac crest in patients who have osteonecrosis secondary to corticosteroid therapy or alcohol abuse. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(7):1047-1053. |