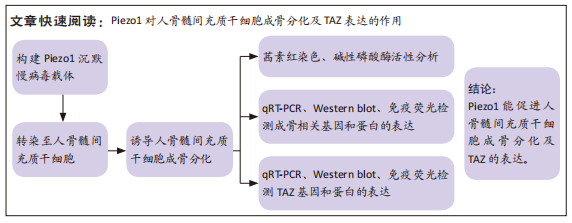
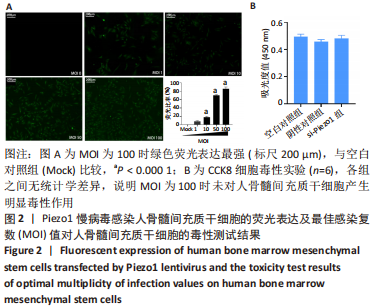
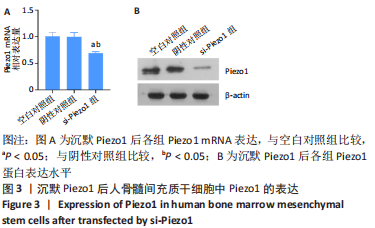
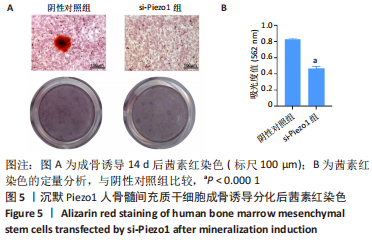
[1] HINES JT, JO WL, CUI Q, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: an Updated Review of ARCO on Pathogenesis, Staging and Treatment. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(24):e177.
[2] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110.
[3] RAHMANI-MOGHADAM E, ZARRIN V, MAHMOODZADEH A, et al. Comparison of the Characteristics of Breast Milk-derived Stem Cells with the Stem Cells Derived from the Other Sources: A Comparative Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;17(1):71-90.
[4] XU Y, JIANG Y, XIA C, et al. Stem cell therapy for osteonecrosis of femoral head: Opportunities and challenges. Regen Ther. 2020;15:295-304.
[5] 吴竖光.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗股骨头坏死的进展[J].中国医药指南,2021,19(12):22-23.
[6] SUN Y, YUAN Y, WU W, et al. The effects of locomotion on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell fate: insight into mechanical regulation and bone formation. Cell Biosci. 2021;11(1):88.
[7] SUGIMOTO A, MIYAZAKI A, KAWARABAYASHI K, et al. Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 functions as a regulator of the cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17696.
[8] 魏腾飞,何晓铭,韦雨柔,等.Piezo1在激素性和酒精性股骨头坏死骨组织中的差异表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):270-275.
[9] JEONG MG, KIM HK, HWANG ES. The essential role of TAZ in normal tissue homeostasis. Arch Pharm Res. 2021;44(3):253-262.
[10] CAI X, WANG KC, MENG Z. Mechanoregulation of YAP and TAZ in Cellular Homeostasis and Disease Progression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:673599.
[11] 吴忠书,韦雨柔,陈哓俊,等.活血通络胶囊促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中的ERα-Wnt/β-catenin信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(25):3937-3943.
[12] TSCHUMPERLIN DJ. Mechanotransduction. Compr Physiol. 2011;1(2): 1057-1073.
[13] UDA Y, AZAB E, SUN N, et al. Osteocyte Mechanobiology. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(4):318-325.
[14] BRODERS-BONDON F, NGUYEN HO-BOULDOIRES TH, FERNANDEZ-SANCHEZ ME, et al. Mechanotransduction in tumor progression: The dark side of the force. J Cell Biol. 2018;217(5):1571-1587.
[15] QIN L, LIU W, CAO H, et al. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020;8:23.
[16] QIN L, HE T, CHEN S, et al. Roles of mechanosensitive channel Piezo1/2 proteins in skeleton and other tissues. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):44.
[17] RANADE SS, SYEDA R, PATAPOUTIAN A. Mechanically Activated Ion Channels. Neuron. 2015;87(6):1162-1179.
[18] COSTE B, MATHUR J, SCHMIDT M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels. Science. 2010;330(6000):55-60.
[19] ZHAO Z, ZLOKOVIC BV. Endothelial Tip Cell Finds Its Way with Piezo1. Neuron. 2020;108(1):5-7.
[20] LIU Y, TIAN H, HU Y, et al. Mechanosensitive Piezo1 is crucial for periosteal stem cell-mediated fracture healing. Int J Biol Sci. 2022; 18(10):3961-3980.
[21] 杨丽丽,康静,刘建勋,等.Piezo1通道在心血管疾病中的作用及中医药研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(24):6533-6540.
[22] 王媛,赵星成,王永春,等.Piezo通道在心血管系统中的作用[J].心脏杂志,2022,34(5):573-578.
[23] 虎瑞. Piezo1调控LIPUS在牙周膜干细胞的内皮分化和血管生成中的作用研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2022.
[24] XU X, LIU S, LIU H, et al. Piezo Channels: Awesome Mechanosensitive Structures in Cellular Mechanotransduction and Their Role in Bone. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6429.
[25] CHEN G, XU R, ZHANG C, et al. Responses of MSCs to 3D Scaffold Matrix Mechanical Properties under Oscillatory Perfusion Culture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(2):1207-1218.
[26] SHI F, XIAO D, ZHANG C, et al. The effect of macropore size of hydroxyapatite scaffold on the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells under perfusion culture. Regen Biomater. 2021;8(6):rbab050.
[27] LIM KT, PATEL DK, DUTTA SD, et al. Fluid Flow Mechanical Stimulation-Assisted Cartridge Device for the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Micromachines (Basel). 2021;12(8):927.
[28] MOUSAWI F, PENG H, LI J, et al. Chemical activation of the Piezo1 channel drives mesenchymal stem cell migration via inducing ATP release and activation of P2 receptor purinergic signaling. Stem Cells. 2020;38(3):410-421.
[29] 王林,王熙,季楠,等.机械激活性离子通道压电蛋白Piezo1通过Notch信号通路介导牙周膜干细胞成骨分化作用机制研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2020,38(6):628-636.
[30] YAN L, JIANG J, MA C, et al. Effect of knocking down Piezo1 mechanically sensitive protein on migration of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(1):28-34.
[31] YONEDA M, SUZUKI H, HATANO N, et al. PIEZO1 and TRPV4, which Are Distinct Mechano-Sensors in the Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells, Modify Cell-Proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4960.
[32] WANG L, YOU X, LOTINUN S, et al. Mechanical sensing protein PIEZO1 regulates bone homeostasis via osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):282.
[33] LI X, HAN L, NOOKAEW I, et al. Stimulation of Piezo1 by mechanical signals promotes bone anabolism. Elife. 2019;8:e49631.
[34] SUN W, CHI S, LI Y, et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation. Elife. 2019;8:e47454.
[35] HONG JH, HWANG ES, MCMANUS MT, et al. TAZ, a transcriptional modulator of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Science. 2005; 309(5737):1074-1078.
[36] MERRICK D, MISTRY K, WU J, et al. Polycystin-1 regulates bone development through an interaction with the transcriptional coactivator TAZ. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(1):16-30.
[37] YANG W, LU X, ZHANG T, et al. TAZ inhibits osteoclastogenesis by attenuating TAK1/NF-κB signaling. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):33.
[38] ZHANG Y, WANG Z, DING L, et al. Lentivirus-TAZ Administration Alleviates Osteoporotic Phenotypes in the Femoral Neck of Ovariectomized Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1):283-294.
[39] YU B, HUO L, LIU Y, et al. PGC-1α Controls Skeletal Stem Cell Fate and Bone-Fat Balance in Osteoporosis and Skeletal Aging by Inducing TAZ. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23(2):193-209.e5.
[40] PANCIERA T, AZZOLIN L, CORDENONSI M, et al. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017; 18(12):758-770.
[41] ARAGONA M, PANCIERA T, MANFRIN A, et al. A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell. 2013;154(5):1047-1059.
[42] COBBAUT M, KARAGIL S, BRUNO L, et al. Dysfunctional Mechanotransduction through the YAP/TAZ/Hippo Pathway as a Feature of Chronic Disease. Cells. 2020;9(1):151.
[43] XIE Z, HOU L, SHEN S, et al. Mechanical force promotes dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1-mediated hydrolysis of the metabolite asymmetric dimethylarginine to enhance bone formation. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):50.
[44] WEI Q, HOLLE A, LI J, et al. BMP-2 Signaling and Mechanotransduction Synergize to Drive Osteogenic Differentiation via YAP/TAZ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(15):1902931.
[45] XIAO Z, BAUDRY J, CAO L, et al. Polycystin-1 interacts with TAZ to stimulate osteoblastogenesis and inhibit adipogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(1):157-174.
[46] WANG L, LU Y, CAI G, et al. Polycystin-2 mediates mechanical tension-induced osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by activating transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif. Front Physiol. 2022;13:917510.
[47] HE MC, ZHANG J, CHEN XJ, et al. Osteoclastic activity was associated with the development of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):1036-1046.
[48] ZHAO J, ZHANG X, GUAN J, et al. Identification of key biomarkers in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head and their correlation with immune infiltration by bioinformatics analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):67.
[49] TIAN L, WEN Q, DANG X, et al. Immune response associated with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway leads to steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:18.
[50] FAN X, XU X, WU X, et al. The protective effect of DNA aptamer on osteonecrosis of the femoral head by alleviating TNF-α-mediated necroptosis via RIP1/RIP3/MLKL pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2022; 36:44-51.
[51] ATCHA H, JAIRAMAN A, HOLT JR, et al. Mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1 modulates macrophage polarization and stiffness sensing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3256.
[52] LIU Q, WANG D, YANG X, et al. The Mechanosensitive Ion Channel PIEZO1 in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Mediates Inflammation through the NOD-Like Receptor 3 Pathway in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023;29(1):103-115.
[53] NOWELL CS, ODERMATT PD, AZZOLIN L, et al. Chronic inflammation imposes aberrant cell fate in regenerating epithelia through mechanotransduction. Nat Cell Biol. 2016;18(2):168-180.
[54] YANG Y, WANG D, ZHANG C, et al. Piezo1 mediates endothelial atherogenic inflammatory responses via regulation of YAP/TAZ activation. Hum Cell. 2022;35(1):51-62. |