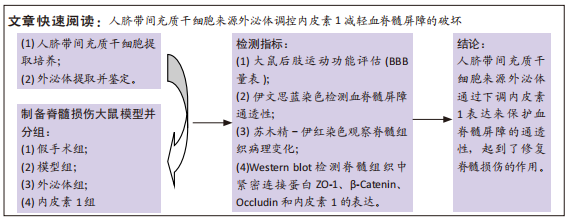
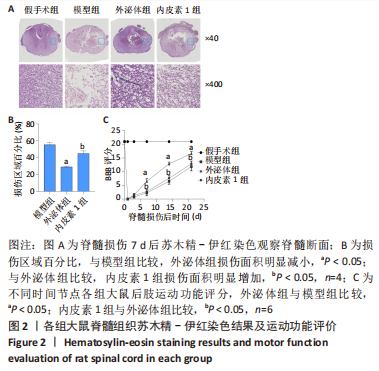
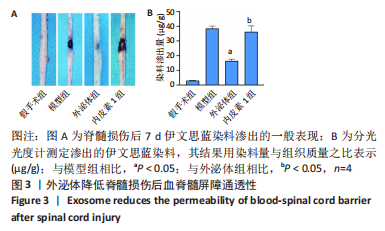
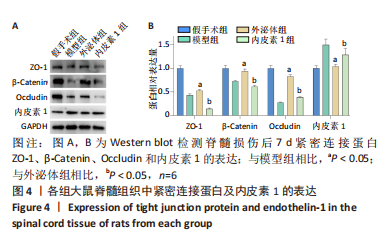
[1] KUMAR R, LIM J, MEKARY RA, et al. Traumatic Spinal Injury: Global Epidemiology and Worldwide Volume. World Neurosurg. 2018;113: e345-e363.
[2] FAN B, WEI Z, YAO X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866.
[3] TAKAHASHI A, NAKAJIMA H, UCHIDA K, et al. Comparison of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Isolated from Murine Adipose Tissue and Bone Marrow in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(7):1126-1139.
[4] MATSUSHITA T, LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, et al. Diffuse and persistent blood-spinal cord barrier disruption after contusive spinal cord injury rapidly recovers following intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Neurol. 2015;267:152-164.
[5] ABBASZADEH HA, NIKNAZAR S, DARABI S, et al. Stem cell transplantation and functional recovery after spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anat Cell Biol. 2018;51(3):180-188.
[6] WANG C, SHI D, SONG X, et al. Calpain inhibitor attenuates ER stress-induced apoptosis in injured spinal cord after bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation. Neurochem Int. 2016;97:15-25.
[7] 张勇,马迅,孙麟,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体减轻大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞氧糖剥夺/复氧损伤所致的水肿[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):4011-4017.
[8] SUN G, LI G, LI D, et al. hucMSC derived exosomes promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury mice via attenuating inflammation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:194-204.
[9] LIU W, WANG Y, GONG F, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury by Suppressing the Activation of A1 Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(3):469-484.
[10] MCKENZIE AL, HALL JJ, AIHARA N, et al. Immunolocalization of endothelin in the traumatized spinal cord: relationship to blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(3):257-268.
[11] SALZMAN SK, ACOSTA R, BECK G, et al. Spinal endothelin content is elevated after moderate local trauma in the rat to levels associated with locomotor dysfunction after intrathecal injection. J Neurotrauma. 1996;13(2):93-101.
[12] 姜亮,刘忠军,党耕町.内皮素在急性脊髓损伤中的变化[J].中华骨科杂志,1998,18(10):594-597.
[13] 刘明明,程建,马勇,等.脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障病变机制研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015,50(12):1827-1830.
[14] 彭新生,李佛保,潘滔,等.内皮素与脊髓损伤后血脊屏障损害的关系[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2000,10(5):280-282.
[15] REN ZW, ZHOU JG, XIONG ZK, et al. Effect of exosomes derived from MiR-133b-modified ADSCs on the recovery of neurological function after SCI. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(1):52-60.
[16] HUANG JH, YIN XM, XU Y, et al. Systemic Administration of Exosomes Released from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Attenuates Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Promotes Angiogenesis after Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(24):3388-3396.
[17] KORNILOV R, PUHKA M, MANNERSTRÖM B, et al. Efficient ultrafiltration-based protocol to deplete extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1422674.
[18] HU Y, RAO SS, WANG ZX, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):169-184.
[19] FRANZEN CA, BLACKWELL RH, TODOROVIC V, et al. Urothelial cells undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition after exposure to muscle invasive bladder cancer exosomes. Oncogenesis. 2015;4(8):e163.
[20] EKSTRÖM EJ, BERGENFELZ C, VON BÜLOW V, et al. WNT5A induces release of exosomes containing pro-angiogenic and immunosuppressive factors from malignant melanoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:88.
[21] 周燕,王琳,裴双,等.骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可减少脊髓损伤后A1型星形胶质细胞的活化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21): 3294-3301.
[22] RONG Y, LIU W, LV C, et al. Neural stem cell small extracellular vesicle-based delivery of 14-3-3t reduces apoptosis and neuroinflammation following traumatic spinal cord injury by enhancing autophagy by targeting Beclin-1. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(18):7723-7745.
[23] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[24] 胡伟,谢兴奇,屠冠军.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):992-998.
[25] JIN LY, LI J, WANG KF, et al. Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier in Spinal Cord Injury: A Review. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(9):1203-1224.
[26] MANNELLO F, GAZZANELLI G. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases and programmed cell death: conundrums, controversies and potential implications. Apoptosis. 2001;6(6):479-482.
[27] BARTANUSZ V, JEZOVA D, ALAJAJIAN B, et al. The blood-spinal cord barrier: morphology and clinical implications. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(2):194-206.
[28] FIGLEY SA, KHOSRAVI R, LEGASTO JM, et al. Characterization of vascular disruption and blood-spinal cord barrier permeability following traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2014;31(6):541-552.
[29] ZHENG B, YE L, ZHOU Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor attenuates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption via PI3K/Akt/Rac1 pathway after acute spinal cord injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(6):1062-1075.
[30] YE LB, YU XC, XIA QH, et al. Erratum to: Regulation of Caveolin-1 and Junction Proteins by bFGF Contributes to the Integrity of Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier and Functional Recovery. Neurotherapeutics. 2017;14(3):828-829.
[31] FlACK JA, SHARMA KD, XIE JY. Delving into the recent advancements of spinal cord injury treatment: a review of recent progress. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(2):283-291.
[32] CHEN X, LAN X, ROCHE I, et al. Caffeine protects against MPTP-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction in mouse striatum. J Neurochem. 2008;107(4):1147-1157.
[33] LIU C, YANG TH, LI HD, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are a potential treatment for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(10):2246-2251.
[34] YU B, ZHANG X, LI X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.
[35] VILLARROYA-BELTRI C, BAIXAULI F, GUTIÉRREZ-VÁZQUEZ C, et al. Sorting it out: regulation of exosome loading. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;28:3-13.
[36] VLASSOV AV, MAGDALENO S, SETTERQUIST R, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(7):940-948.
[37] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745.
[38] LIEBNER S, CZUPALLA CJ, WOLBURG H. Current concepts of blood-brain barrier development. Int J Dev Biol. 2011;55(4-5):467-476.
[39] LEE JY, KIM HS, CHOI HY, et al. Fluoxetine inhibits matrix metalloprotease activation and prevents disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 8):2375-2389.
[40] PARK CS, LEE JY, CHOI HY, et al. Protocatechuic acid improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury by attenuating blood-spinal cord barrier disruption and hemorrhage in rats. Neurochem Int. 2019;124:181-192.
[41] ZHANG Q, WANG J, GU Z, et al. Effect of lycopene on the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury in mice. Biosci Trends. 2016;10(4): 288-293.
[42] YU DS, WANG YS, BI YL, et al. Salvianolic acid A ameliorates the integrity of blood-spinal cord barrier via miR-101/Cul3/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2017;1657:279-287.
[43] GUO J, LI Y, HE Z, et al. Targeting endothelin receptors A and B attenuates the inflammatory response and improves locomotor function following spinal cord injury in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(1):74-82.
[44] SINESCU C, POPA F, GRIGOREAN VT, et al. Molecular basis of vascular events following spinal cord injury. J Med Life. 2010;3(3):254-261.
[45] MICHINAGA S, KIMURA A, HATANAKA S, et al. Delayed Administration of BQ788, an ETB Antagonist, after Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury Promotes Recovery of Blood-Brain Barrier Function and a Reduction of Cerebral Edema in Mice. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(13):1481-1494.
[46] HAO Y, MIAO J, LIU W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Carry MicroRNA-125a to Protect Against Diabetic Nephropathy by Targeting Histone Deacetylase 1 and Downregulating Endothelin-1. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:1405-1418.
[47] ZHANG Y, CHEN L, LI Z, et al. Endothelin-1, over-expressed in SOD1G93A mice, aggravates injury of NSC34-hSOD1G93A cells through complicated molecular mechanism revealed by quantitative proteomics analysis. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1069617.
[48] A JC, LI ZY, LONG QF, et al. MiR-379-5p improved locomotor function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by reducing endothelin 1 and inhibiting astrocytes expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(22):9738-9745.
|