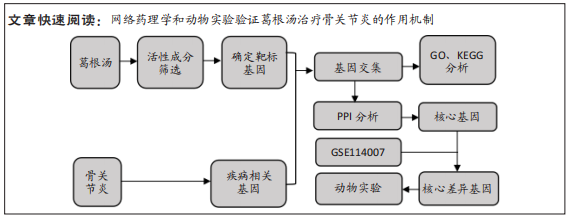
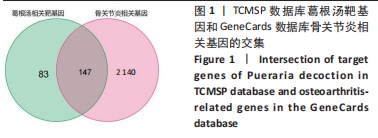
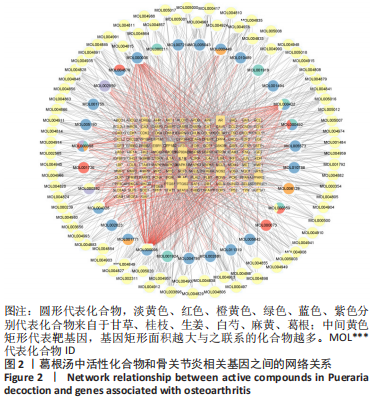
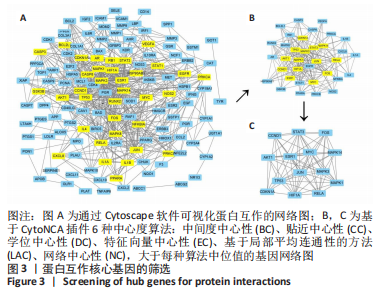
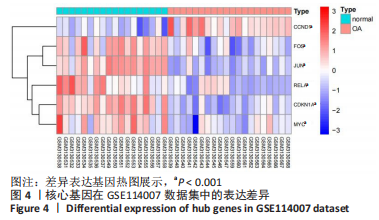
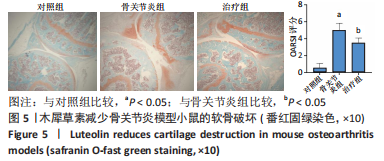
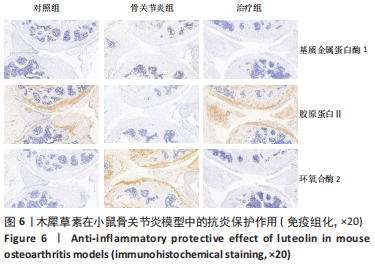
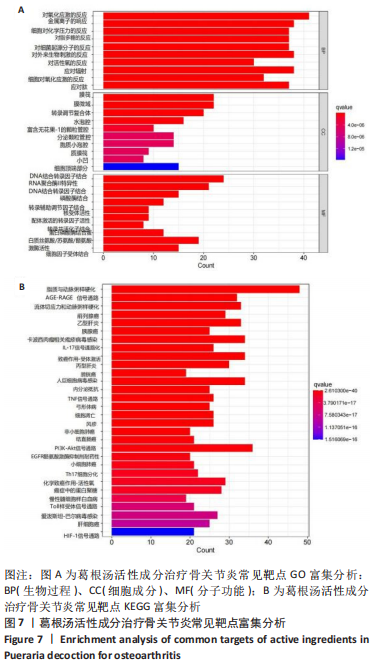
[1] EMERY CA, WHITTAKER JL, MAHMOUDIAN A, et al. Establishing outcome measures in early knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(7):438-448.
[2] XIONG Y, MI BB, LIU MF, et al. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2246-2256.
[3] COHEN SP, VASE L, HOOTEN WM. Chronic pain: an update on burden, best practices, and new advances. Lancet. 2021;397(10289):2082-2097.
[4] CHEN S, CHEN M, WU X, et al. Global, regional and national burden of low back pain 1990-2019: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. J Orthop Translat. 2021;32:49-58.
[5] MILLER RJ, MALFAIT AM, MILLER RE. The innate immune response as a mediator of osteoarthritis pain. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):562-571.
[6] YOU R, LIU S, TAN J. Screening and identification of osteoarthritis related differential genes and construction of a risk prognosis model based on bioinformatics analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(8):444.
[7] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, SMITH E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819-828.
[8] LU K, MA F, YI D, et al. Molecular signaling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;32:21-27.
[9] VINCENT TL. Targeting mechanotransduction pathways in osteoarthritis: a focus on the pericellular matrix. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(3):449-454.
[10] SHEN S, WU Y, CHEN J, et al. CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):826-836.
[11] SCHULZE-TANZIL G. Intraarticular Ligament Degeneration Is Interrelated with Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019;8(9):990.
[12] MEDVEDEVA EV, GREBENIK EA, GORNOSTAEVA SN, et al. Repair of Damaged Articular Cartilage: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(8):2366.
[13] BHOSALE AM, RICHARDSON JB. Articular cartilage: structure, injuries and review of management. Br Med Bull. 2008;87:77-95.
[14] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781.
[15] IOLASCON G, GIMÉNEZ S, MOGYORÓSI D. A Review of Aceclofenac: Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Musculoskeletal Disorders. J Pain Res. 2021;14: 3651-3663.
[16] WONG G. Pharmacological management of chronic non-cancer pain in frail older people. Aust Prescr. 2022;45(1):2-7.
[17] 周军,方素萍,齐云霍,等.葛根汤对大鼠佐剂性关节炎防治作用研究[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2001,7(2):29-30,38.
[18] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[19] LIN Z, ZHANG Z, YE X, et al. Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking to predict the mechanism of Huangqi in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2022;17(5):e0263291.
[20] LIU T, SHAO Q, WANG W, et al. Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to decipher the mechanism of the Chinese herbal prescription JieZe-1 in protecting against HSV-2 infection. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1): 451-466.
[21] WU Z, LI W, LIU G, et al. Network-Based Methods for Prediction of Drug-Target Interactions. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1134.
[22] KONG Y, MA X, ZHANG X, et al. The potential mechanism of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi promoting osteogenetic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental identification. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):10640-10653.
[23] LIU S, ZHANG Q, LIU W, et al. Research on the mechanisms of Shu Yu wan in the treatment of cervical cancer based on network pharmacology analyses and molecular docking technology. Nat Prod Res. 2023;37(4):646-650.
[24] CHU M, GAO T, ZHANG X, et al. Elucidation of Potential Targets of San-Miao-San in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:7663212.
[25] CHEN P, ZHOU J, RUAN A, et al. Cinnamic Aldehyde, the main monomer component of Cinnamon, exhibits anti-inflammatory property in OA synovial fibroblasts via TLR4/MyD88 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(3):913-924.
[26] GOYAL A, AGRAWAL N. Quercetin: A Potential Candidate for the Treatment of Arthritis. Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(4):325-335.
[27] WANG XP, XIE WP, BI YF, et al. Quercetin suppresses apoptosis of chondrocytes induced by IL-1β via inactivation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(5):468.
[28] TSAI SW, LIN CC, LIN SC, et al. Isorhamnetin ameliorates inflammatory responses and articular cartilage damage in the rats of monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019;41(4):504-512.
[29] LO S, LEUNG E, FEDRIZZI B, et al. Syntheses of mono-acylated luteolin derivatives, evaluation of their antiproliferative and radical scavenging activities and implications on their oral bioavailability. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12595.
[30] XIE K, CHAI YS, LIN SH, et al. Luteolin Regulates the Differentiation of Regulatory T Cells and Activates IL-10-Dependent Macrophage Polarization against Acute Lung Injury. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:8883962.
[31] JIA T, QIAO J, GUAN D, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Licochalcone A on IL-1β-Stimulated Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2017;40(6):1894-1902.
[32] HUANG X, PAN Q, MAO Z, et al. Kaempferol inhibits interleukin‑1β stimulated matrix metalloproteinases by suppressing the MAPK‑associated ERK and P38 signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(3):2697-2704.
[33] GAUR R, MENSAH KA, STRICKER J, et al. CC-99677, a novel, oral, selective covalent MK2 inhibitor, sustainably reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022;24(1):199.
[34] MIMPEN JY, BALDWIN MJ, CRIBBS AP, et al. Interleukin-17A Causes Osteoarthritis-Like Transcriptional Changes in Human Osteoarthritis-Derived Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts In Vitro. Front Immunol. 2021;12:676173.
[35] AMATYA N, GARG AV, GAFFEN SL. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017;38(5):310-322.
[36] SNELLING SJ, BAS S, PUSKAS GJ, et al. Presence of IL-17 in synovial fluid identifies a potential inflammatory osteoarthritic phenotype. PLoS One. 2017;12(4):e0175109.
[37] ZHANG K, LI Z, LU Y, et al. Silencing of Vangl2 attenuates the inflammation promoted by Wnt5a via MAPK and NF-κB pathway in chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):136.
[38] LU J, ZHANG H, PAN J, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):142.
[39] BARRETO G, MANNINEN M, EKLUND KK. Osteoarthritis and Toll-Like Receptors: When Innate Immunity Meets Chondrocyte Apoptosis. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(4):65.
[40] WON Y, YANG JI, PARK S, et al. Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein and CD14, Cofactors of Toll-like Receptors, Are Essential for Low-Grade Inflammation-Induced Exacerbation of Cartilage Damage in Mouse Models of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(8):1451-1460.
[41] QI W, CHEN Y, SUN S, et al. Inhibiting TLR4 signaling by linarin for preventing inflammatory response in osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(4):5369-5382.
[42] FERNÁNDEZ-TORRES J, ZAMUDIO-CUEVAS Y, MARTÍNEZ-NAVA GA, et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIFs) in the articular cartilage: a systematic review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(12):2800-2810.
[43] BOUAZIZ W, SIGAUX J, MODROWSKI D, et al. Interaction of HIF1α and β-catenin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and prevents cartilage damage in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(19):5453-5458.
[44] HAN M, LIN J, YANG Y, et al. Xinshuaining preparation protects H9c2 cells from H2O2-induced oxidative damage through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf-2 signaling pathway. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2022:1-9. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2022.2131806.
[45] LI W, MAO Y, HUA B, et al. Sasanquasaponin inhibited epithelial to mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Smad pathways. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):1865-1875.
[46] MEHRA S, SRINIVASAN S, SINGH S, et al. Urolithin A attenuates severity of chronic pancreatitis associated with continued alcohol intake by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2022;323(4):G375-G386.
[47] CHEN P, WU S, DONG X, et al. Formosanin C induces autophagy-mediated apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Hematology. 2022;27(1):977-986.
[48] JIANG Y, XIE Z, YU J, et al. Resveratrol inhibits IL-1β-mediated nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3): BSR20190043.
[49] PARK C, JEONG JW, LEE DS, et al. Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2308.
[50] ZHANG XF, MA JX, WANG YL, et al. Calcyclin (S100A6) Attenuates Inflammatory Response and Mediates Apoptosis of Chondrocytes in Osteoarthritis via the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):1094-1101.
[51] TONG KM, SHIEH DC, CHEN CP, et al. Leptin induces IL-8 expression via leptin receptor, IRS-1, PI3K, Akt cascade and promotion of NF-kappaB/p300 binding in human synovial fibroblasts. Cell Signal. 2008;20(8):1478-1488.
|