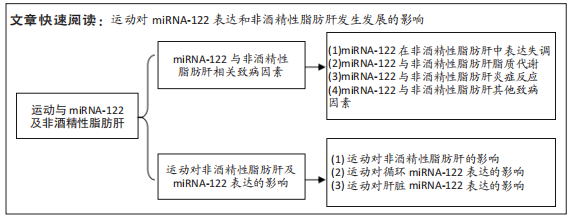
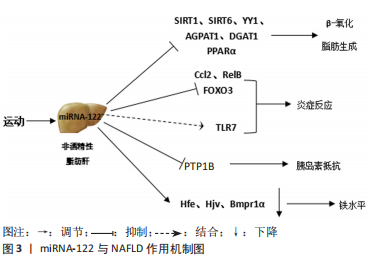
[1] FARZANEGI P, DANA A, EBRAHIMPOOR Z, et al. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur J Sport Sci. 2019;19(7):994-1003.
[2] HSU SH, WANG B, KOTA J, et al. Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2871-2883.
[3] GIRARD M, JACQUEMIN E, MUNNICH A, et al. miR-122, a paradigm for the role of microRNAs in the liver. J Hepatol. 2008;48(4):648-656.
[4] SEKINE S, OGAWA R, ITO R, et al. Disruption of Dicer1 induces dysregulated fetal gene expression and promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(7): 2304-2315.e1-4.
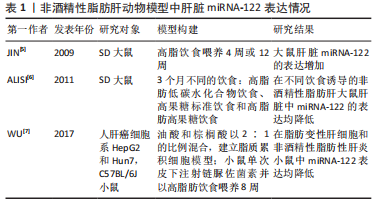
[5] JIN X, YE YF, CHEN SH, et al. MicroRNA expression pattern in different stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41(4): 289-297.
[6] ALISI A, DA SACCO L, BRUSCALUPI G, et al. Mirnome analysis reveals novel molecular determinants in the pathogenesis of diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lab Invest. 2011;91(2):283-293.
[7] WU GY, RUI C, CHEN JQ, et al. MicroRNA-122 Inhibits Lipid Droplet Formation and Hepatic Triglyceride Accumulation via Yin Yang 1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(4): 1651-1664.
[8] CHEUNG O, PURI P, EICKEN C, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with altered hepatic MicroRNA expression. Hepatology. 2008;48(6):1810-1820.
[9] 黄慧. MicroRNA122在非酒精性脂肪肝病的表达及临床意义[D].南充:川北医学院,2013.
[10] MIYAAKI H, ICHIKAWA T, KAMO Y, et al. Significance of serum and hepatic microRNA-122 levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2014; 34(7):e302-e307.
[11] PIROLA CJ, FERNÁNDEZ GIANOTTI T, CASTAÑO GO, et al. Circulating microRNA signature in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: from serum non-coding RNAs to liver histology and disease pathogenesis. Gut. 2015;64(5):800-812.
[12] CERMELLI S, RUGGIERI A, MARRERO JA, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with chronic hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS one. 2011;6(8):e23937.
[13] YAMADA H, SUZUKI K, ICHINO N, et al. Associations between circulating microRNAs (miR-21, miR-34a, miR-122 and miR-451) and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;424:99-103.
[14] 陈轶,陈益耀,蔡蔓妮,等.miR-122在非酒精性脂肪肝病患者血清中的表达及其临床意义[J].武警医学,2015,26(1):11-12,15.
[15] SALVOZA NC, KLINZING DC, GOPEZ-CERVANTES J, et al. Association of Circulating Serum miR-34a and miR-122 with Dyslipidemia among Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153497.
[16] AUGUET T, ARAGONÈS G, BERLANGA A, et al. miR33a/miR33b* and miR122 as Possible Contributors to Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Obese Women with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10):1620.
[17] JAMPOKA K, MUANGPAISARN P, KHONGNOMNAN K, et al. Serum miR-29a and miR-122 as Potential Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Microrna. 2018;7(3):215-222.
[18] DAN Y, ZHANG T, LOU G, et al. Plasma miR-17, miR-20a, miR-20b and miR-122 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of NAFLD in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Life Sci. 2018;208:201-207.
[19] LIU CH, AMPUERO J, GIL-GÓMEZ A, et al. miRNAs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2018;69(6):1335-1348.
[20] BRANDT S, ROOS J, INZAGHI E, et al. Circulating levels of miR-122 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in pre-pubertal obese children. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13(3):175-182.
[21] 张广玉,钤培国,孙晓娜,等.消脂护肝汤对非酒精性脂肪性肝炎患者肝脏的影响[J].中医学报,2019,34(8):1735-1739.
[22] DONNELLY KL, SMITH CI, SCHWARZENBERG SJ, et al. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(5):1343-1351.
[23] LAMBERT JE, RAMOS-ROMAN M, BROWNING JD, et al. Increased De Novo Lipogenesis Is a Distinct Characteristic of Individuals With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(3):726-735.
[24] JU UI, JEONG DW, SEO J, et al. Neddylation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c is a potential therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):283.
[25] 刘丽雅.复方茵陈脂肝颗粒调控miR-122及其下游通路治疗非酒精性脂肪肝病的作用机制研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2014.
[26] SU Q, KUMAR V, SUD N, et al. MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of progressive liver injury in NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;129:54-63.
[27] CHAI C, RIVKIN M, BERKOVITS L, et al. Metabolic Circuit Involving Free Fatty Acids, microRNA 122, and Triglyceride Synthesis in Liver and Muscle Tissues. Gastroenterology. 2017;153(5):1404-1415.
[28] CHAI C, COX B, YAISH D, et al. Agonist of RORA Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Progression in Mice via Up-regulation of MicroRNA 122. Gastroenterology. 2020;159(3):999-1014.e9.
[29] ELHANATI S, BEN-HAMO R, KANFI Y, et al. Reciprocal Regulation between SIRT6 and miR-122 Controls Liver Metabolism and Predicts Hepatocarcinoma Prognosis. Cell Rep. 2016;14(2):234-242.
[30] 杨立英.水飞蓟宾通过调控miR-122的表达改善非酒精性脂肪肝的体内外研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2019.
[31] ESAU C, DAVIS S, MURRAY SF, et al. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006;3(2):87-98.
[32] LONG JK, DAI W, ZHENG YW, et al. miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Med. 2019;25(1):26.
[33] SENDI H, MEAD I, WAN M, et al. miR-122 inhibition in a human liver organoid model leads to liver inflammation, necrosis, steatofibrosis and dysregulated insulin signaling. PLoS One. 2018;13(7):e0200847.
[34] SCHUSTER S, CABRERA D, ARRESE M, et al. Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(6):349-364.
[35] TAN DY, SHI HY, LI CP, et al. Effect of nuclear factor-κB and angiotensin Ⅱ receptor type 1 on the pathogenesis of rat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(19):5877-5883.
[36] HAJIGHASEM A, FARZANEGI P, MAZAHERI Z. Effects of combined therapy with resveratrol, continuous and interval exercises on apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory biomarkers in the liver of old rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2019;125(2):142-149.
[37] EL-DIN SH, SABRA AN, HAMMAM OA, et al. Pharmacological and antioxidant actions of garlic and.or onion in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in rats. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 2014;44(2):295-308.
[38] CLARKE JD, SHARAPOVA T, LAKE AD, et al. Circulating microRNA 122 in the methionine and choline-deficient mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Appl Toxicol. 2014;34(6):726-732.
[39] HSU KH, WEI CW, SU YR, et al. Upregulation of RelB in the miR-122 knockout mice contributes to increased levels of proinflammatory chemokines/cytokines in the liver and macrophages. Immunol Lett. 2020;226:22-30.
[40] TSAI WC, HSU SD, HSU CS, et al. MicroRNA-122 plays a critical role in liver homeostasis and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(8):2884-2897.
[41] WANG Y, LIANG H, JIN F, et al. Injured liver-released miRNA-122 elicits acute pulmonary inflammation via activating alveolar macrophage
TLR7 signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(13):6162-6171.
[42] CASTOLDI M, VUJIC SPASIC M, ALTAMURA S, et al. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122 controls systemic iron homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(4):1386-1396.
[43] YANG YM, SEO SY, KIM TH, et al. Decrease of microRNA-122 causes hepatic insulin resistance by inducing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, which is reversed by licorice flavonoid. Hepatology. 2012;56(6):2209-2220.
[44] BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism. 2016;65(8):1038-1048.
[45] CHALASANI N, YOUNOSSI Z, LAVINE JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328-357.
[46] STEVANOVI J, BELEZA J, COXITO P, et al. Physical exercise and liver “fitness”: Role of mitochondrial function and epigenetics-related mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Metab. 2020;32:1-14.
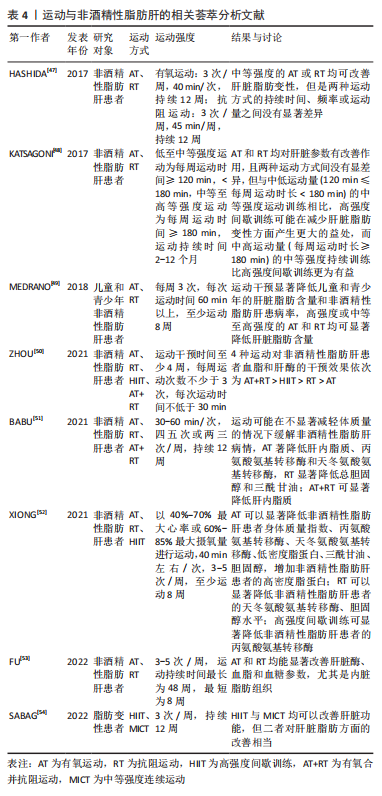
[47] HASHIDA R, KAWAGUCHI T, BEKKI M, et al. Aerobic vs. resistance exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. J Hepatol. 2017;66(1):142-152.
[48] KATSAGONI CN, GEORGOULIS M, PAPATHEODORIDIS GV, et al. Effects of lifestyle interventions on clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2017;68:119-132.
[49] MEDRANO M, CADENAS-SANCHEZ C, ALVAREZ-BUENO C, et al. Evidence-Based Exercise Recommendations to Reduce Hepatic Fat Content in Youth- a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;61(2):222-231.
[50] ZHOU BJ, HUANG G, WANG W, et al. Intervention effects of four exercise modalities on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(24):7687-7697.
[51] BABU AF, CSADER S, LOK J, et al. Positive Effects of Exercise Intervention without Weight Loss and Dietary Changes in NAFLD-Related Clinical Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021;13(9):3135.
[52] XIONG Y, PENG Q, CAO C, et al. Effect of Different Exercise Methods on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3242.
[53] FU L, ZHANG W, AO Y, et al. Efficacy of aerobic and resistance exercises in improving visceral adipose in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Z Gastroenterol. 2022;60(11):1644-1658.
[54] SABAG A, BARR L, ARMOUR M, et al. The Effect of High-intensity Interval Training vs Moderate-intensity Continuous Training on Liver Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(3):862-881.
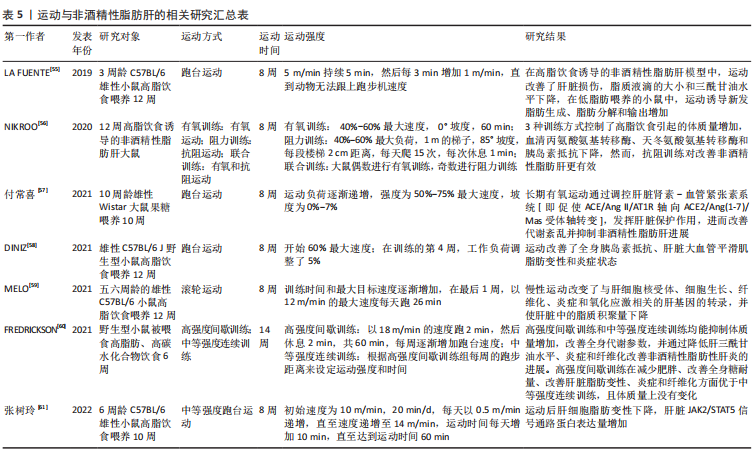
[55] LA FUENTE FP, QUEZADA L, SEPULVEDA C, et al. Exercise regulates lipid droplet dynamics in normal and fatty liver. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019; 1864(12):158519.
[56] NIKROO H, HOSSEINI SRA, FATHI M, et al. The effect of aerobic, resistance, and combined training on PPAR-α, SIRT1 gene expression, and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD male rats. Physiol Behav. 2020;227:113149.
[57] 付常喜,陆阿明,孙一.有氧运动调控肝脏肾素-血管紧张素系统对大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病的作用与机制[J].山东体育学院学报,2021,37(4):75-85.
[58] DINIZ TA, DE LIMA JUNIOR EA, TEIXEIRA AA, et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-alpha signaling in obese mice. Life Sci. 2021;266:118868.
[59] MELO L, BILICI M, HAGAR A, et al. The effect of endurance training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Physiol Rep. 2021;9(15):e14926.
[60] FREDRICKSON G, BARROW F, DIETSCHE K, et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101270.
[61] 张树玲,李军汉,王佳倩,等.有氧运动干预非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏JAK2/STAT5信号通路的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2690-2695.
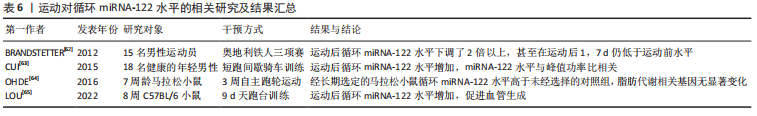
[62] BRANDSTETTER S. Exhaustive exercise such as an Ironman triathlon alters MicroRNA expression pattern in whole blood. Wien: Universität Wien,2012.
[63] CUI SF, LI W, NIU J, et al. Acute responses of circulating microRNAs to low-volume sprint interval cycling. Front Physiol. 2015;6:311.
[64] OHDE D, BRENMOEHL J, WALZ C, et al. Comparative analysis of hepatic miRNA levels in male marathon mice reveals a link between obesity and endurance exercise capacities. J Comp Physiol B. 2016;186(8):1067-1078.
[65] LOU J, WU J, FENG M, et al. Exercise promotes angiogenesis by enhancing endothelial cell fatty acid utilization via liver-derived extracellular vesicle miR-122-5p. J Sport Health Sci. 2022;11(4):495-508.
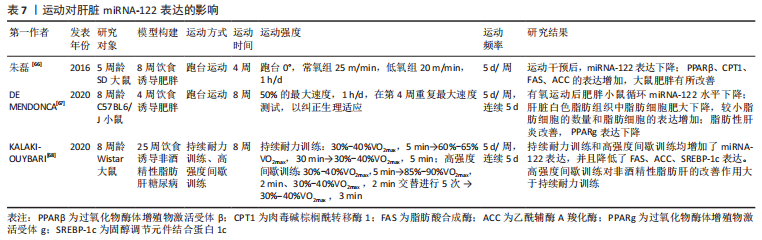
[66] 朱磊.低氧训练诱导miR-27/PPARγ、miR-122/PPARβ调控肥胖大鼠肝脏脂代谢机理的研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2016.
[67] DE MENDONCA M, ROCHA KC, DE SOUSA E, et al. Aerobic exercise training regulates serum extracellular vesicle miRNAs linked to obesity to promote their beneficial effects in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2020;319(3):E579-E591.
[68] KALAKI-JOUYBARI F, SHANAKI M, DELFAN M, et al. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) alleviated NAFLD feature via miR-122 induction in liver of high-fat high-fructose diet induced diabetic rats. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2020;126(3):242-249. |