[1] JAMES SL, CASTLE CD, DINGELS ZV, et al. Global injury morbidity and mortality from 1990 to 2017: results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Inj Prev. 2020;26(1):96-114.
[2] OGURTSOVA K, DA ROCHA FERNANDES JD, HUANG Y, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40-50.
[3] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. 12. Older Adults: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(1):139-147.
[4] ROSENBERG IH. Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr. 1997; 127(5l):990-991.
[5] 姜珊,康琳,刘晓红.2019亚洲肌少症诊断及治疗共识解读[J].中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(4):373-376.
[6] IZZO A, MASSIMINO E, RICCARDI G, et al. A Narrative Review on Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Associated Factors. Nutrients. 2021;13(1):183.
[7] 白友菊,康霜,李颖,等.基于简易指标的综合指数对老年2型糖尿病患者肌少症的诊断价值[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(8):662-667.
[8] 陆玉凤,刘富甜,朱小红,等.住院2型糖尿病患者肌少症相关因素影响分析[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2021,29(4):284-287.
[9] KIM YK, LEE HS, RYU JJ, et al. Sarcopenia increases the risk for mortality in patients who undergo amputation for diabetic foot. J Foot Ankle Res. 2018;19(11):32.
[10] BAUMGARTNER RN, WAYNE SJ, WATERS DL, et al. Sarcopenic obesity predicts instrumental activities of daily living disability in the elderly. Obes Res. 2004;12(12):1995-2004.
[11] No authors listed. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 21-1987. A 68-year-old man with diabetes mellitus and progressive muscle weakness. N Engl J Med. 1987;316(21):1326-1335.
[12] No authors listed. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 50-1991. A 71-year-old woman with a sensorimotor neuropathy and radiographically demonstrable abnormalities. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(24):1723-1735.
[13] BAUMGARTNER RN, KOEHLER KM, GALLAGHER D, et al. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am J Epidemiol. 1998; 147(8):755-763.
[14] SAADEDDINE D, ITANI L, KREIDIEH D, et al. Association between Levels of Physical Activity, Sarcopenia, Type 2 Diabetes and the Quality of Life of Elderly People in Community Dwellings in Lebanon. Geriatrics (Basel). 2021;6(1):28.
[15] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423.
[16] ANBALAGAN VP, VENKATARAMAN V, PRADEEPA R, et al. The prevalence of presarcopenia in Asian Indian individuals with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15(9):768-775.
[17] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014; 15(2):95-101.
[18] WANG T, FENG X, ZHOU J, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risks of sarcopenia and pre-sarcopenia in Chinese elderly. Sci Rep. 2016;13(6):38937.
[19] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31.
[20] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315-409.
[21] 李颖,林文弢,翁锡全.不同运动强度干预2型糖尿病模型大鼠的内脂素及糖代谢变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(26):4196-4200.
[22] 张建伟,吕邵钧,王继,等.太极拳对不同性别2型糖尿病患者治疗效果的比较研究[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,55(1): 545-550.
[23] 何清华,常鑫淼,孙明晓,等.2型糖尿病患者肌肉质量和力量的变化特点[J].中华老年医学杂志,2020,39(5):550-554.
[24] HOUSTON DK, NEIBERG RH, MILLER ME, et al. Physical Function Following a Long-Term Lifestyle Intervention Among Middle Aged and Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: The Look AHEAD Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018;73(11):1552-1559.
[25] DE FREITAS MM, DE OLIVEIRA VLP, GRASSI T, et al. Difference in sarcopenia prevalence and associated factors according to 2010 and 2018 European consensus (EWGSOP) in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp Gerontol. 2020;132:110835.
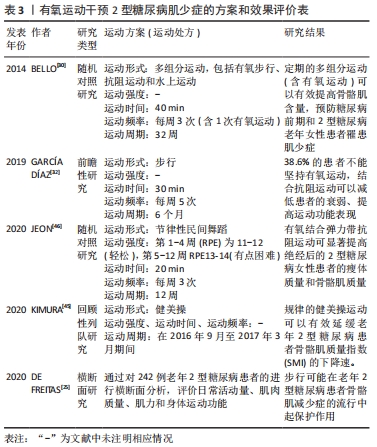
[26] KNOWLER WC, BARRETT-CONNOR E, FOWLER SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002;46(6):393-403.
[27] SAZLINA SG, LEE PY, CHAN YM, et al. The prevalence and factors associated with sarcopenia among community living elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus in primary care clinics in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2020; 15(5):e0233299.
[28] STEFFL M, BOHANNON RW, SONTAKOVA L, et al. Relationship between sarcopenia and physical activity in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2017;12:835-845.
[29] GORDON PL, VANNIER E, HAMADA K, et al. Resistance training alters cytokine gene expression in skeletal muscle of adults with type 2 diabetes. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006;19(4):739-749.
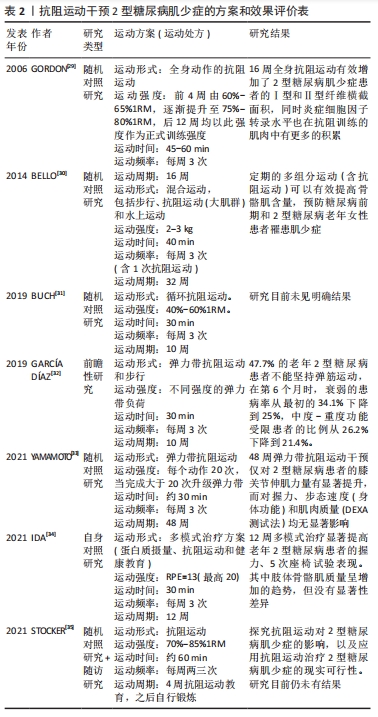
[30] BELLO M, SOUSA MC, NETO G, et al. The effect of a long-term, community-based exercise program on bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. J Hum Kinet. 2014;43:43-48.
[31] BUCH A, ELDOR R, KIS O, et al. The effect of circuit resistance training, empagliflozin or “vegeterranean diet” on physical and metabolic function in older subjects with type 2 diabetes: a study protocol for a randomized control trial (CEV-65 trial). BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):228.
[32] GARCÍA DÍAZ E, ALONSO RAMÍREZ J, HERRERA FERNÁNDEZ N, et al. Effect of strength exercise with elastic bands and aerobic exercise in the treatment of frailty of the elderly patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2019;66(9):563-570.
[33] YAMAMOTO Y, NAGAI Y, KAWANABE S, et al. Effects of resistance training using elastic bands on muscle strength with or without a leucine supplement for 48 weeks in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr J. 2021;68(3):291-298.
[34] IDA S, KANEKO R, IMATAKA K, et al. Multimodal treatment program for elderly diabetic patients with sarcopenia improves the muscle strength and physical function. Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 2021;58(1):143-151.
[35] STOCKER R, SHAW J, TAYLOR GS, et al. EXercise to Prevent frailty and Loss Of independence in insulin treated older people with DiabetEs (EXPLODE): protocol for a feasibility randomised controlled trial (RCT). BMJ Open. 2021;11(12):e048932.
[36] AL-OZAIRI E, ALSAEED D, ALROUDHAN D, et al. Skeletal Muscle and Metabolic Health: How Do We Increase Muscle Mass and Function in People with Type 2 Diabetes?. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021;106(2):309-317.
[37] 王继,周越.2型糖尿病与肌萎缩研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2017,36(7):645-650.
[38] IBANEZ J, GOROSTIAGA EM, ALONSO AM, et al. Lower muscle strength gains in older men with type 2 diabetes after resistance training . Journal of diabetes and its complications. 2008;22(2):112-118.
[39] GEIRSDOTTIR OG, ARNARSON A, BRIEM K, et al. Effect of 12-week resistance exercise program on body composition, muscle strength, physical function, and glucose metabolism in healthy, insulin-resistant, and diabetic elderly Icelanders. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012; 67(11):1259-1265.
[40] ATO S , KIDO K, SATO K, et al. Type 2 diabetes causes skeletal muscle atrophy but does not impair resistance training‐mediated myonuclear accretion and muscle mass gain in rats. Exp Physiol. 2019;104(10):1518-1531.
[41] APRÓ W, MOBERG M, HAMILTON DL, et al. Resistance exercise-induced S6K1 kinase activity is not inhibited in human skeletal muscle despite prior activation of AMPK by high-intensity interval cycling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015;308(6):470-581.
[42] MAZO CE, D’LUGOS AC, SWEENEY KR, et al. The effects of acute aerobic and resistance exercise on mTOR signaling and autophagy markers in untrained human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021;121(10): 2913-2924.
[43] SNIJDERS T, SMEETS JS, VAN KRANENBURG J, et al. Changes in myonuclear domain size do not precede muscle hypertrophy during prolonged resistance-type exercise training. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2016; 216(2):231-239.
[44] DARYABEYGI-KHOTBEHSARA R, WHITE KM, DJAFARIAN K, et al. Short-term effectiveness of a theory-based intervention to promote diabetes management behaviours among adults with type 2 diabetes in Iran: A randomised control trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(5):e13994.
[45] KIMURA T, OKAMURA T, IWAI K, et al. Japanese radio calisthenics prevents the reduction of skeletal muscle mass volume in people with type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):e001027.
[46] JEON YK, KIM SS, KIM JH, et al. Combined Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Training Reduces Circulating Apolipoprotein J Levels and Improves Insulin Resistance in Postmenopausal Diabetic Women. Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):103-112.
[47] CHEN GQ, MOU CY, YANG YQ, et al. Exercise training has beneficial anti-atrophy effects by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced MuRF1 upregulation in rats with diabetes. Life Sci. 2011;89(2):44-49.
[48] AKAGAWA M, MIYAKOSHI N, KASUKAWA Y, et al. Effects of activated vitamin D, alfacalcidol, and low-intensity aerobic exercise on osteopenia and muscle atrophy in type 2 diabetes mellitus model rats. PLoS One. 2018;13(10):e0204857.
[49] LIU HW, CHANG SJ. Moderate Exercise Suppresses NF-kappaB Signaling and Activates the SIRT1-AMPK-PGC1alpha Axis to Attenuate Muscle Loss in Diabetic db/db Mice. Front Physiol. 2018;9(6):36-46.
[50] 王继,杨中亚,张龙,等.AMPK/PGC-1α在有氧运动改善2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌萎缩中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3180-3185.
[51] 高前进,柏海平,王彦伟.有氧运动对糖尿病大鼠自噬性肌萎缩的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016,31(7):739-745.
[52] TAKAMURA Y, NOMURA M, UCHIYAMA A, et al. Effects of Aerobic Exercise Combined with Panaxatriol Derived from Ginseng on Insulin Resistance and Skeletal Muscle Mass in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2017;63(5):339-348.
[53] KIM HJ, LEE WJ. Low-intensity aerobic exercise training: inhibition of skeletal muscle atrophy in high-fat-diet-induced ovariectomized rats. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2017;21(3):19-25.
|