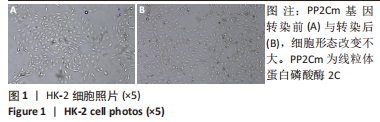
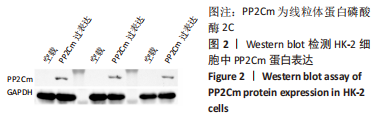
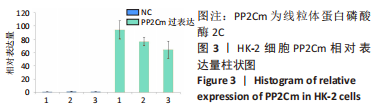
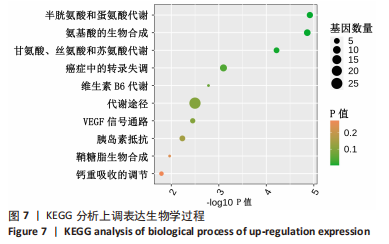
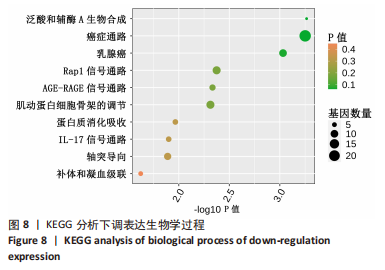
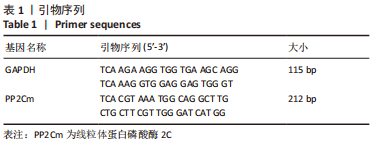
[1] ENE-IORDACHE B, PERICO N, BIKBOV B, et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): a cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob Health. 2016;4(5):e307-e319.
[2] HWANG SJ, LIN MY, CHEN HC. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China. Lancet. 2012;380(9838):213; author reply 214-216.
[3] GLASSOCK RJ, WARNOCK DG, DELANAYE P. The global burden of chronic kidney disease: estimates, variability and pitfalls. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017;13(2):104-114.
[4] 上海慢性肾脏病早发现及规范化诊治与示范项目专家组,高翔,梅长林.慢性肾脏病筛查诊断及防治指南[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2017,37(1):28-34.
[5] YAN MT, CHAO CT, LIN SH. Chronic Kidney Disease: Strategies to Retard Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):10084.
[6] SHIMADA K, MATSUI I, INOUE K, et al. Dietary casein, egg albumin, and branched-chain amino acids attenuate phosphate-induced renal tubulointerstitial injury in rats. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19038.
[7] ZHOU M, LU G, GAO C, et al. Tissue-specific and nutrient regulation of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase phosphatase, protein phosphatase 2Cm (PP2Cm). J Biol Chem. 2012;287(28):23397-23406.
[8] LU G, SUN H, KORGE P, et al. Functional characterization of a mitochondrial Ser/Thr protein phosphatase in cell death regulation. Methods Enzymol. 2009;457:255-273.
[9] LU G, SUN H, SHE P, et al. Protein phosphatase 2Cm is a critical regulator of branched-chain amino acid catabolism in mice and cultured cells. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1678-1687.
[10] LIAN K, DU C, LIU Y, et al. Impaired adiponectin signaling contributes to disturbed catabolism of branched-chain amino acids in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2015;64(1):49-59.
[11] 郭雄.支链氨基酸代谢紊乱在糖尿病小鼠不同应激下心肌易损性增加中的作用及机制研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2017.
[12] LIAN K, GUO X, WANG Q, et al. PP2Cm overexpression alleviates MI/R injury mediated by a BCAA catabolism defect and oxidative stress in diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;866:172796.
[13] WU G, GUO Y, LI M, et al. Exercise Enhances Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism and Decreases Cardiac Vulnerability to Myocardial Ischemic Injury. Cells. 2022;11(10):1706.
[14] DOLATABAD MR, GUO LL, XIAO P, et al. Crystal structure and catalytic activity of the PPM1K N94K mutant. J Neurochem. 2019;148(4):550-560.
[15] CARAGNANO A, ALEKSOVA A, BULFONI M, et al. Autophagy and Inflammasome Activation in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10):1519.
[16] ZHU Y, CUI H, XIA Y, et al. RIPK3-Mediated Necroptosis and Apoptosis Contributes to Renal Tubular Cell Progressive Loss and Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Rats. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0156729.
[17] GHERGHINA ME, PERIDE I, TIGLIS M, et al. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6):3188.
[18] NING B, GUO C, KONG A, et al. Calcium Signaling Mediates Cell Death and Crosstalk with Autophagy in Kidney Disease. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3204.
[19] WANG H, WANG Y, WANG X, et al. PTEN alleviates maladaptive repair of renal tubular epithelial cells by restoring CHMP2A-mediated phagosome closure. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12):1087.
[20] TESCH GH, MA FY, NIKOLIC-PATERSON DJ. Targeting apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in acute and chronic kidney disease. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020;303(10):2553-2560.
[21] FAN Z, CHEN J, YANG Q, et al. Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Reveal the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Chongcaoyishen Decoction Against Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:847812.
[22] XIE ZY, DONG W, ZHANG L, et al. NFAT inhibitor 11R-VIVIT ameliorates mouse renal fibrosis after ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(8):2081-2093.
[23] YEA JH, YOON YM, LEE JH, et al. Exosomes isolated from melatonin-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells improve kidney function by regulating inflammation and fibrosis in a chronic kidney disease mouse model. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:20417314211059624.
[24] YONG C, ZHANG Z, HUANG G, et al. Exploring the Critical Components and Therapeutic Mechanisms of Perilla frutescens L. in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease via Network Pharmacology. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:717744.
[25] PAN BF, GAO C, REN SX, et al. Regulation of PP2Cm expression by miRNA-204/211 and miRNA-22 in mouse and human cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36(12):1480-1486.
[26] HALL ECR, SEMENOVA EA, BONDAREVA EA, et al. Association of Genetically Predicted BCAA Levels with Muscle Fiber Size in Athletes Consuming Protein. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(3):397.
[27] CHEN S, YANG M, YANG H, et al. Identification and validation of a 9-gene signature for the prognosis of ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatical analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(19):1059.
[28] CUI M, ZHANG H, HAN S, et al. Screening of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Genes Genet Syst. 2022;97(3):101-110.
[29] WANG J, WANG W, ZHU F, et al. The role of branched chain amino acids metabolic disorders in tumorigenesis and progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113390.
[30] SANDOVAL-PLATA G, MORGAN K, ABHISHEK A. Variants in urate transporters, ADH1B, GCKR and MEPE genes associate with transition from asymptomatic hyperuricaemia to gout: results of the first gout versus asymptomatic hyperuricaemia GWAS in Caucasians using data from the UK Biobank. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(9):1220-1226.
[31] HU W, LIU Z, YU W, et al. Effects of PPM1K rs1440581 and rs7678928 on serum branched-chain amino acid levels and risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Med. 2021;53(1):1316-1326.
[32] LIU X, ZHANG F, ZHANG Y, et al. PPM1K Regulates Hematopoiesis and Leukemogenesis through CDC20-Mediated Ubiquitination of MEIS1 and p21. Cell Rep. 2018;23(5):1461-1475.
|