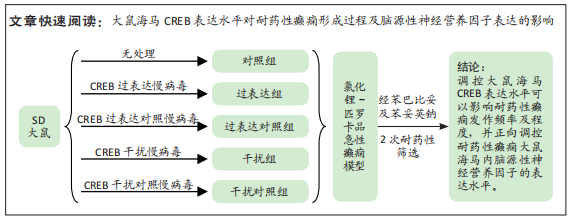
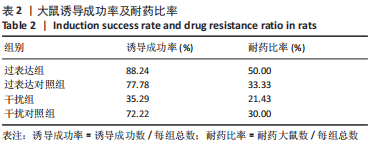
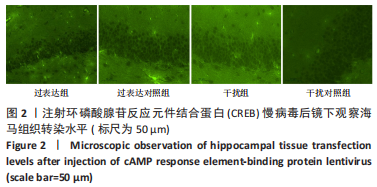
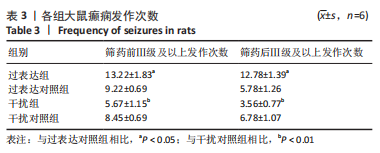
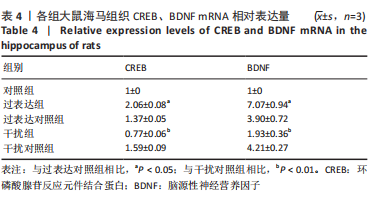
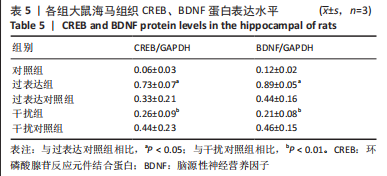
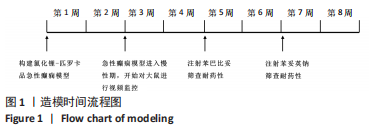
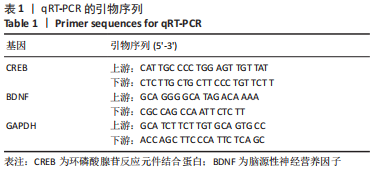
[1] FALCO-WALTER JJ, SCHEFFER IE, FISHER RS. The new definition and classification of seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2018;139:73-79.
[2] FISHER RS, ACEVEDO C, ARZIMANOGLOU A, et al. ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55(4):475-482.
[3] BERETTA S, CARONE D, ZANCHI C, et al. Long-term applicability of the new ILAE definition of epilepsy. Results from the PRO-LONG study. Epilepsia. 2017;58(9):1518-1523.
[4] 陈佳,吴逊.难治性癫痫诊疗新思路[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(9): 643-645.
[5] CHOW J, JENSEN M, AMINI H, et al. Dissecting the genetic basis of comorbid epilepsy phenotypes in neurodevelopmental disorders. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):65.
[6] KALILANI L, SUN X, PELGRIMS B, et al. The epidemiology of drug-resistant epilepsy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia. 2018;59(12):2179-2193.
[7] KATYAYAN A, DIAZ-MEDINA G. Epilepsy: Epileptic Syndromes and Treatment. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(3):779-795.
[8] YU J, SWIETEK B, PRODDUTUR A, et al. Dentate cannabinoid-sensitive interneurons undergo unique and selective strengthening of mutual synaptic inhibition in experimental epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;89: 23-35.
[9] BALESTRINI S, SISODIYA SM. Pharmacogenomics in epilepsy. Neurosci Lett. 2018;667:27-39.
[10] ARAIN FM, BOYD KL, GALLAGHER MJ. Decreased viability and absence-like epilepsy in mice lacking or deficient in the GABAA receptor α1 subunit. Epilepsia. 2012;53(8):e161-e165.
[11] RAOL YH, LUND IV, BANDYOPADHYAY S, et al. Enhancing GABA(A) receptor alpha 1 subunit levels in hippocampal dentate gyrus inhibits epilepsy development in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2006;26(44):11342-11346.
[12] SAURA CA, CARDINAUX JR. Emerging Roles of CREB-Regulated Transcription Coactivators in Brain Physiology and Pathology. Trends Neurosci. 2017;40(12):720-733.
[13] GUO J, WANG H, WANG Q, et al. Expression of p-CREB and activity-dependent miR-132 in temporal lobe epilepsy. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(5):1297-1306.
[14] PULIMOOD NS, RODRIGUES WDS JUNIOR, ATKINSON DA, et al. The Role of CREB, SRF, and MEF2 in Activity-Dependent Neuronal Plasticity in the Visual Cortex. J Neurosci. 2017;37(28):6628-6637.
[15] ZHU X, DUBEY D, BERMUDEZ C, et al. Suppressing cAMP response element-binding protein transcription shortens the duration of status epilepticus and decreases the number of spontaneous seizures in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2015;56(12):1870-1878.
[16] IUGHETTI L, LUCACCIONI L, FUGETTO F, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and epilepsy: a systematic review. Neuropeptides. 2018;72:23-29.
[17] SONG M, MARTINOWICH K, LEE FS. BDNF at the synapse: why location matters. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(10):1370-1375.
[18] DIENI CV, PANICHI R, AIMONE JB, et al. Low excitatory innervation balances high intrinsic excitability of immature dentate neurons. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11313.
[19] HEINRICH C, LÄHTEINEN S, SUZUKI F, et al. Increase in BDNF-mediated TrkB signaling promotes epileptogenesis in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;42(1):35-47.
[20] SHARMA P, KUMAR A, SINGH D. Dietary Flavonoids Interaction with CREB-BDNF Pathway: An Unconventional Approach for Comprehensive Management of Epilepsy. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(12):1158-1175.
[21] RACINE RJ. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation: cortical areas. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1975;38(1):1-12.
[22] SUTULA T, CASCINO G, CAVAZOS J, et al. Mossy fiber synaptic reorganization in the epileptic human temporal lobe. Ann Neurol. 1989;26(3):321-330.
[23] LÖSCHER W, BRANDT C. High seizure frequency prior to antiepileptic treatment is a predictor of pharmacoresistant epilepsy in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2010;51(1):89-97.
[24] ZHU X, HAN X, BLENDY JA, et al. Decreased CREB levels suppress epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;45(1):253-263.
[25] YU Y, JIANG J. COX-2/PGE2 axis regulates hippocampal BDNF/TrkB signaling via EP2 receptor after prolonged seizures. Epilepsia Open. 2020;5(3):418-431.
[26] ZHANG H, KONG Q, WANG J, et al. Complex roles of cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling in cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9(1):32.
[27] MCTAGUE A, HOWELL KB, CROSS JH, et al. The genetic landscape of the epileptic encephalopathies of infancy and childhood. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(3):304-316.
[28] WU G, LIU Z, WANG L, et al. Hippocampal Low-Frequency Stimulation Decreased cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein and Increased GABAA Receptor Subunit α1 in Amygdala-Kindled Pharmacoresistant Epileptic Rats. Neuropsychiatry. 2017;7(6):983-993.
[29] MERTZ C, KRARUP S, JENSEN CD, et al. Aspects of cAMP Signaling in Epileptogenesis and Seizures and Its Potential as Drug Target. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(6):1247-1255.
[30] LIN TW, HARWARD SC, HUANG YZ, et al. Targeting BDNF/TrkB pathways for preventing or suppressingbepilepsy. Neuropharmacology. 2020; 167:107734107734.
[31] HU Y, RUSSEK SJ. BDNF and the diseased nervous system: a delicate balance between adaptive and pathological processes of gene regulation. Neurochem. 2008;105(1):1-17.
[32] BINDER DK. The role of BDNF in epilepsy and other diseases of the mature nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;548:34-56.
[33] BINDER DK, SCHARFMAN HE. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors. 2004;22(3):123-131.
[34] ESVALD EE, TUVIKENE J, SIRP A, et al. CREB Family Transcription Factors Are Major Mediators of BDNF Transcriptional Autoregulation in Cortical Neurons. Neurosci. 2020;40(7):1405-1426.
[35] RAFA-ZABŁOCKA K, KREINER G, BAGIŃSKA M, et al. Selective Depletion of CREB in Serotonergic Neurons Affects the Upregulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Evoked by Chronic Fluoxetine Treatments. Front Neurosci. 2018;9(12):637-637.
[36] FALCICCHIA C, PAOLONE G, EMERICH DF, et al. Seizure-Suppressant and Neuroprotective Effects of Encapsulated BDNF-Producing Cells in a Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2018;5(9):211-224.
[37] LAI HC, CHANG QY, HSIEH CL. Signal Transduction Pathways of Acupuncture for Treating Some Nervous System Diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:2909632.
[38] YEH CM, HUANG CC, HSU KS. Prenatal stress alters hippocampal synaptic plasticity in young rat offspring through preventing the proteolytic conversion of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to mature BDNF. J Physiol. 2012;590(4):991-1010.
[39] KLEIN KM, PENDZIWIAT M, COHEN R, et al. Autosomal dominant epilepsy with auditory features: a new LGI1 family including a phenocopy with cortical dysplasia. Neurol. 2016;263(1):11-16.
[40] GORSKI JA, ZEILER SR, TAMOWSKI S, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for the maintenance of cortical dendrites. J Neurosci. 2003;23(17):6856-6865.
[41] LUCARINI N, VERROTTI A, NAPOLIONI V, et al. Genetic polymorphisms and idiopathic generalized epilepsies. Pediatr Neurol. 2007;37:157-164.
|