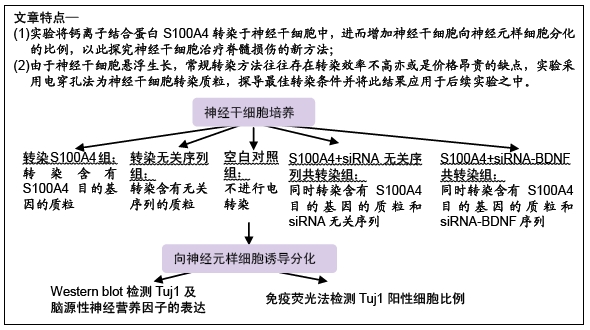
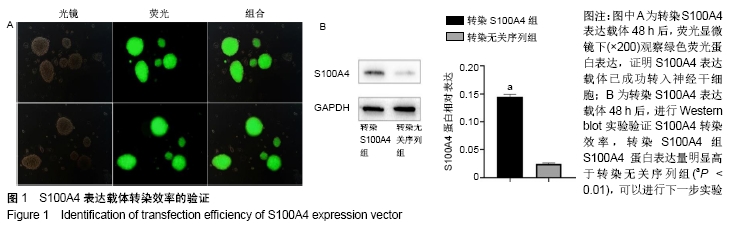
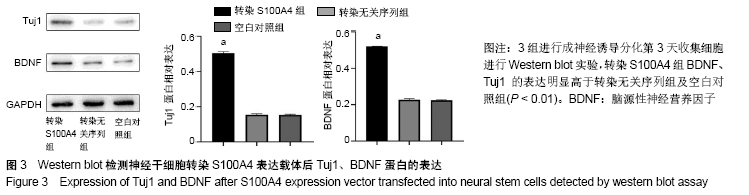
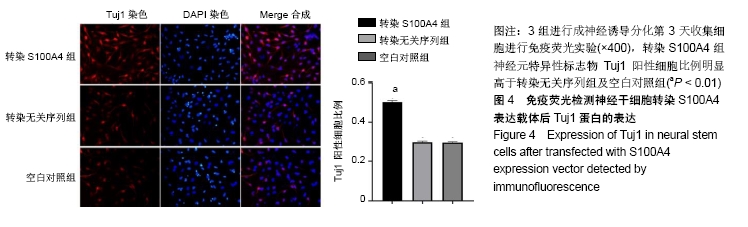
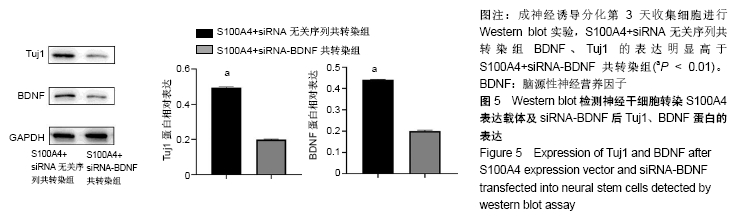
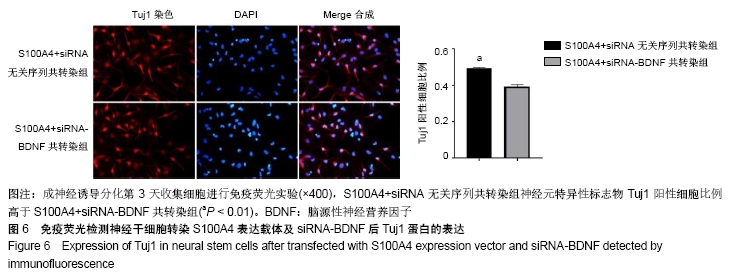
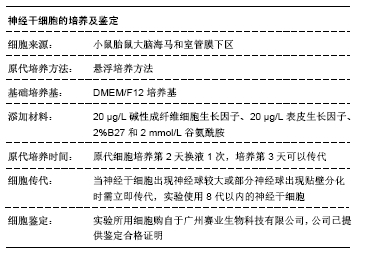
[1] ZHENG W, ZHUGE Q, ZHONG M, et al. Neurogenesis in adult human brain after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30(22): 1872-1880.
[2] BOYE K, MAELANDSMO GM. S100A4 and metastasis: a small actor playing many roles. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(2):528-535.
[3] LEI L, TANG L. Schwann cells genetically modified to express S100A4 increases GAP43 expression in spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Bioengineered. 2017;8(4):404-410.
[4] CHENG G, HE T, XING Y. Silencing of S100A4, a metastasis- associated protein, inhibits retinal neovascularization via the downregulation of BDNF in oxygen-induced ischaemic retinopathy. Eye (Lond). 2016;30(6):877-887.
[5] CHMIELNICKI E, BENRAISS A, ECONOMIDES AN, et al. Adenovirally expressed noggin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor cooperate to induce new medium spiny neurons from resident progenitor cells in the adult striatal ventricular zone. J Neurosci. 2004;24(9):2133-2142.
[6] COULL JA, BEGGS S, BOUDREAU D, et al. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature. 2005;438(7070):1017-1021.
[7] 方康权,曾宪辉.脊髓损伤的生物化学研究概况[J].医学理论与实践, 2018, 31(18):2723-2724,2727.
[8] 黄辉.继发性脊髓损伤发病机制的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2013, 19(7): 1162-1165.
[9] 张盼,赵红卫,卢斌,等.继发性脊髓损伤微环境的研究进展[J].海南医学, 2018, 29(19): 2774-2777.
[10] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045.
[11] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1): 24-25.
[12] SABAPATHY V, THARION G, KUMAR S. Cell Therapy Augments Functional Recovery Subsequent to Spinal Cord Injury under Experimental Conditions. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:132172.
[13] WITIW CD, FEHLINGS MG. Acute Spinal Cord Injury. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(6):202-210.
[14] DOOLEY D, VIDAL P, HENDRIX S. Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141(1):21-31.
[15] TUSZYNSKI MH, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Neural stem cell dissemination after grafting to CNS injury sites. Cell. 2014;156(3): 388-389.
[16] LUDWIG PE, THANKAM FG, PATIL AA, et al. Brain injury and neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(1):7-18.
[17] ORMOND DR, SHANNON C, OPPENHEIM J, et al. Stem cell therapy and curcumin synergistically enhance recovery from spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88916.
[18] MARIANO ED, BATISTA CM, BARBOSA BJ, et al. Current perspectives in stem cell therapy for spinal cord repair in humans: a review of work from the past 10 years. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014;72(6): 451-456.
[19] HORKY LL, GALIMI F, GAGE FH, et al. Fate of endogenous stem/progenitor cells following spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2006;498(4):525-538.
[20] CAWSEY T, DUFLOU J, WEICKERT CS, et al. Nestin-Positive Ependymal Cells Are Increased in the Human Spinal Cord after Traumatic Central Nervous System Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(18):1393-1402.
[21] KADOYA K, LU P, NGUYEN K, et al. Spinal cord reconstitution with homologous neural grafts enables robust corticospinal regeneration. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):479-487.
[22] GARBOSSA D, BOIDO M, FONTANELLA M, et al. Recent therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury treatment: possible role of stem cells. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35(3):293-311.
[23] VAWDA R, WILCOX J, FEHLINGS M. Current stem cell treatments for spinal cord injury. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(1):10-18.
[24] ZHANG SQ, WU MF, PENG CG, et al. Improvements in neuroelectrophysiological and rear limb functions in rats with spinal cord injury after Schwann cell transplantation in combination with a C5a receptor antagonist. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4):15158-15168.
[25] WANG D, ZHANG J. Effects of hypothermia combined with neural stem cell transplantation on recovery of neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(3):1759-1767.
[26] DU XJ, CHEN YX, ZHENG ZC, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation inhibits glial cell proliferation and P2X receptor-mediated neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury rats. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(5):876-885.
[27] LEONG C, ZHAI D, KIM B, et al. Neural stem cell isolation from the whole mouse brain using the novel FABP7-binding fluorescent dye, CDr3. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3):1314-1322.
[28] 陈刚,秦尚振,马廉亭,等.人胚脑与脊髓神经干细胞体外生物学特性的差异[J].脑与神经疾病杂志, 2006,14(3):183-186.
[29] HUANG H, ZHENG HY, LIU ZL, et al. Prognostic significance of relaxin-2 and S100A4 expression in osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(19):2828-2834.
[30] LI HJ, CHEN YX, WANG Q, et al. S100A4 mRNA as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in Wilms tumor (WT). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(6):817-827.
[31] TARABYKINA S, GRIFFITHS TR, TULCHINSKY E, et al. Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007;7(3):217-228.
[32] XU X, SU B, XIE C, et al. Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signaling pathway regulates the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) by mediating a new target gene, S100A4, in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e96441.
[33] KHAN MI, YUAN T, CHOU RH, et al. S100A4 inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with the S100A1-RAGE V domain. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212299.
[34] LINK T, KUHLMANN JD, KOBELT D, et al. Clinical relevance of circulating MACC1 and S100A4 transcripts for ovarian cancer. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(5):1268-1279.
[35] ABERG F, KOZLOVA EN. Metastasis-associated mts1 (S100A4) protein in the developing and adult central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424(2):269-282.
[36] KOBORI N, CLIFTON GL, DASH P. Altered expression of novel genes in the cerebral cortex following experimental brain injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;104(2):148-158.
[37] KOZLOVA EN, LUKANIDIN E. Mts1 protein expression in the central nervous system after injury. Glia. 2002;37(4):337-348.
[38] NOVITSKAYA V, GRIGORIAN M, KRIAJEVSKA M, et al. Oligomeric forms of the metastasis-related Mts1 (S100A4) protein stimulate neuronal differentiation in cultures of rat hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(52):41278-41286.
[39] EYILETEN C, KAPLON-CIESLICKA A, MIROWSKA-GUZEL D, et al. Antidiabetic Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Its Association with Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:2823671.
[40] WURZELMANN M, ROMEIKA J, SUN D. Therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and a small molecular mimics of BDNF for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(1):7-12.
[41] 李小华,冷锦红.脑源性神经营养因子对糖尿病能量代谢及神经病变的影响[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 2019, 27(8): 629-631.
[42] MAROSI K, MATTSON MP. BDNF mediates adaptive brain and body responses to energetic challenges. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 25(2):89-98.
|